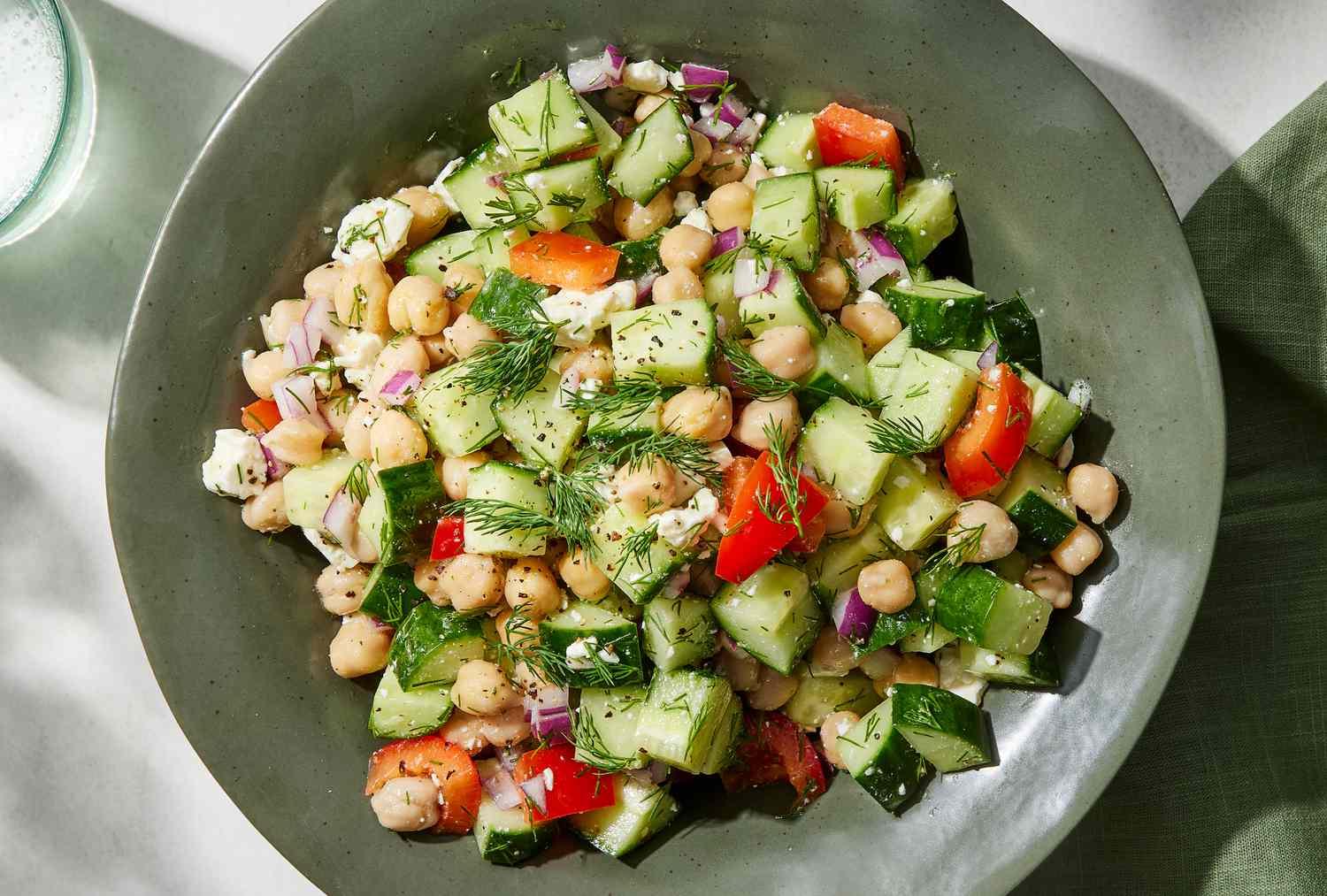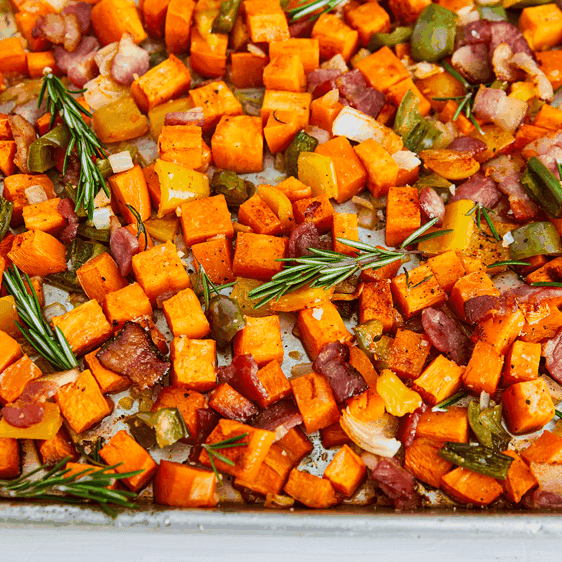Pick your health conditions
and see that we got you covered!
Filter by
Health conditions
Diet type

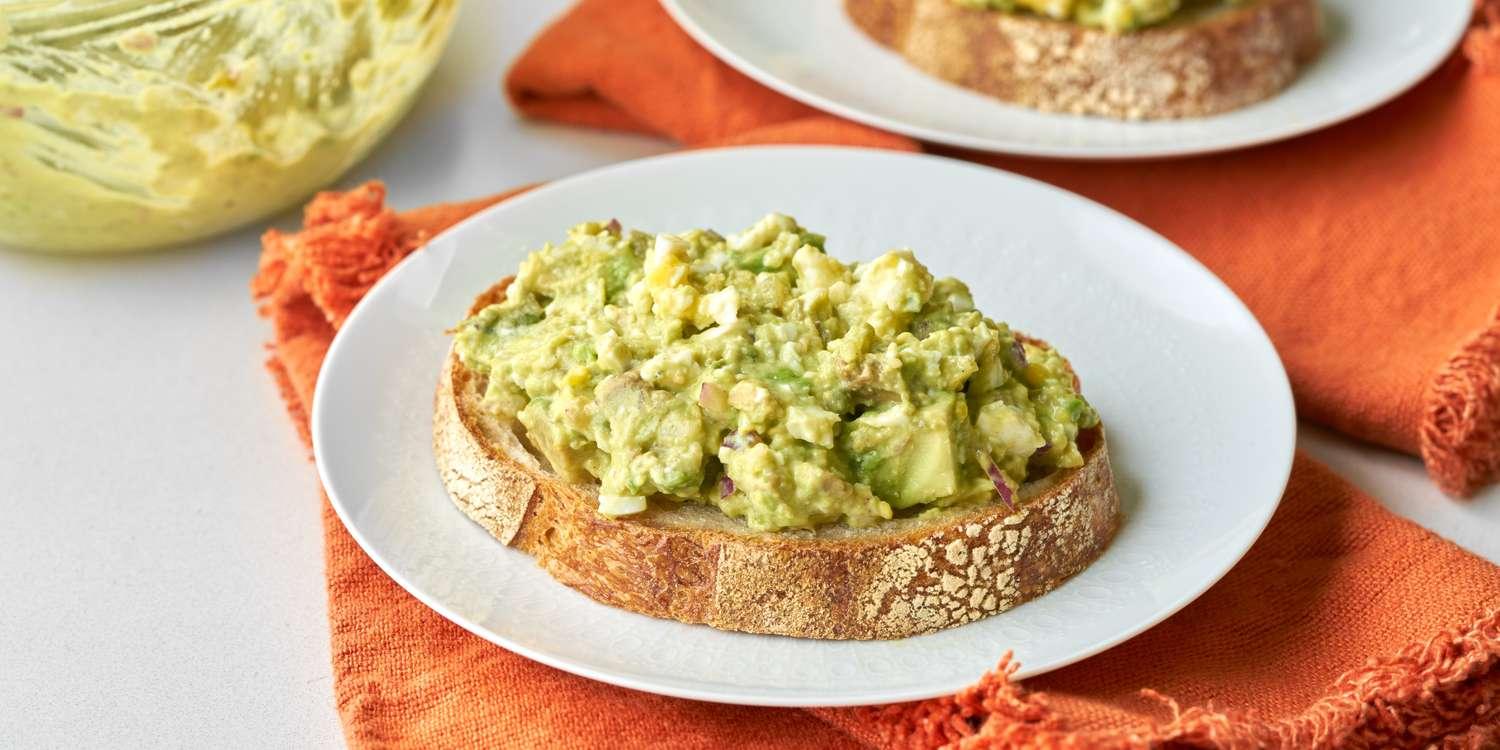
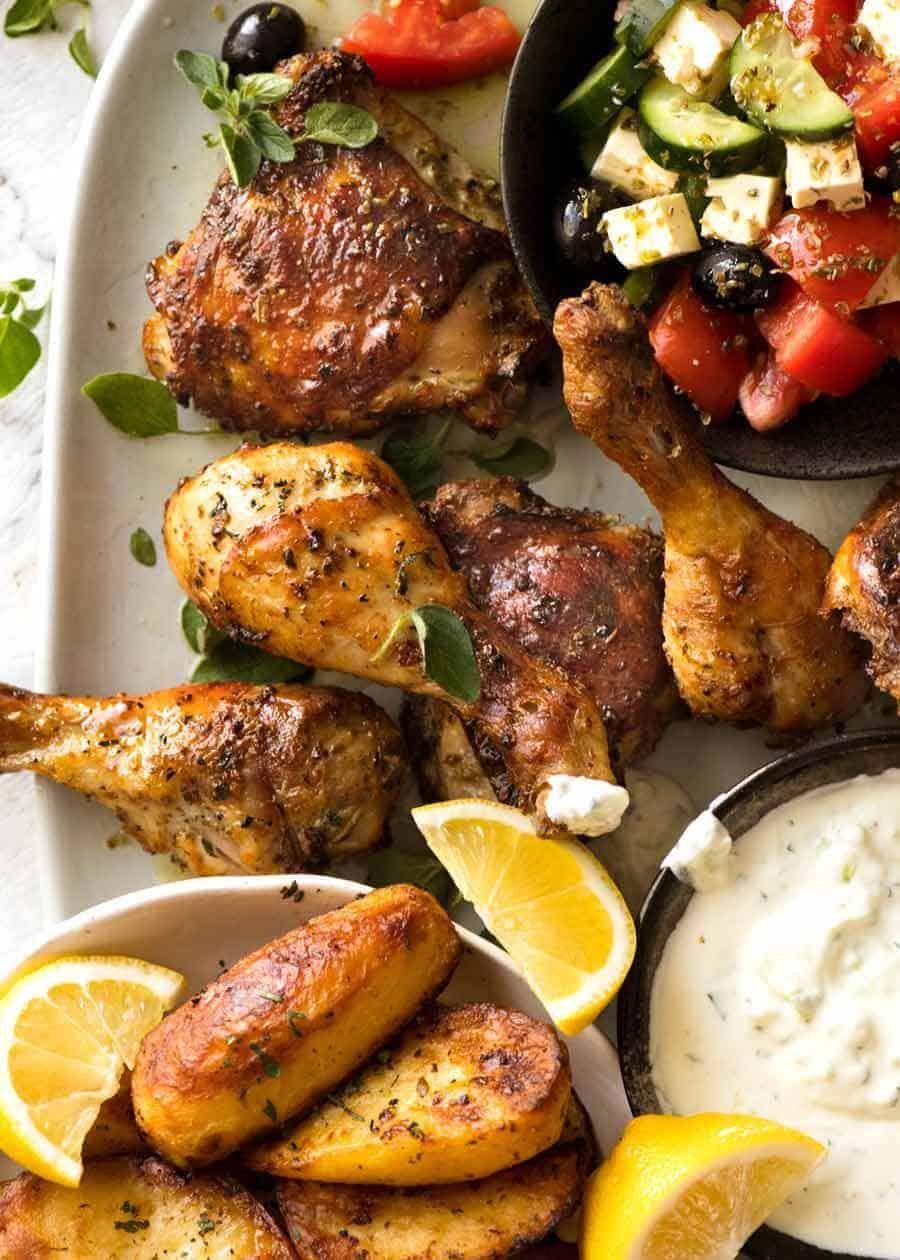
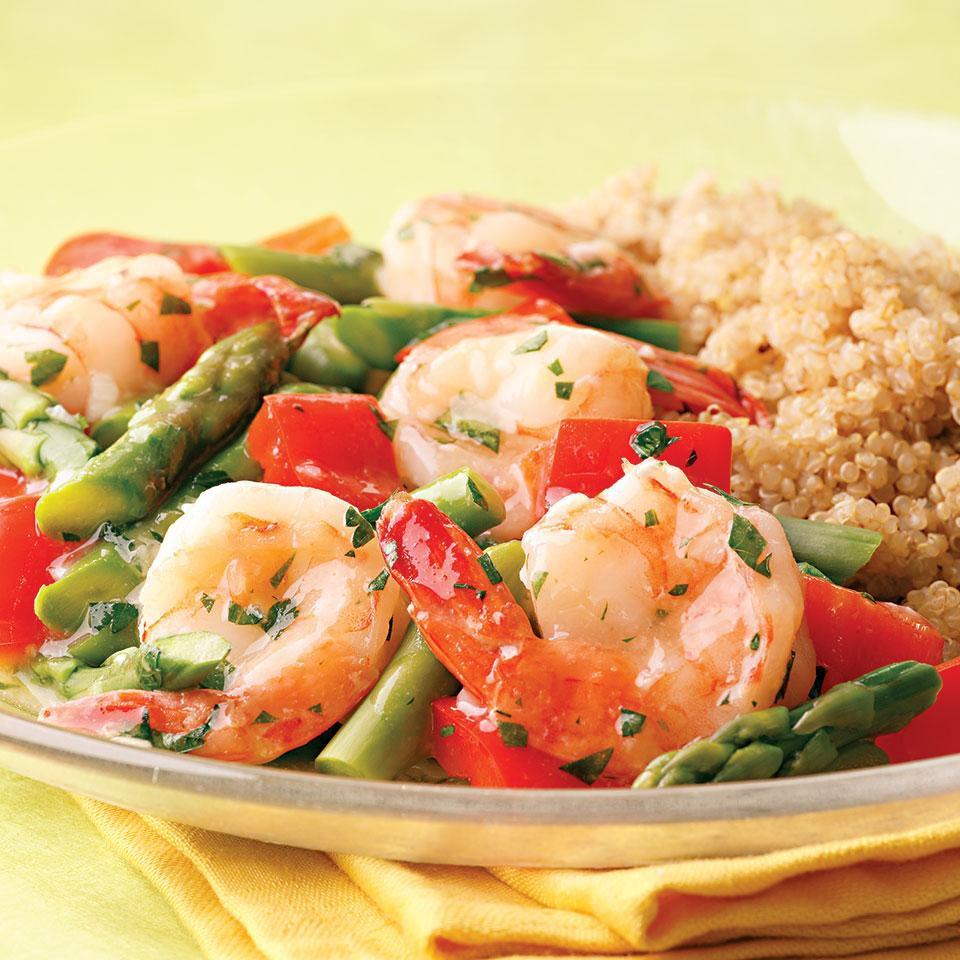
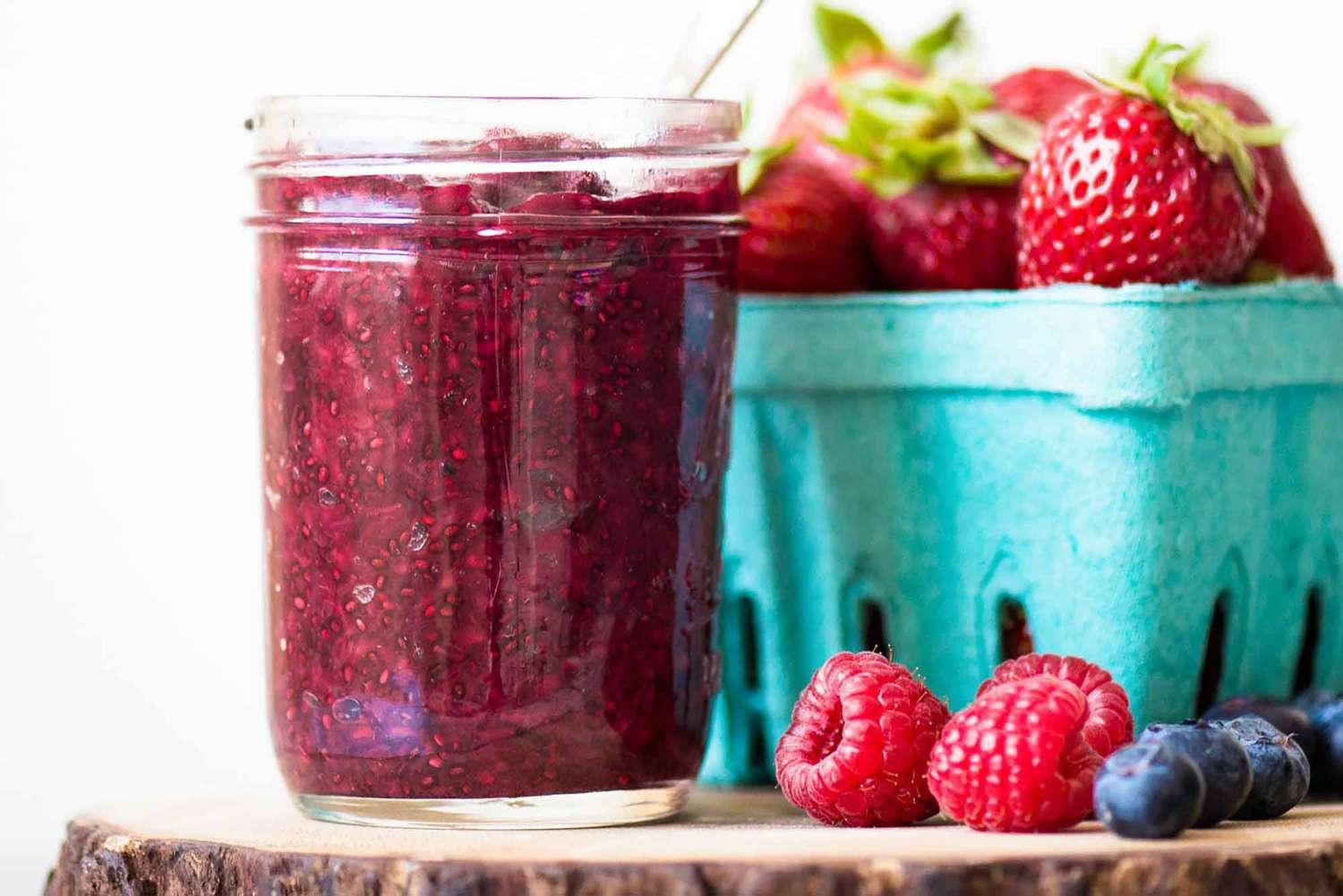
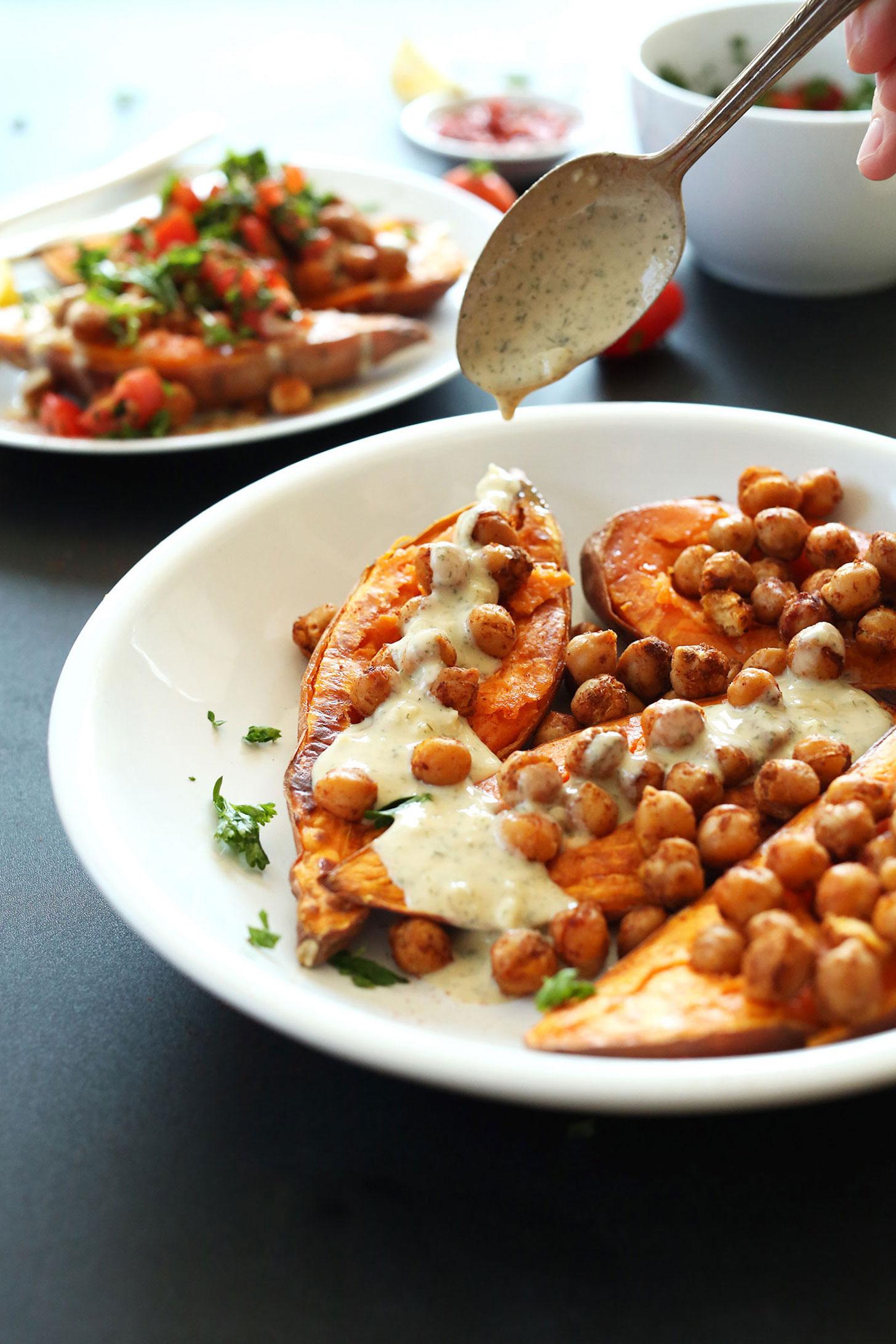
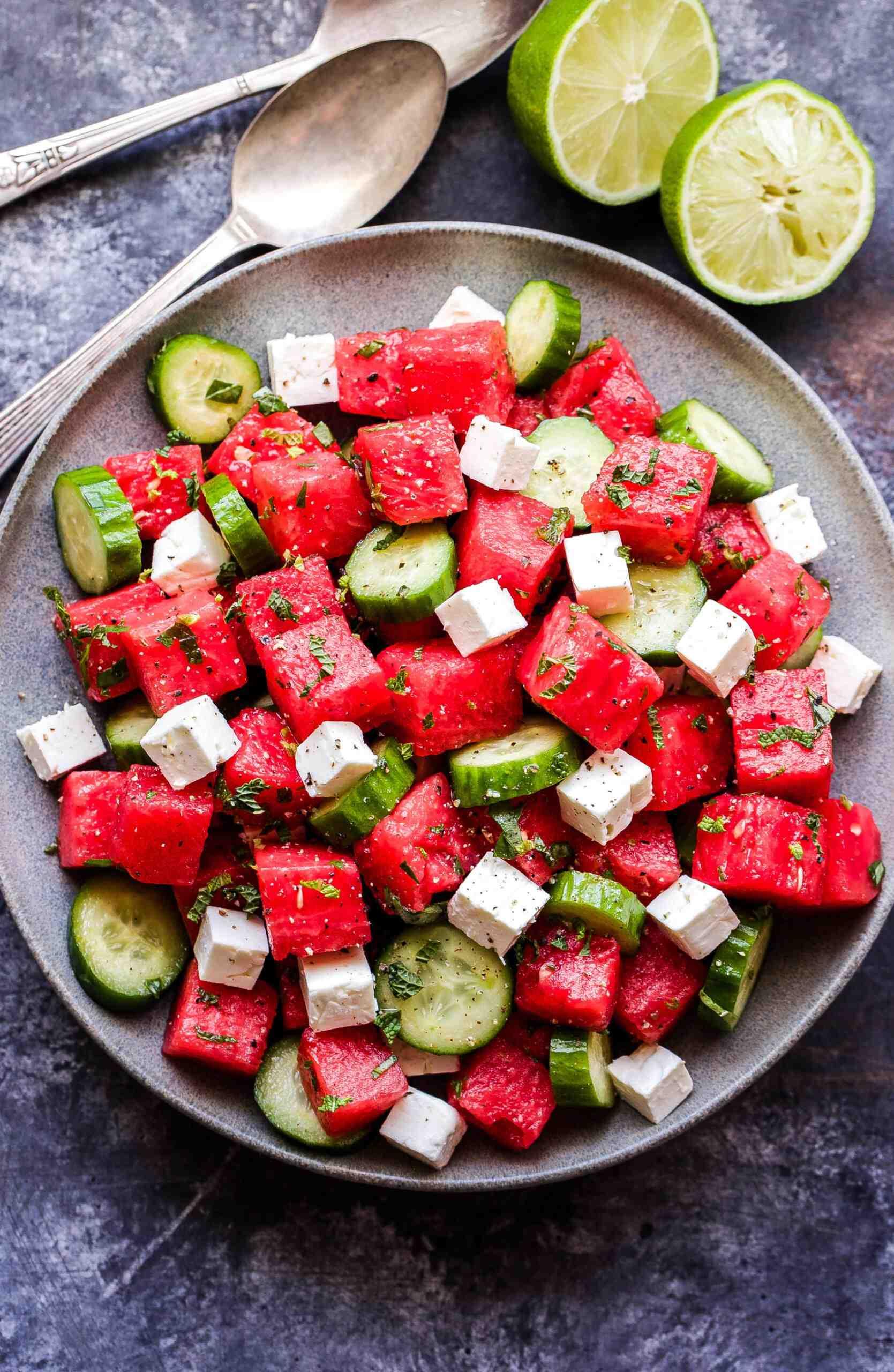
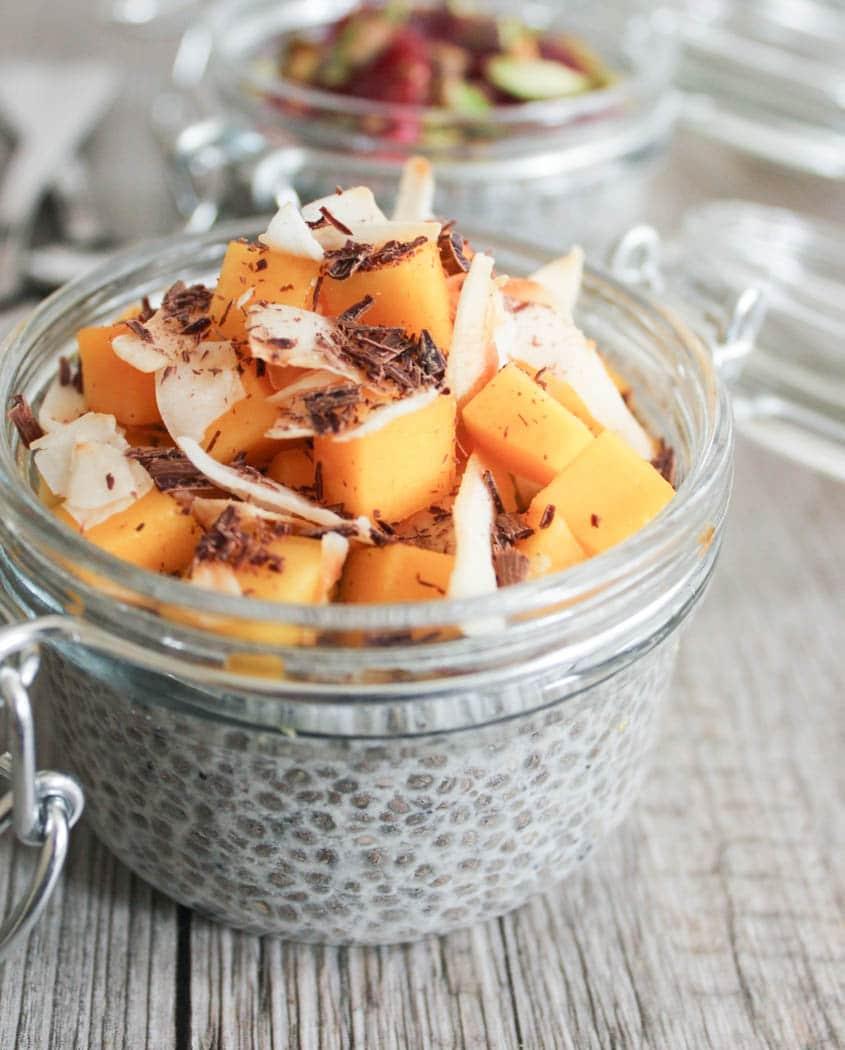
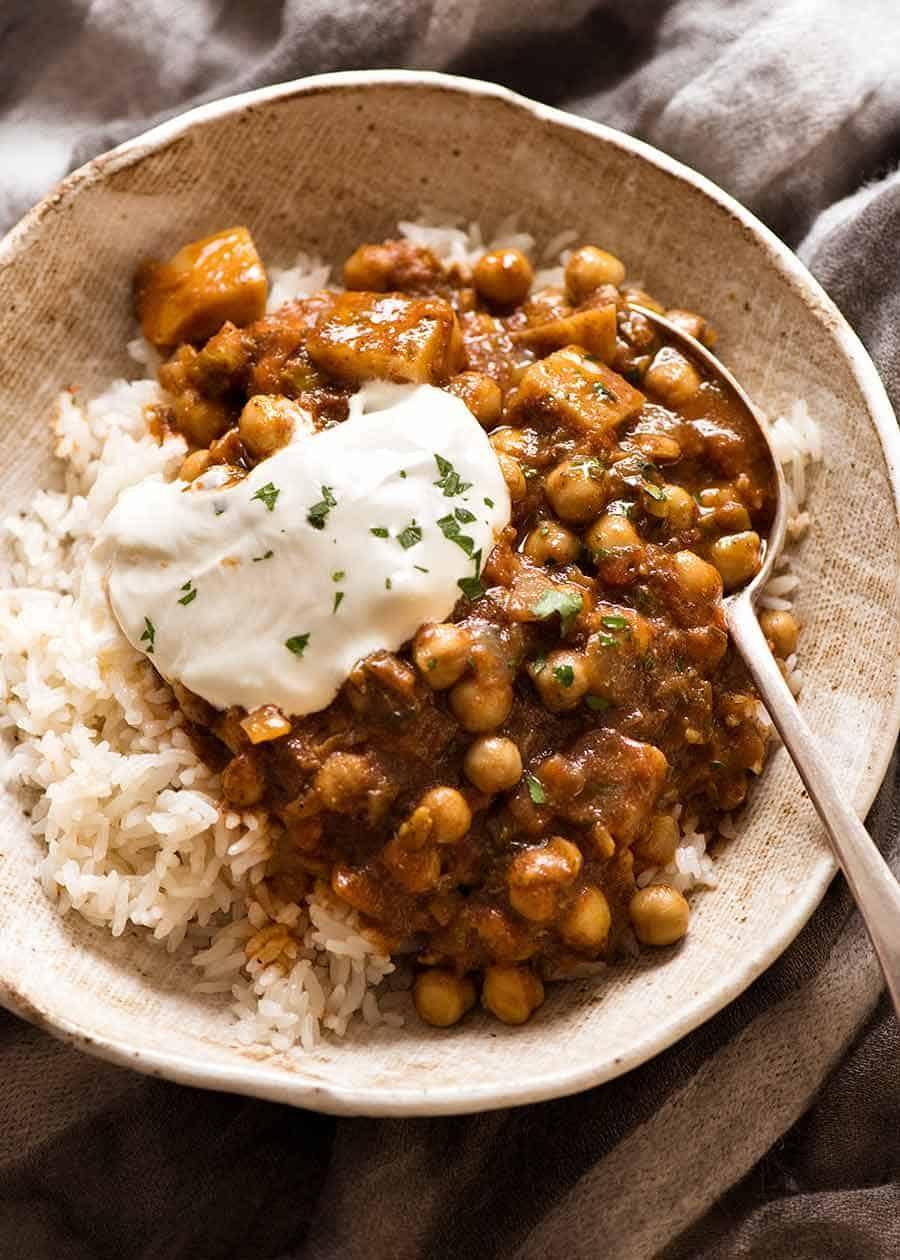
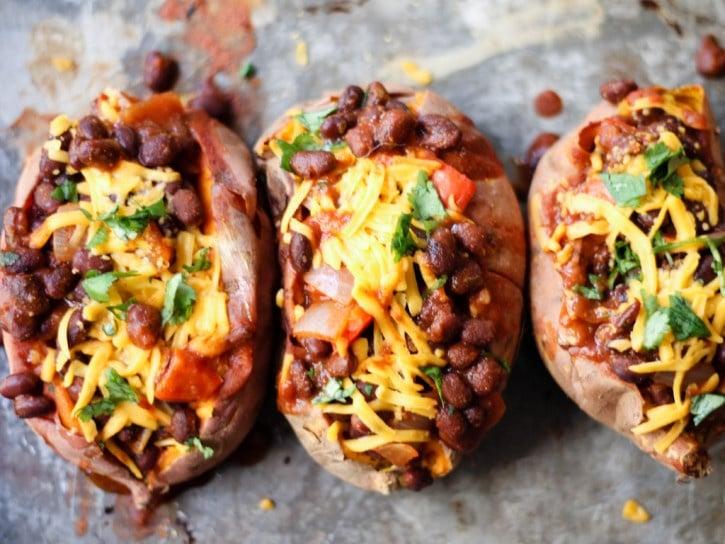
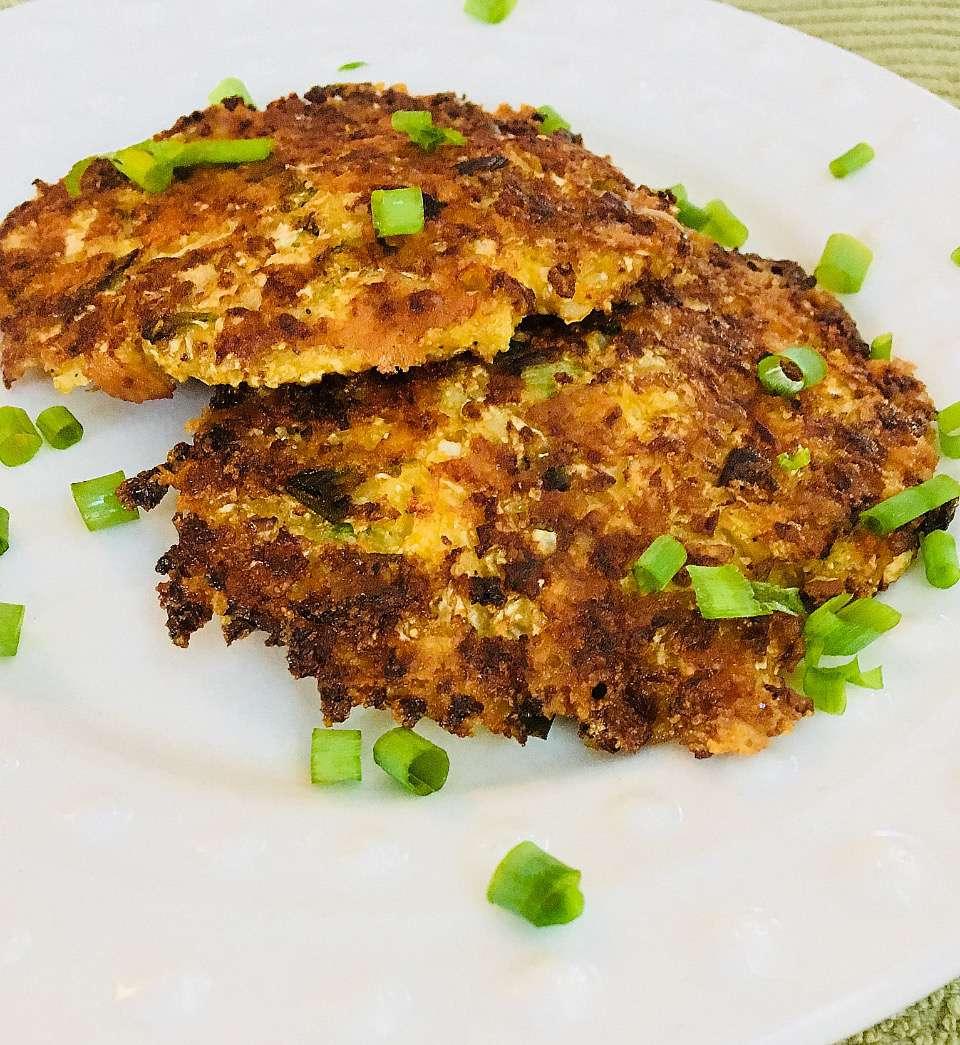
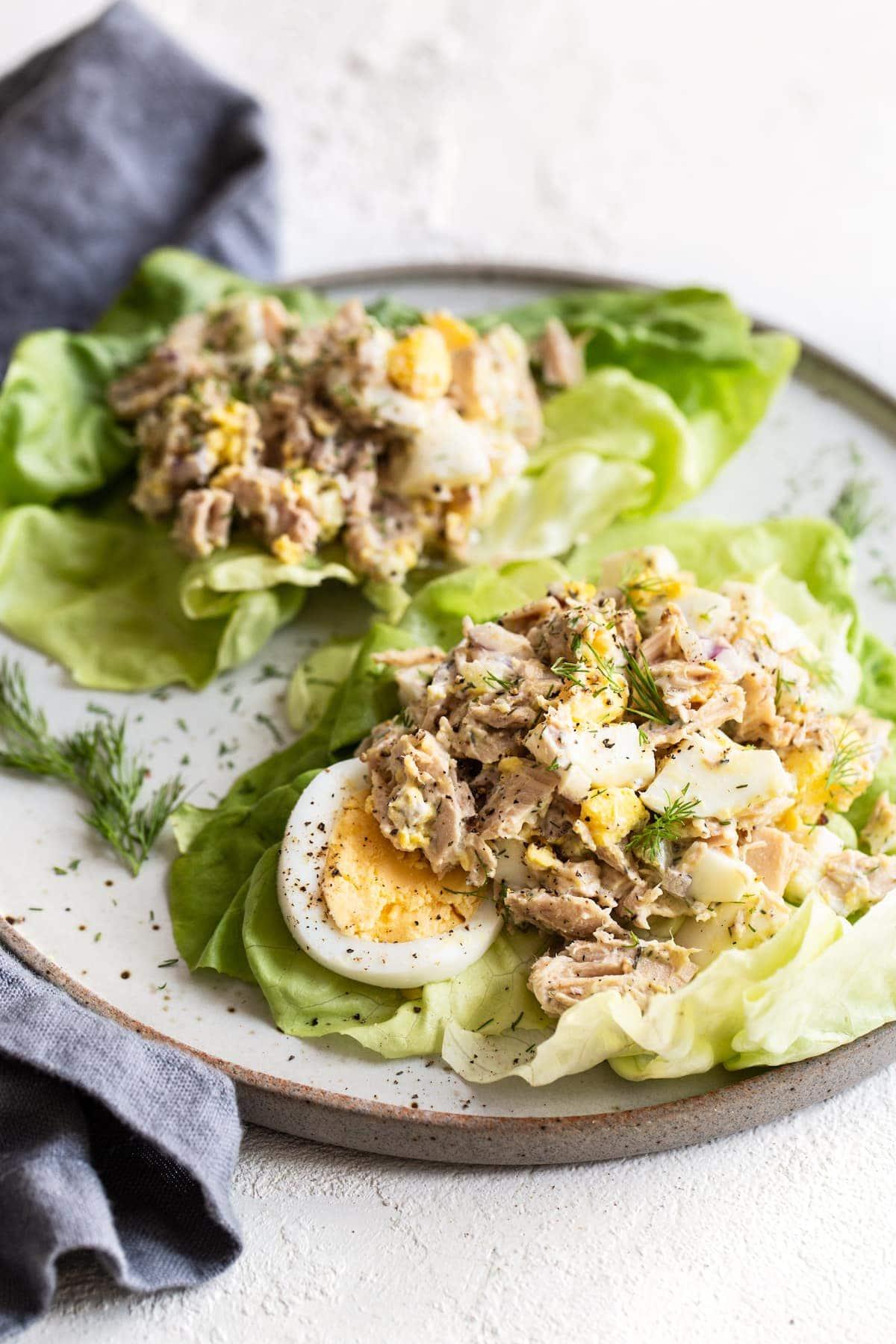
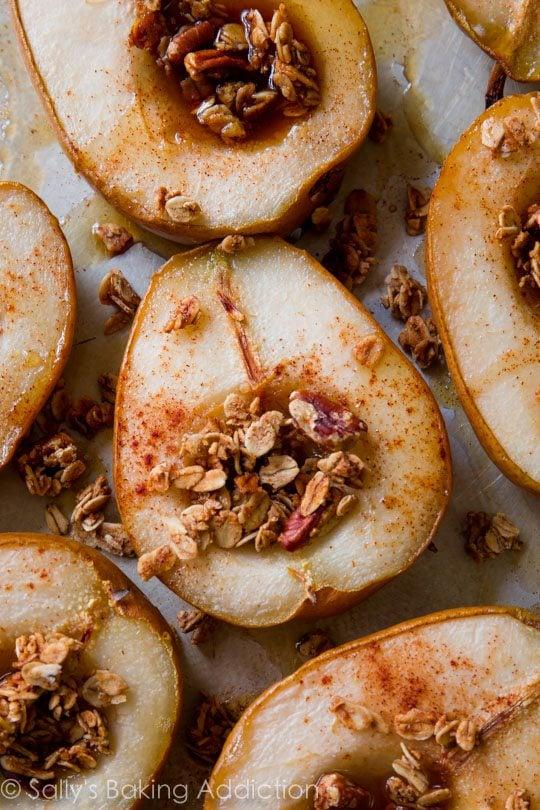
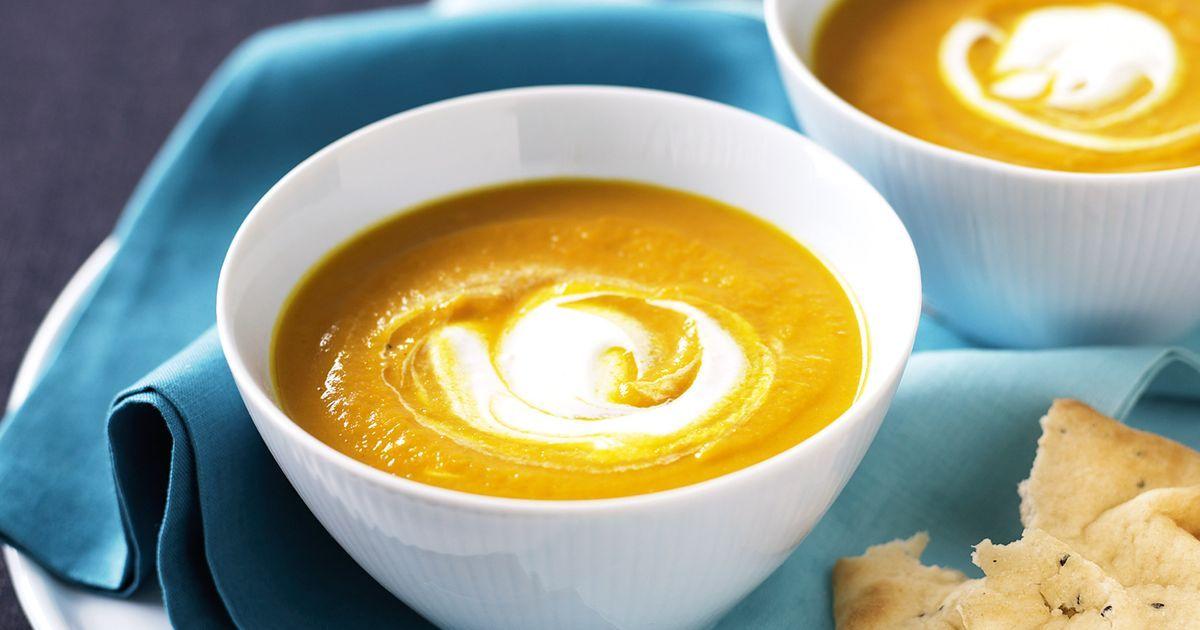
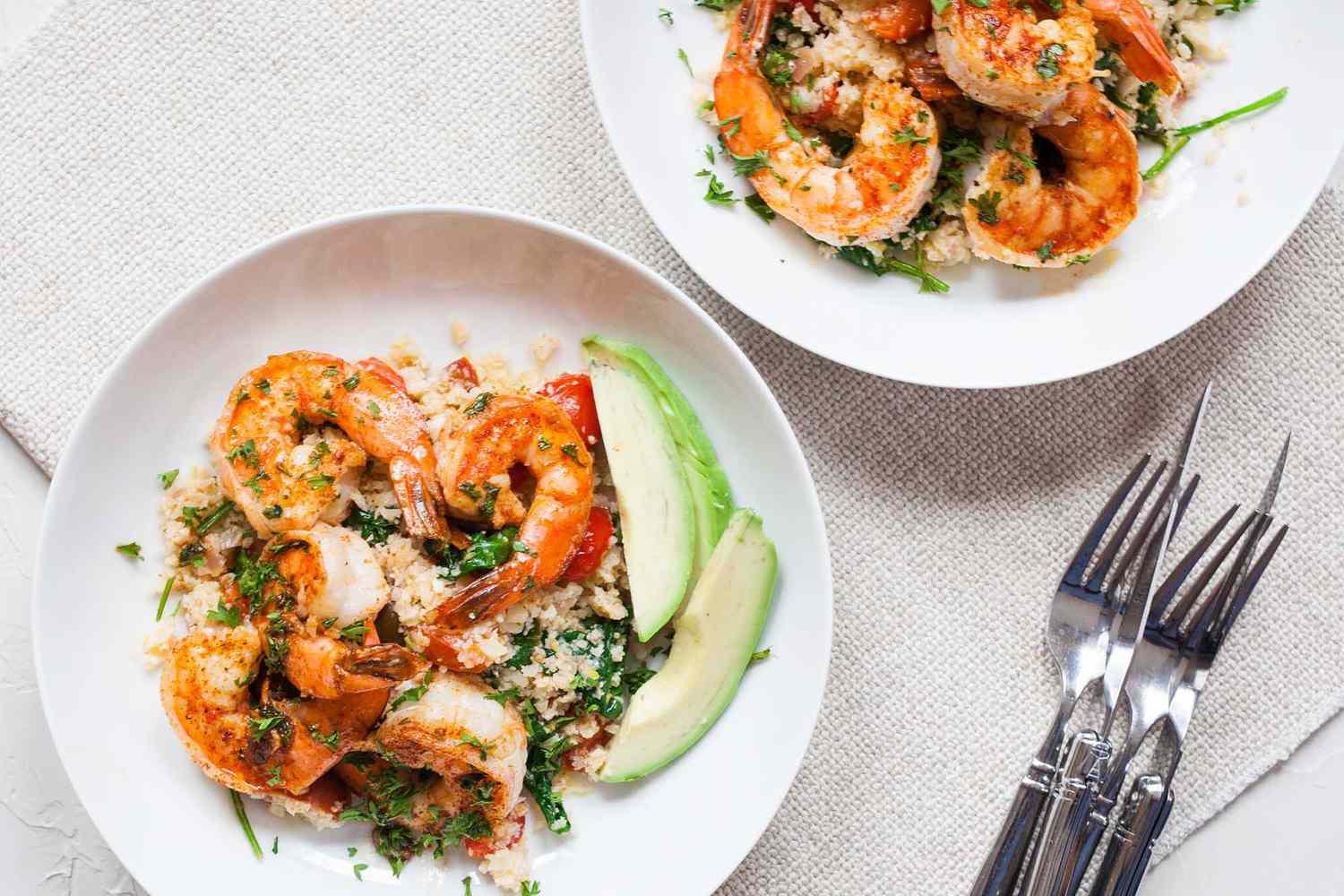
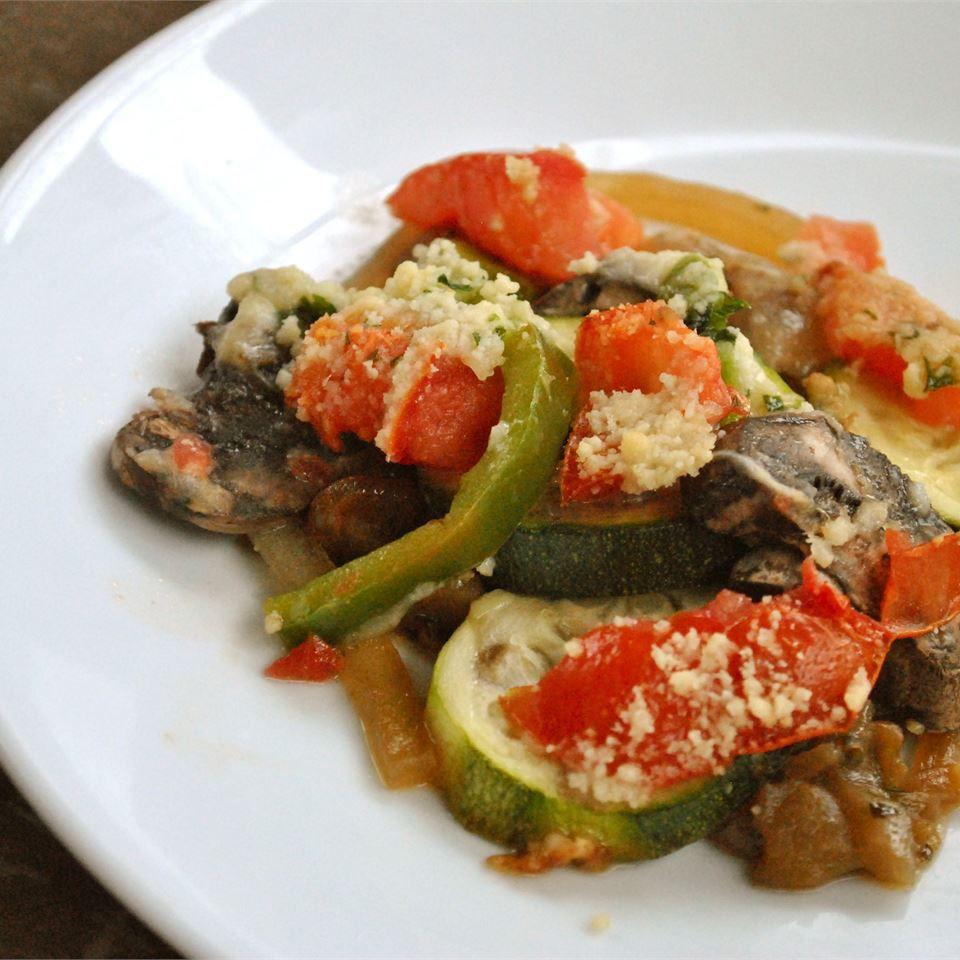
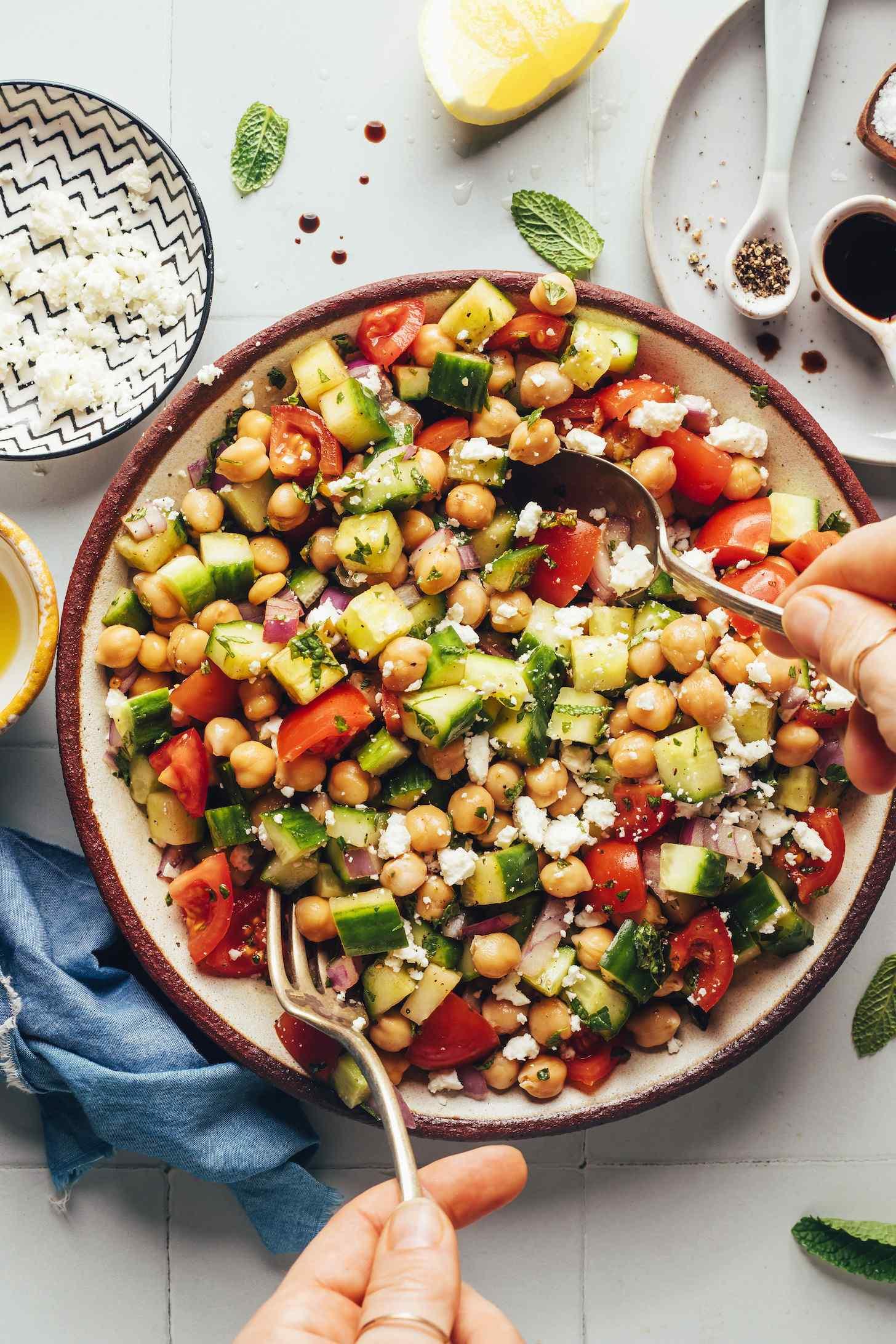
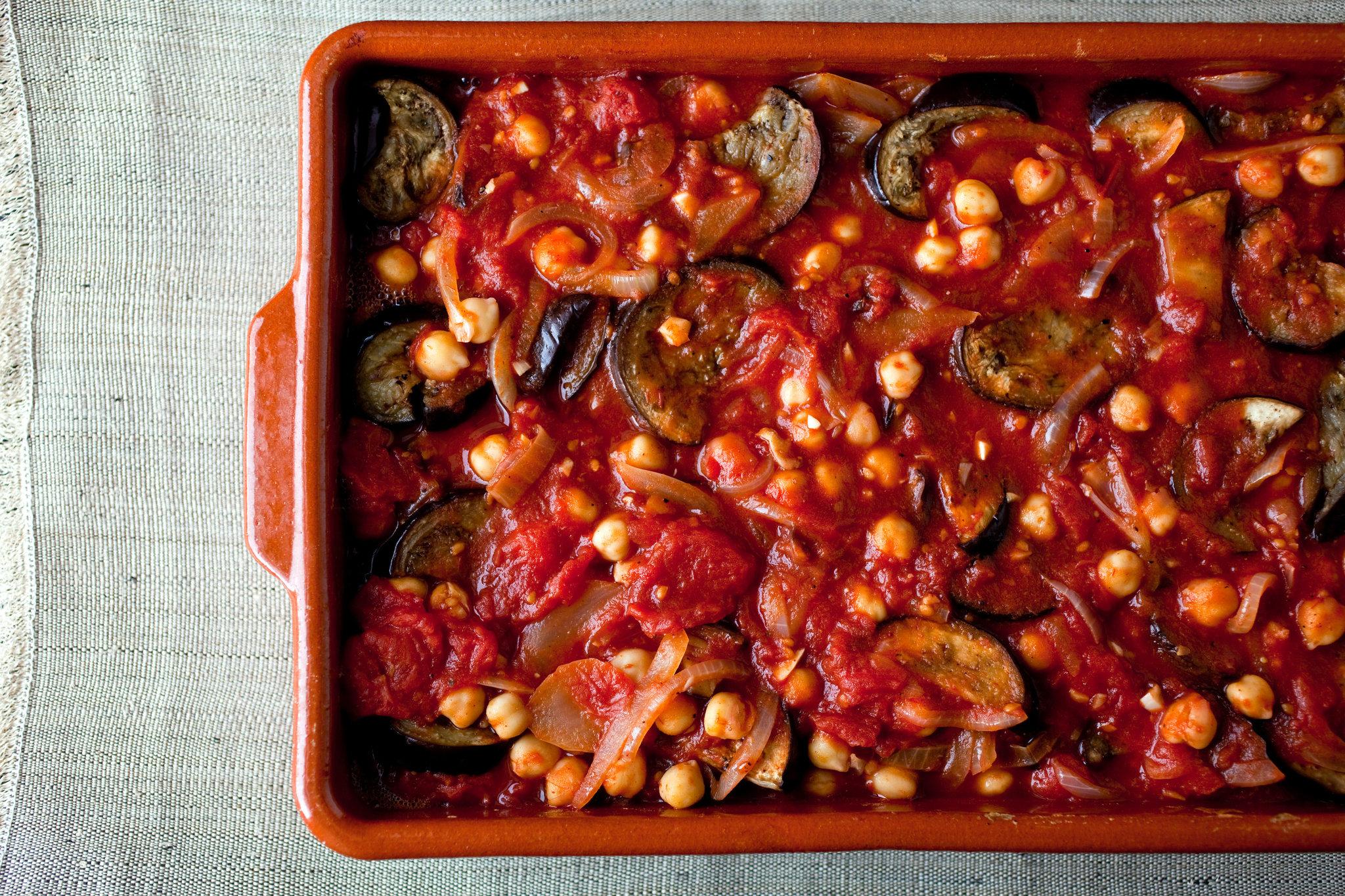
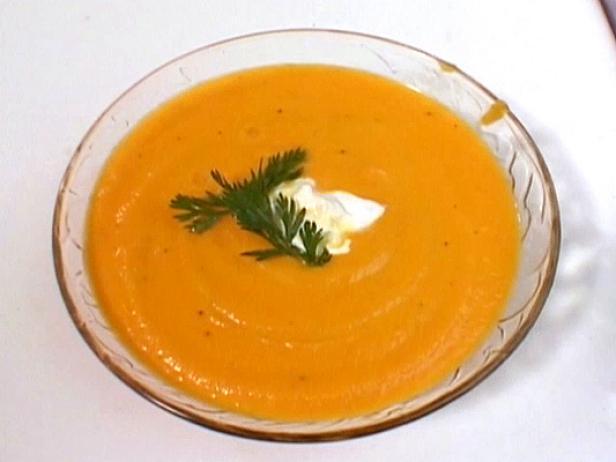
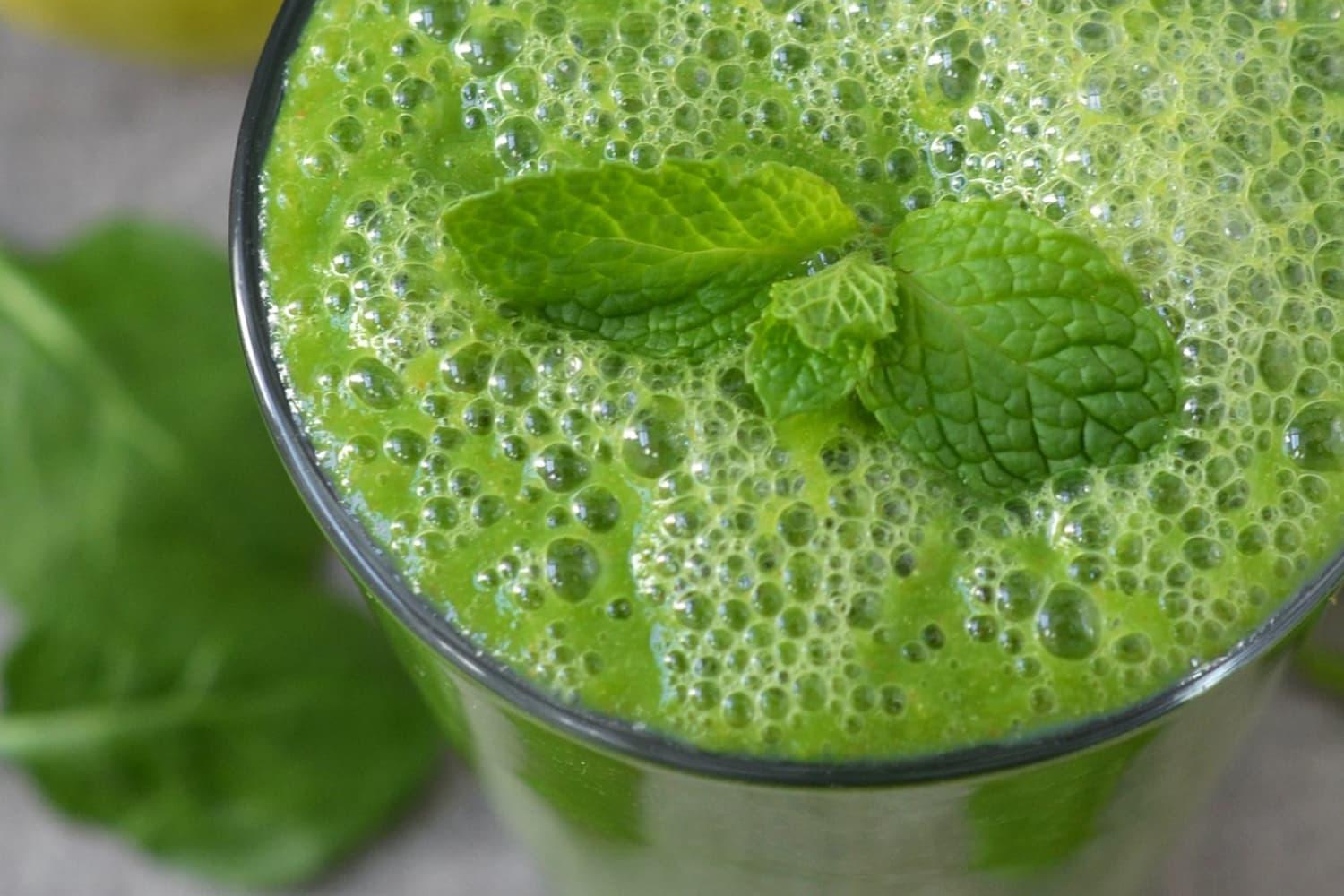
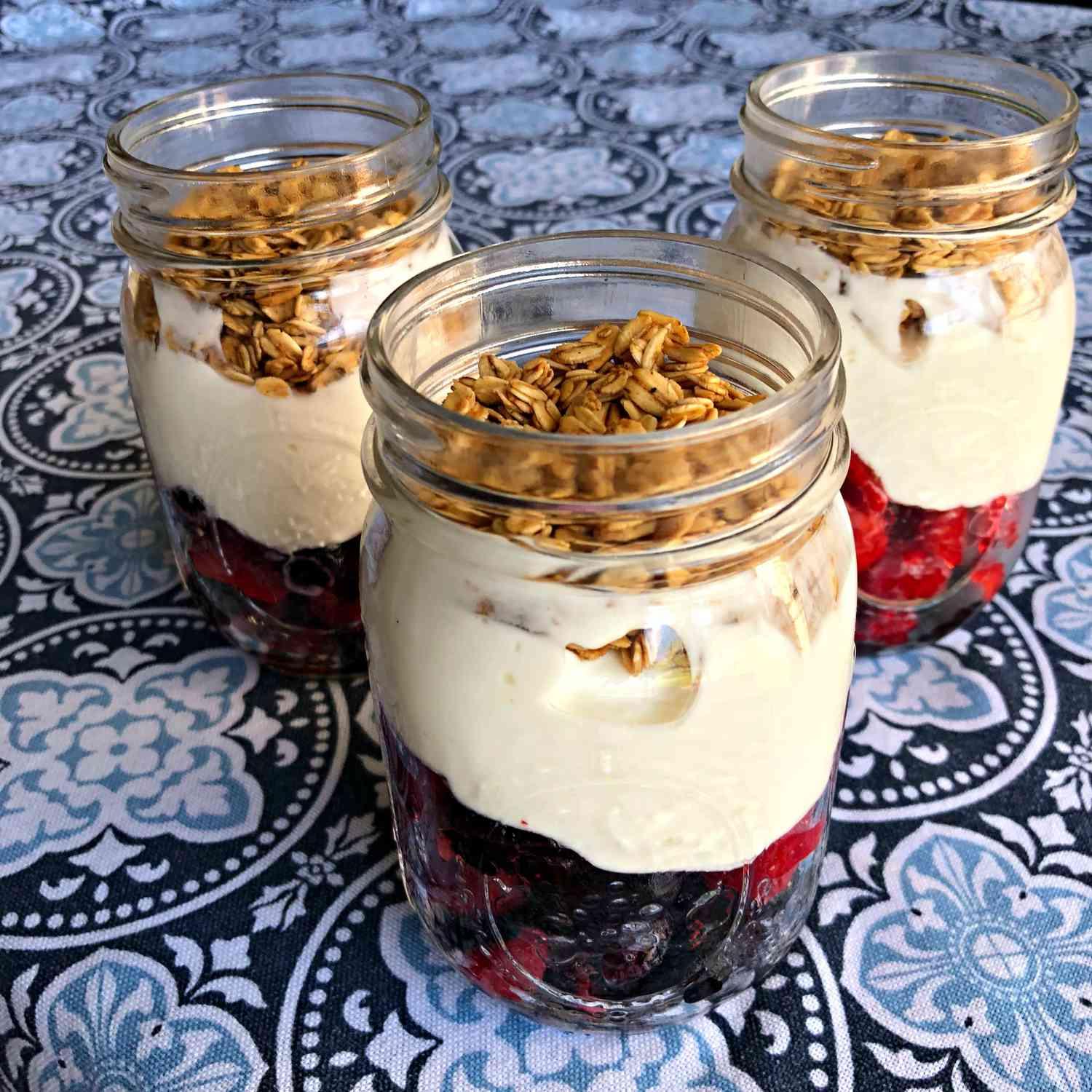
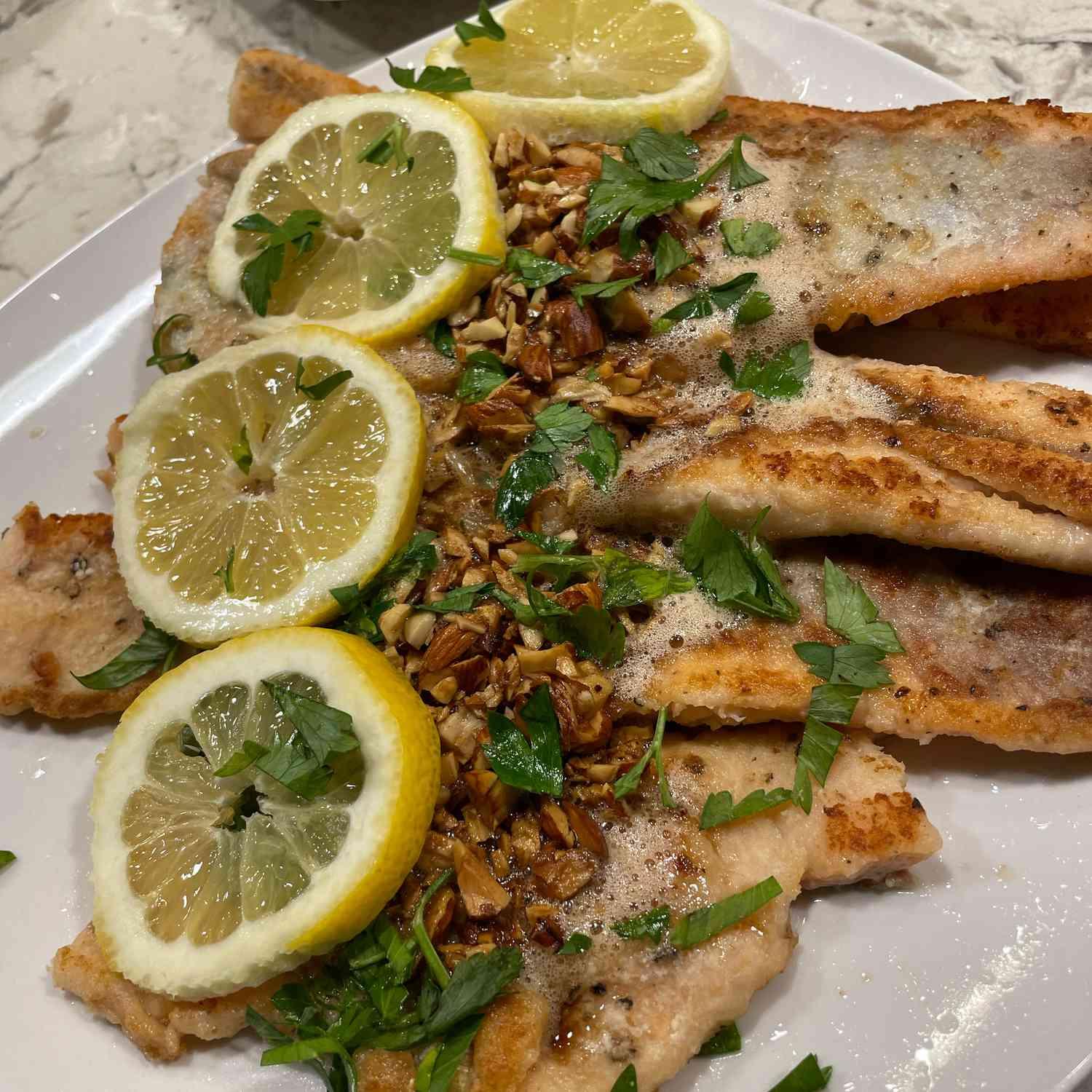
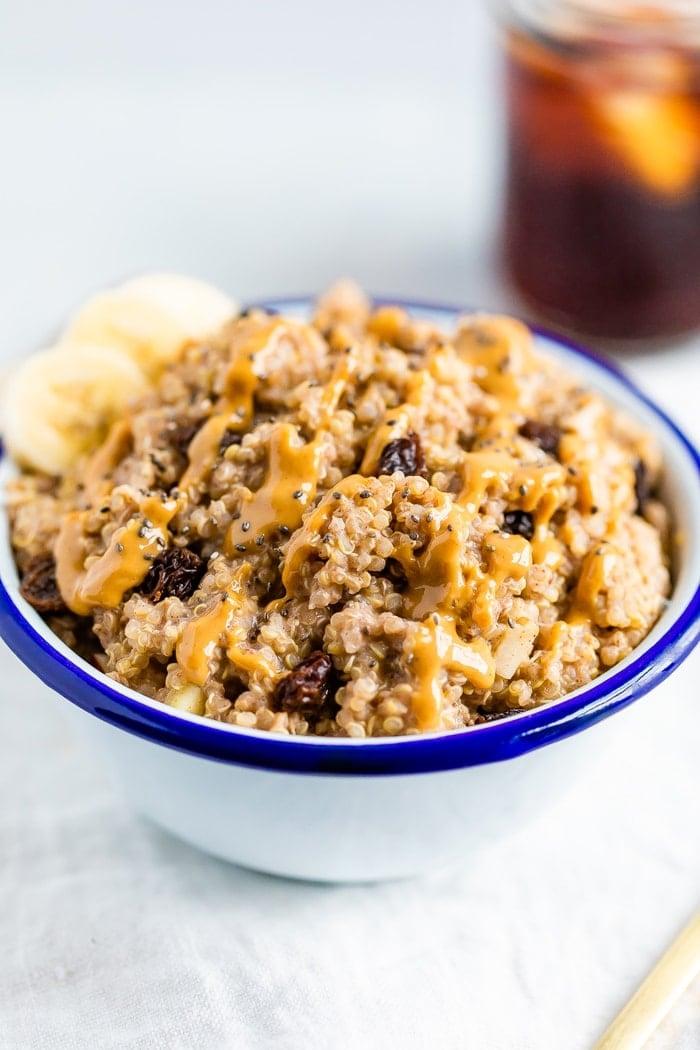
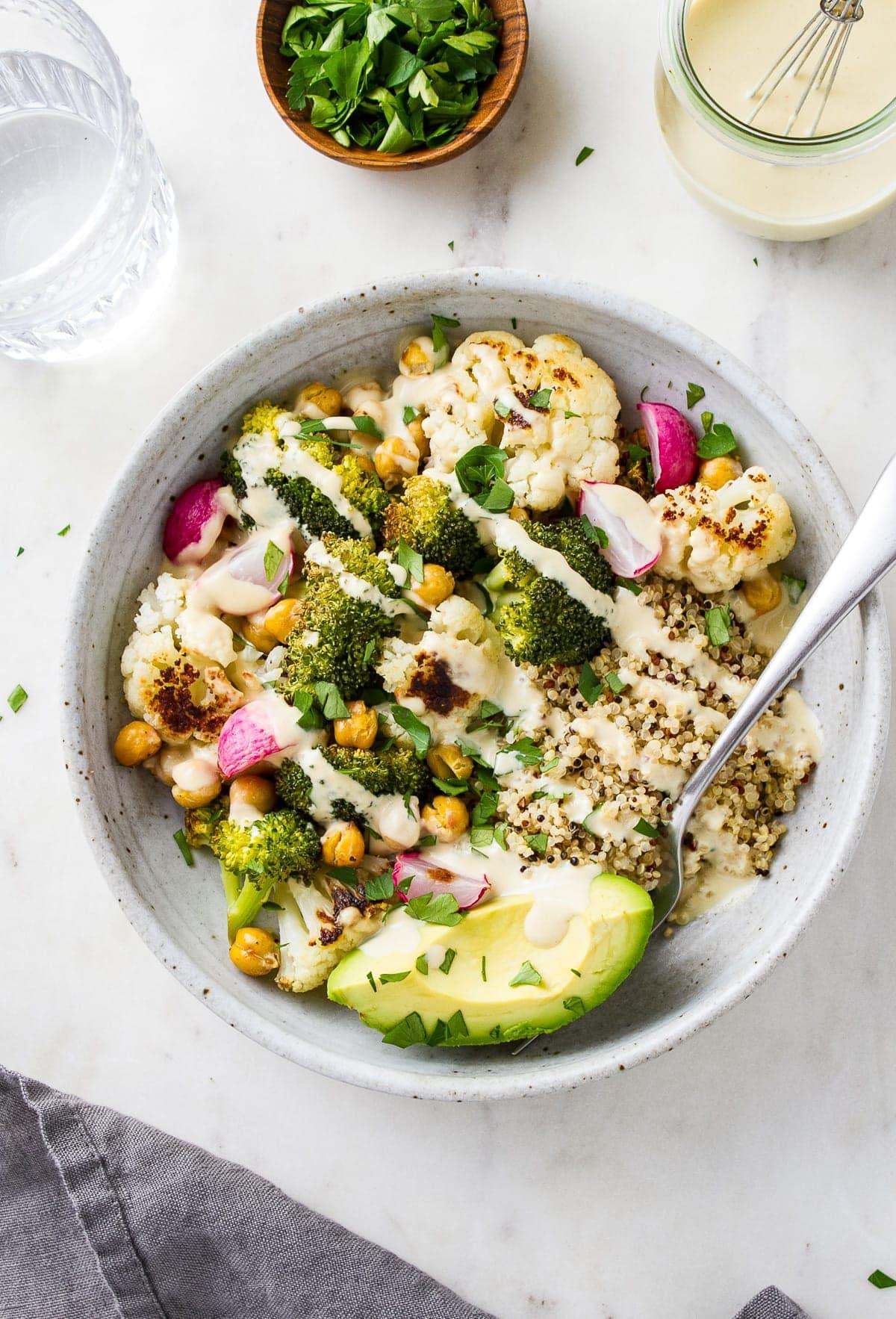
Prioritizes easily digestible, anti-inflammatory foods to minimize Crohn's flare-ups, like well-cooked vegetables, lean proteins, and low-fiber fruits. Completely excludes gluten to accommodate celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, focusing on naturally gluten-free grains like rice, quinoa, and gluten-free oats. Ensures balanced nutrition with adequate vitamins and minerals, avoiding potential deficiencies common in Crohn's and gluten-free diets, such as iron, calcium, and vitamin B12.
For Crohns Disease
Gluten Free
Day 1
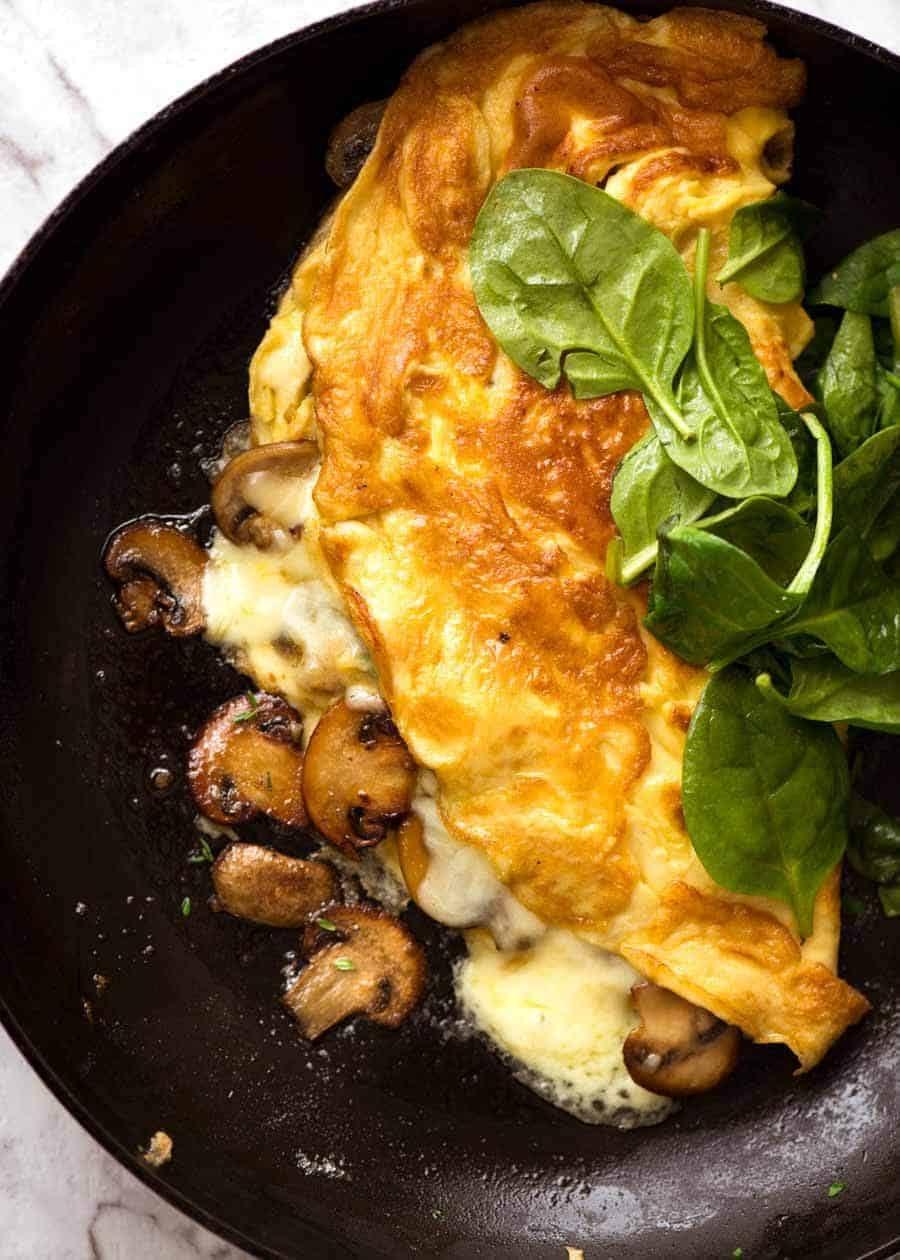
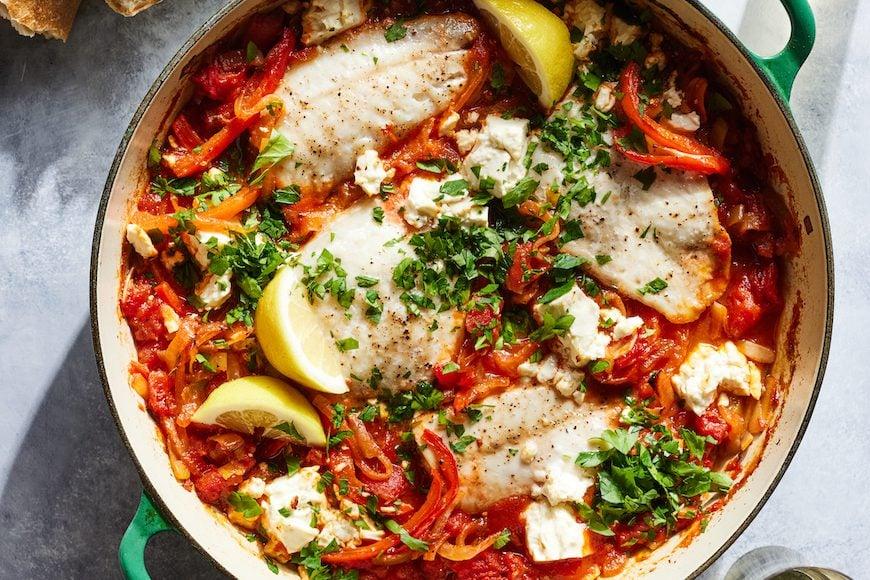
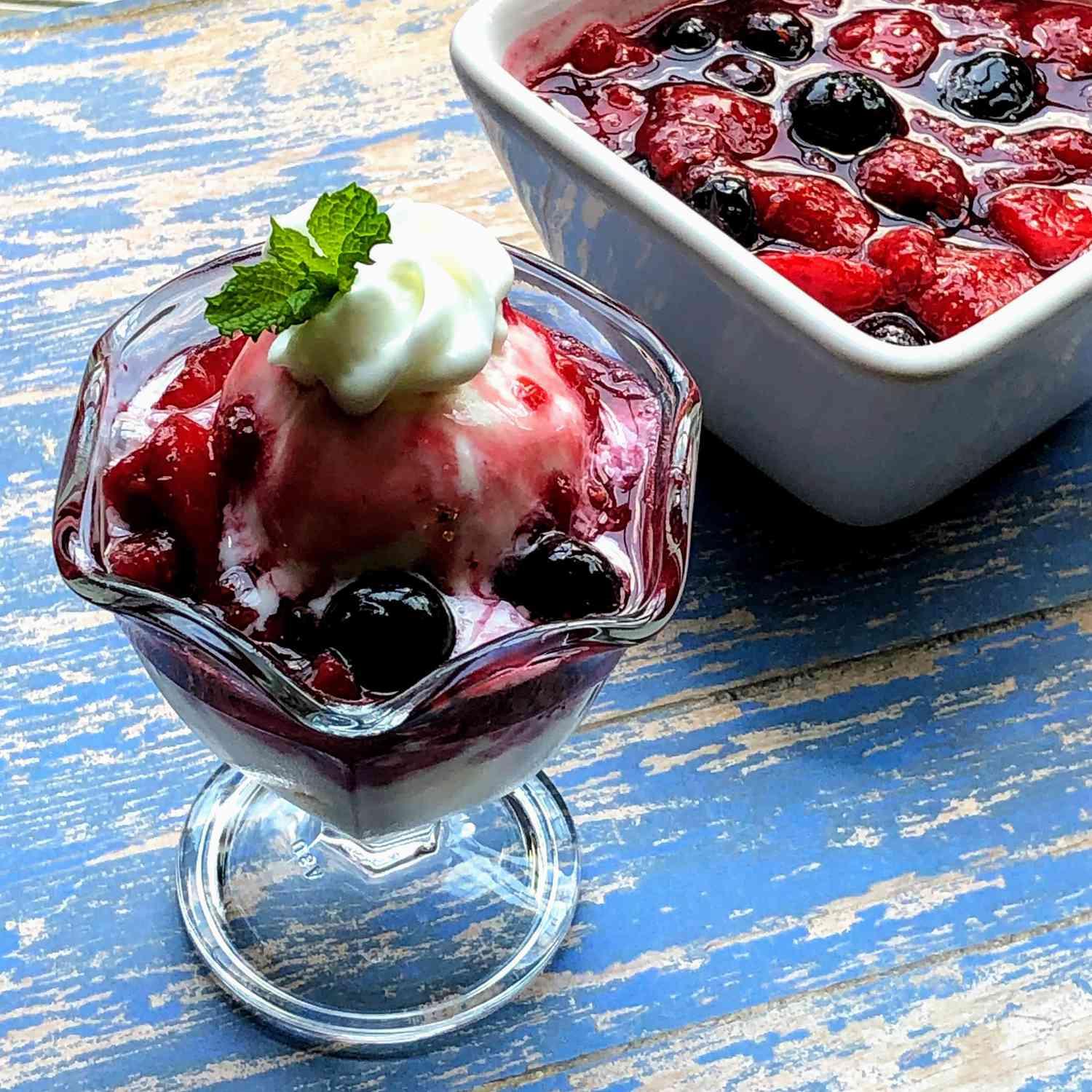
Low-acidic foods: Prioritizes non-citrus fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to minimize heartburn. Small, frequent meals: Eating smaller portions more often can reduce pressure on the stomach and esophagus. Avoid trigger foods: Excludes caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, and high-fat items that can aggravate GERD symptoms.
For Esophageal Reflux Gerd
Alkaline
Day 1
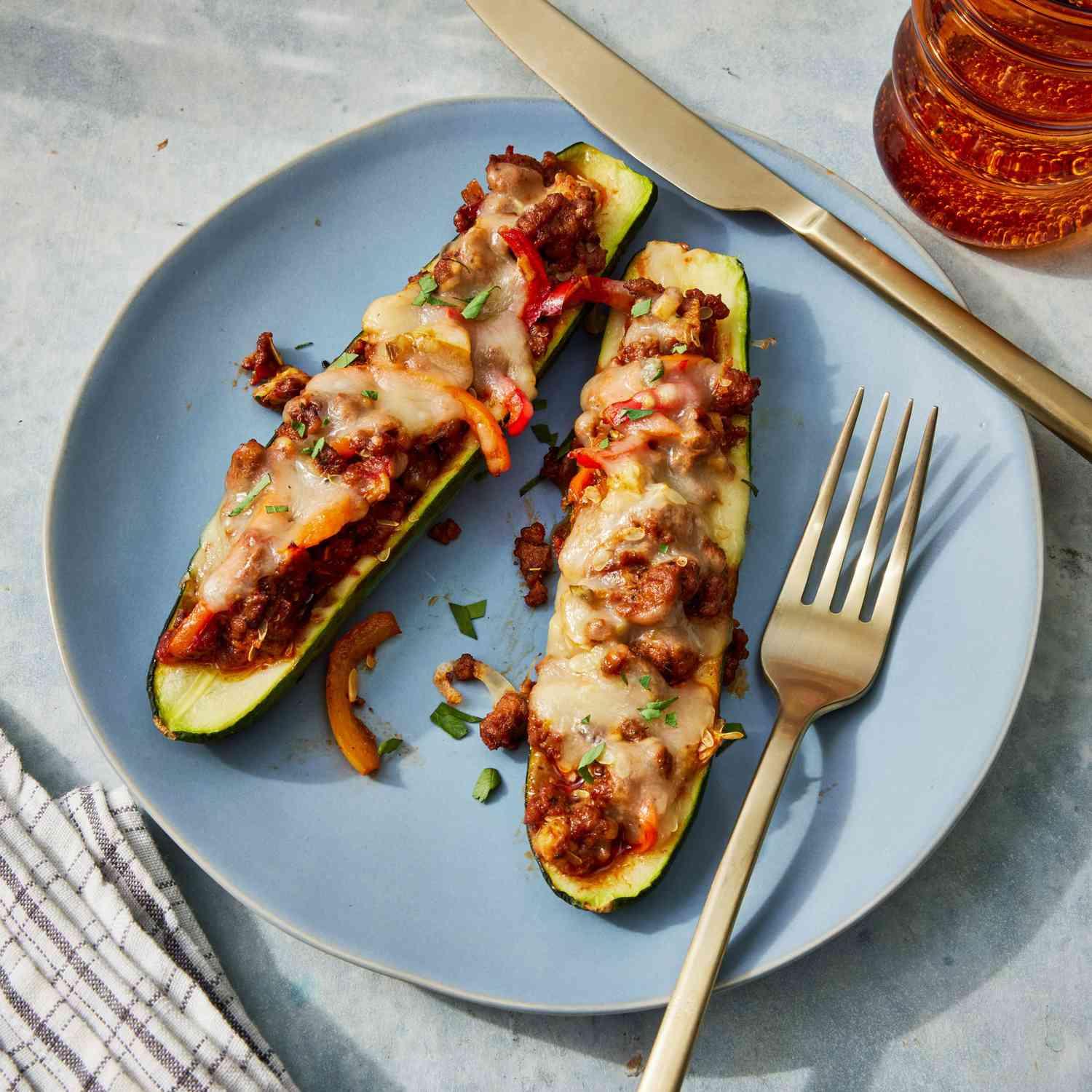
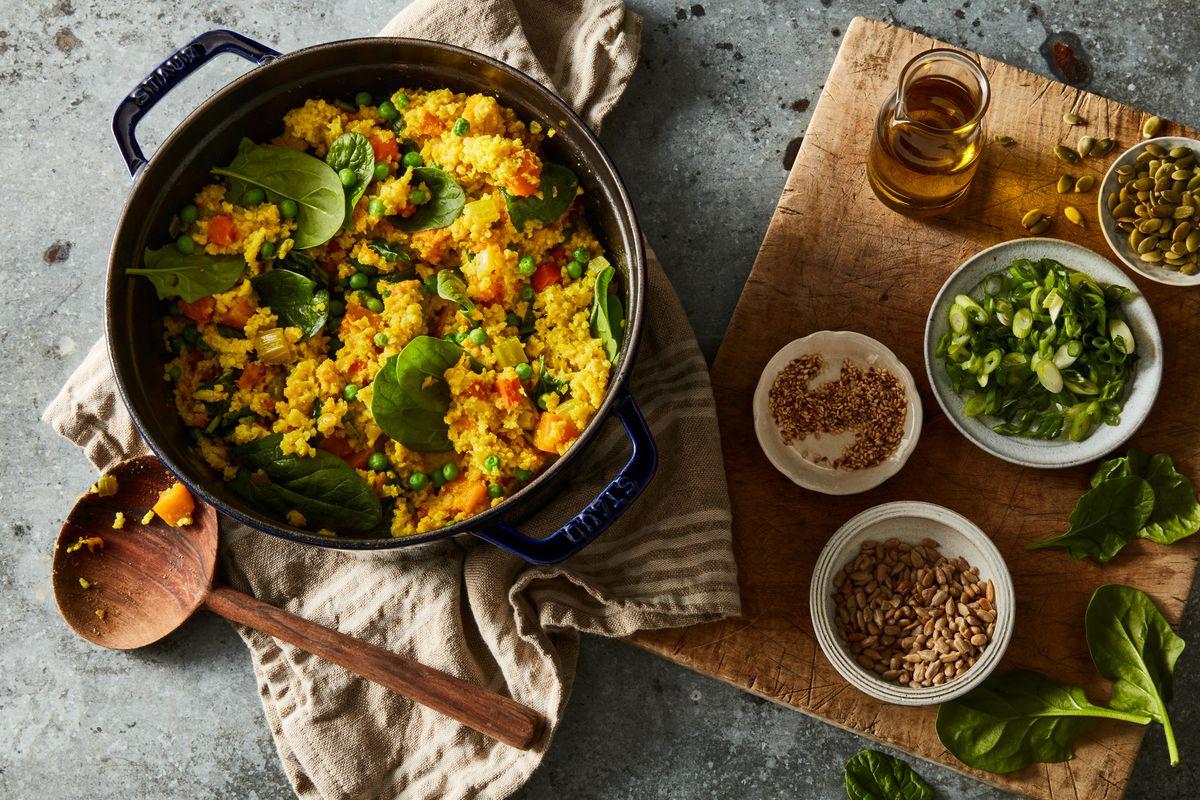
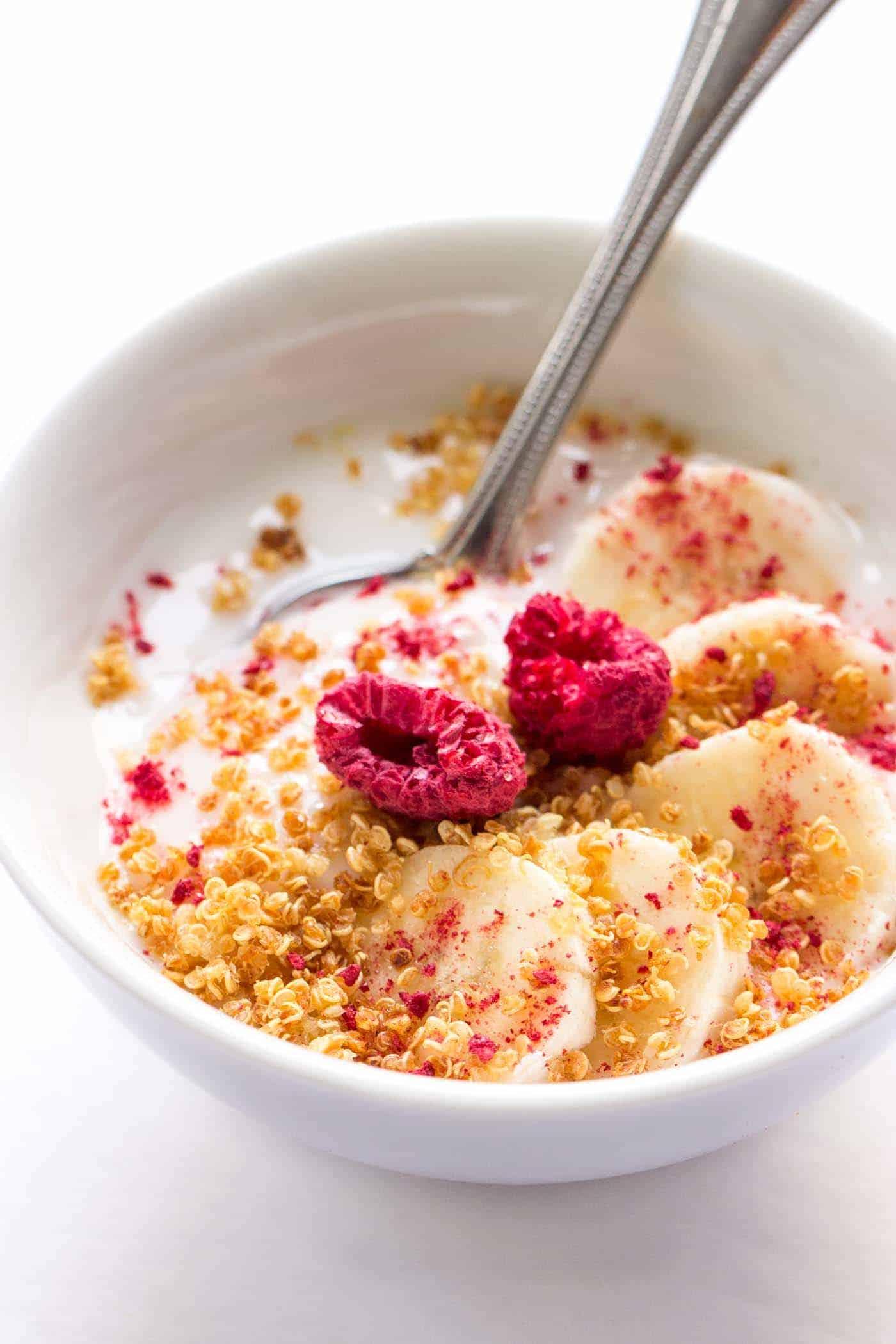
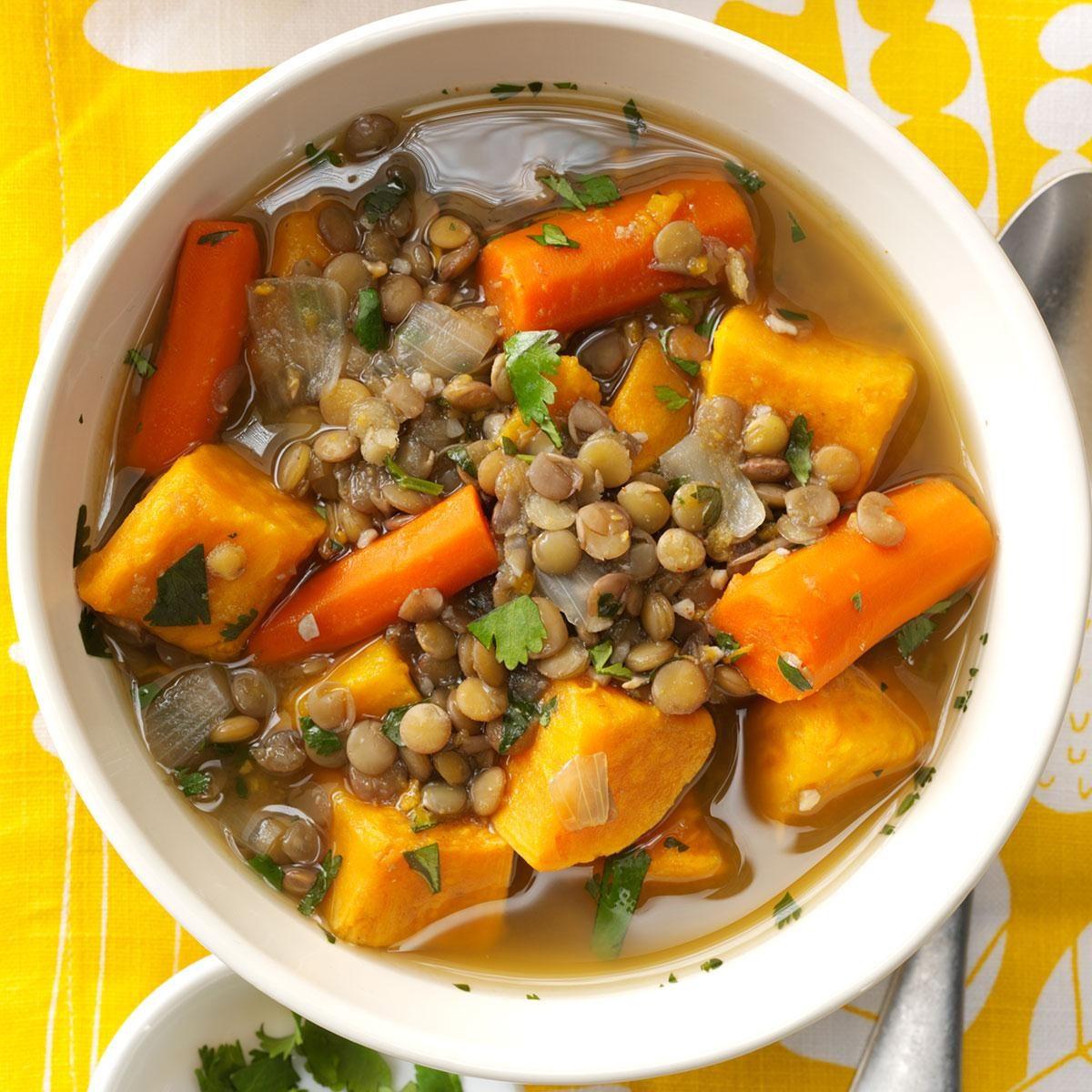
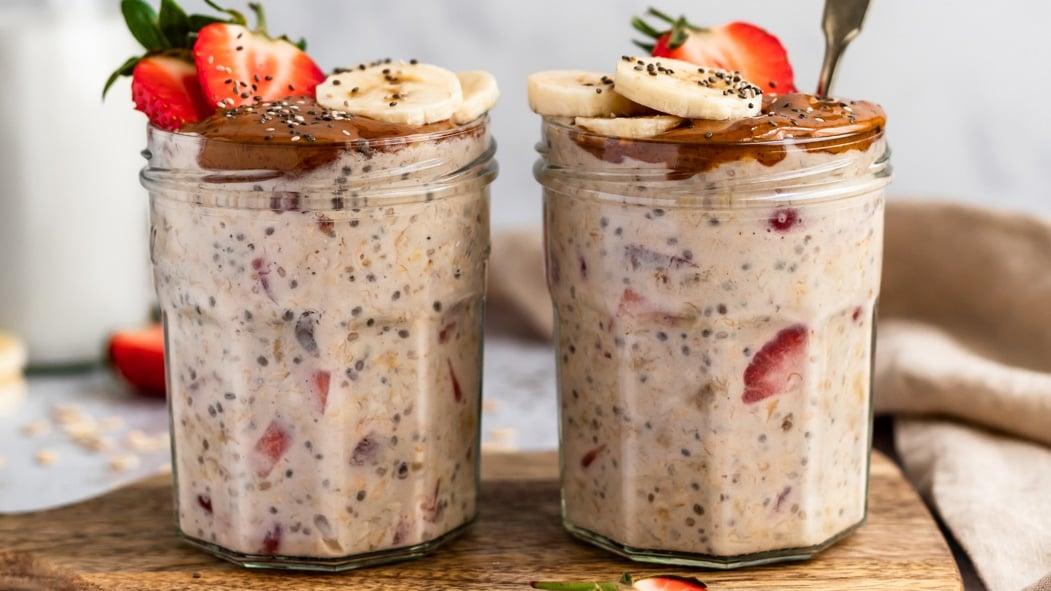
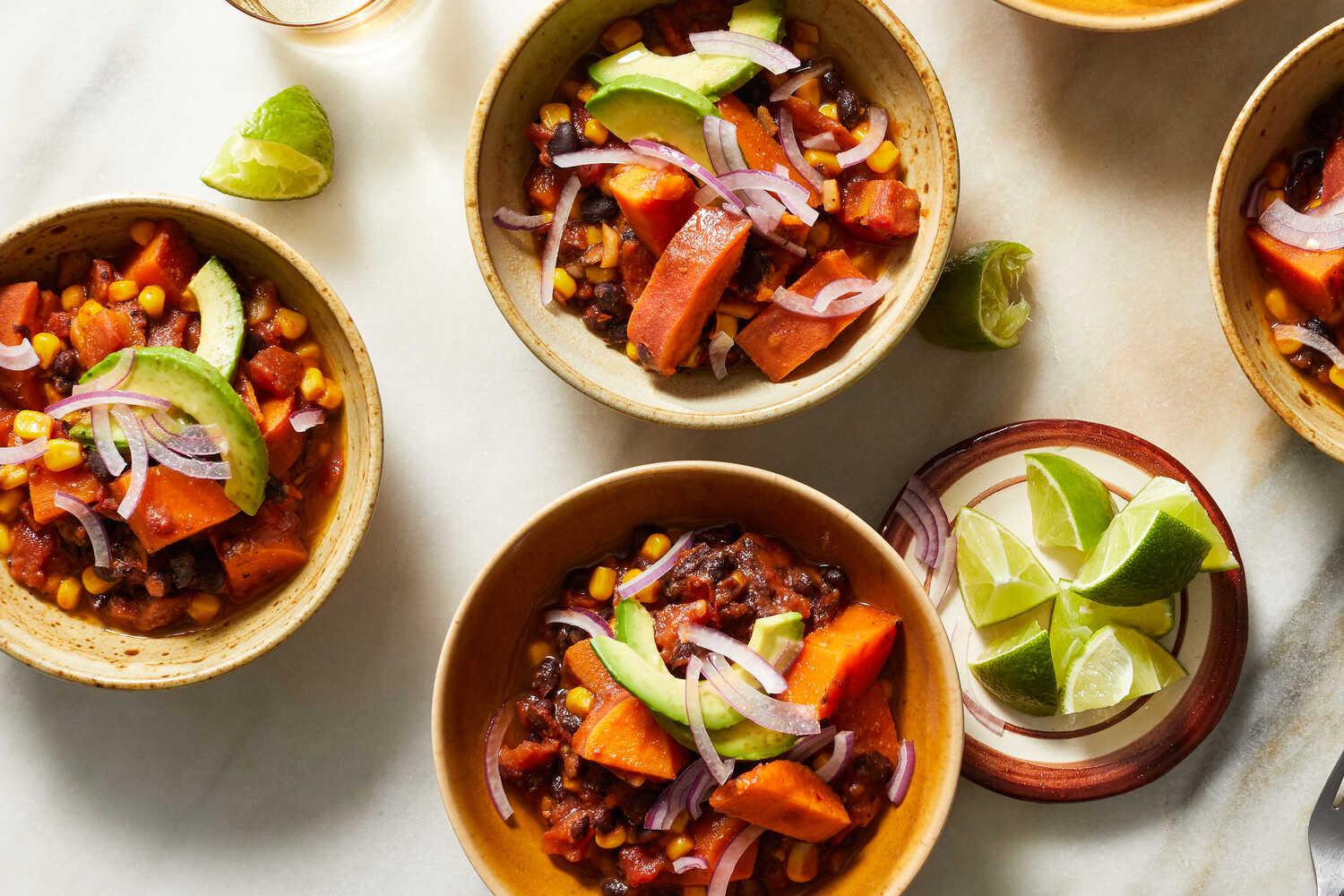
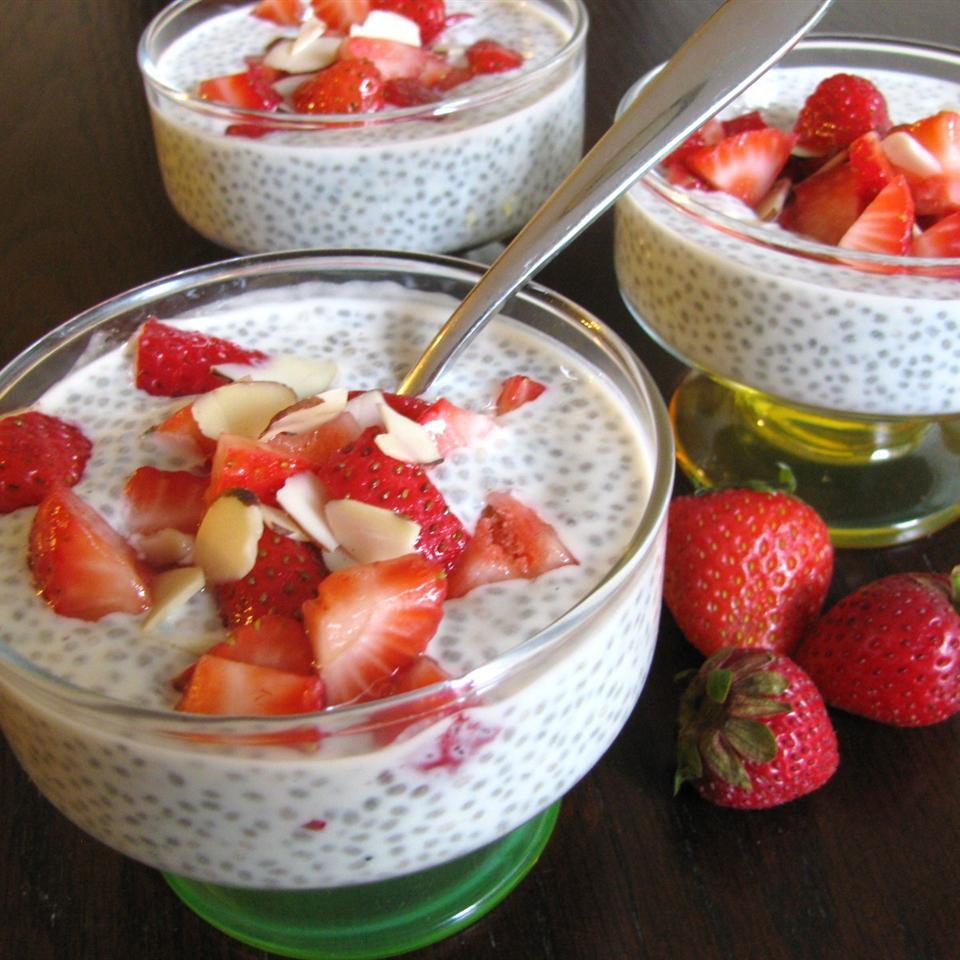
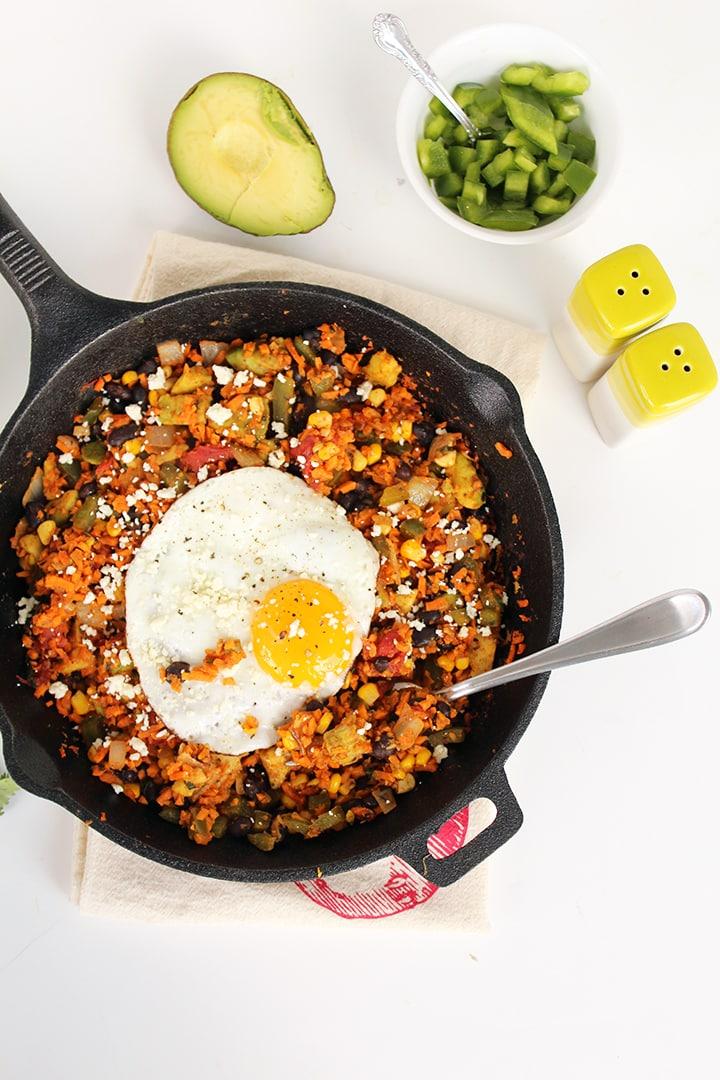
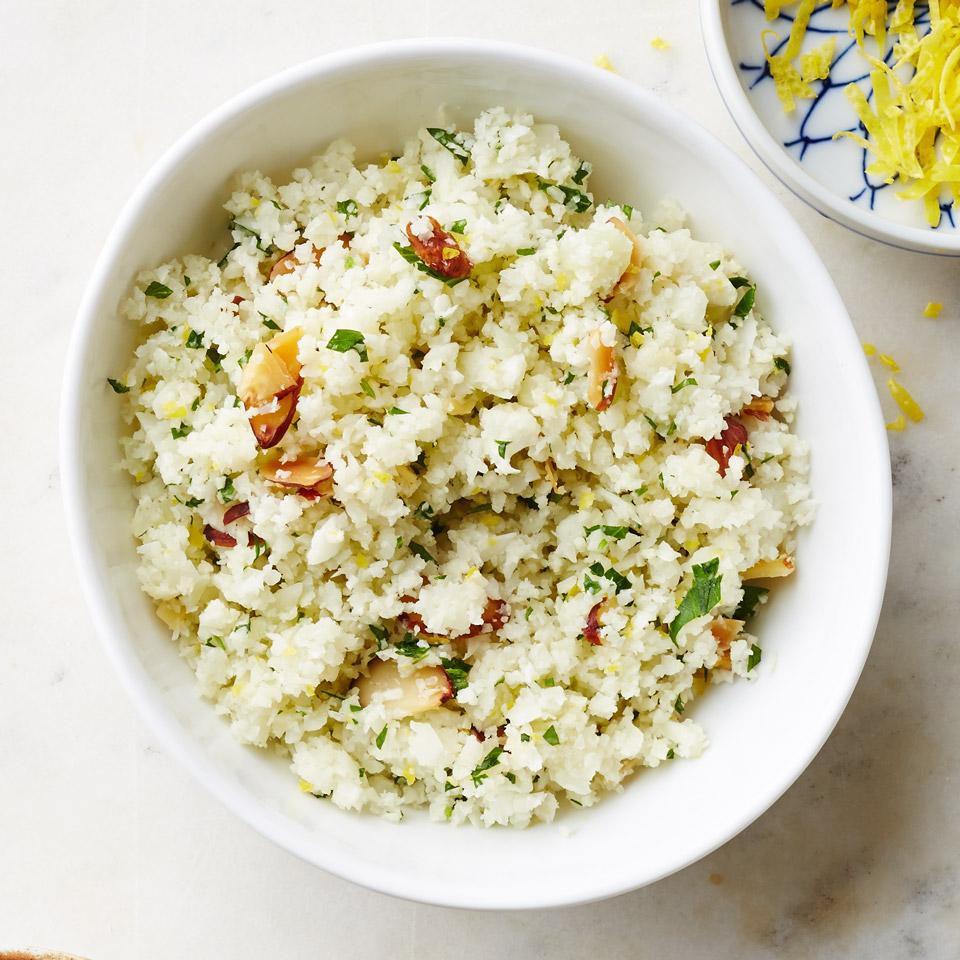
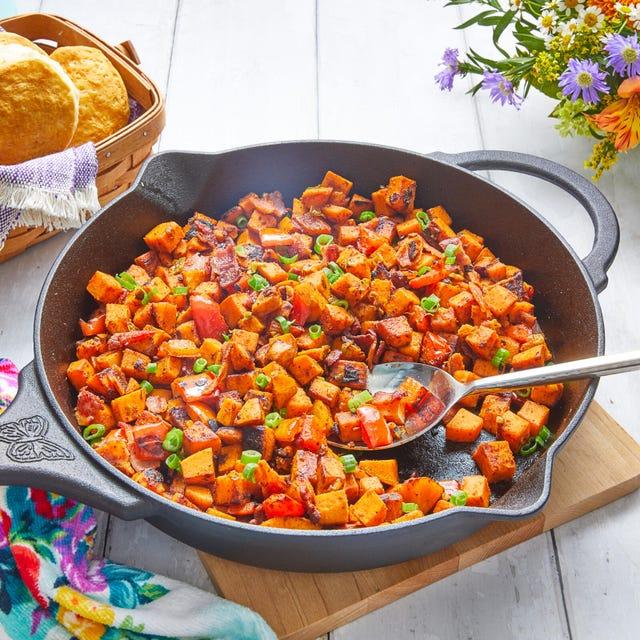
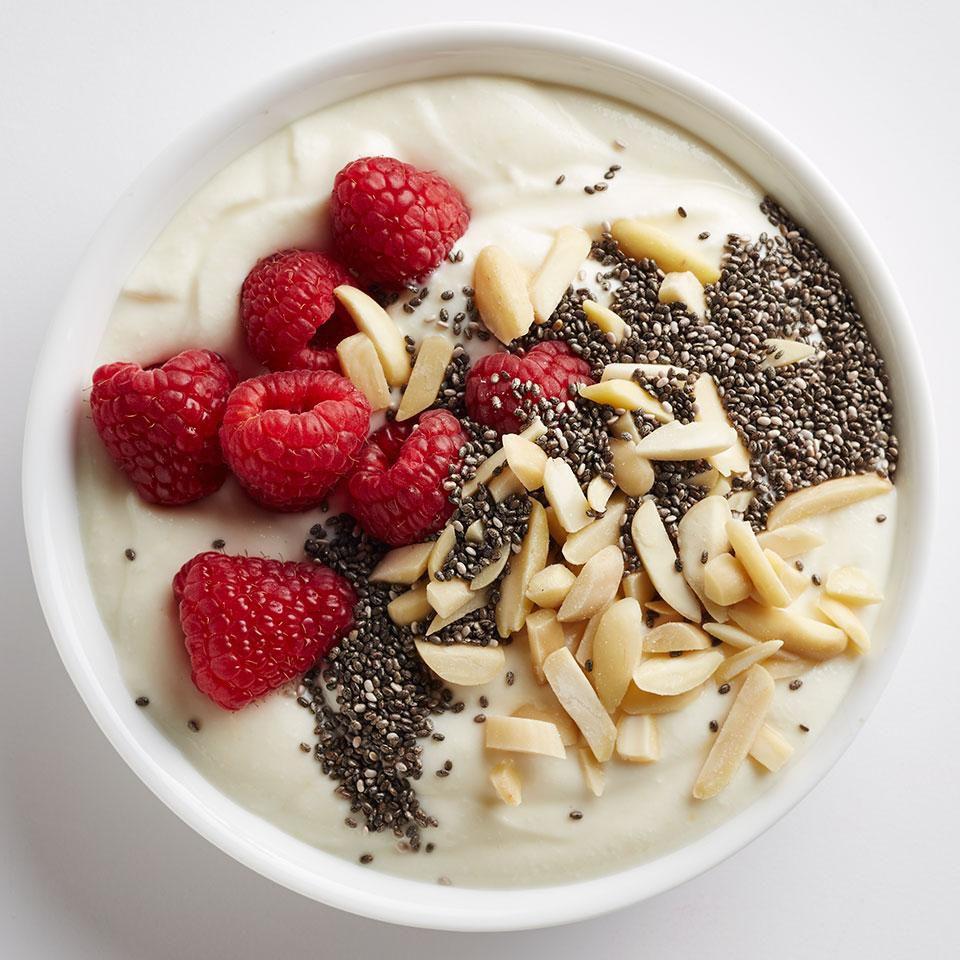
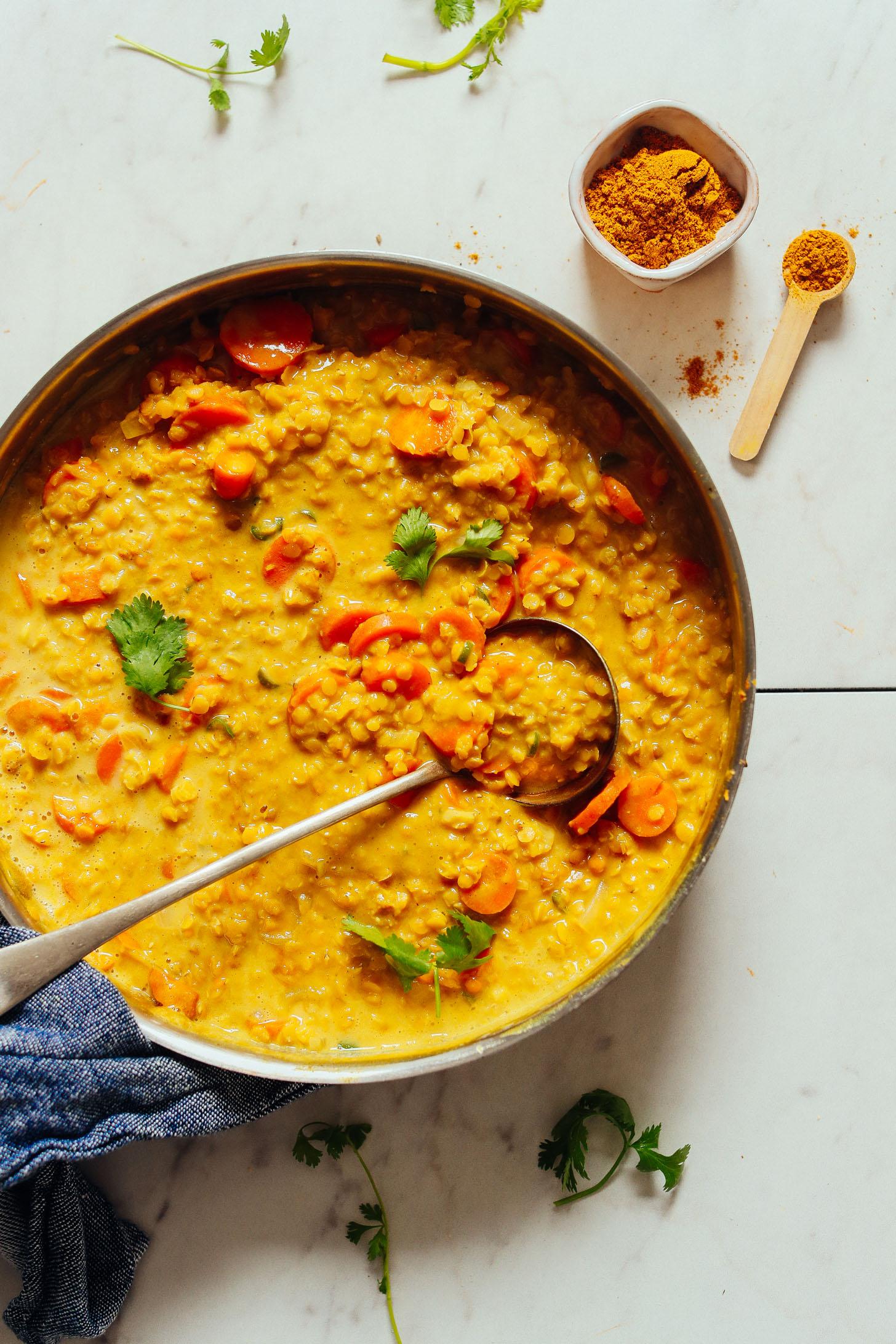
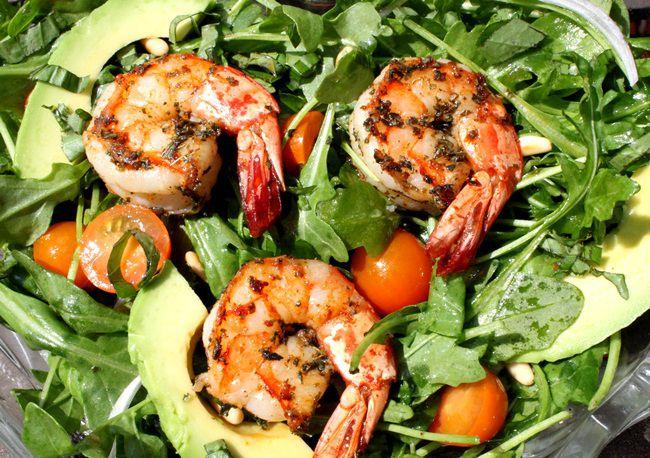
Focus on low-glycemic, plant-based foods to manage blood glucose levels, incorporating high-fiber options like legumes, whole grains, and vegetables to promote satiety and improve insulin sensitivity. Limit intake of refined carbohydrates and sugary foods, while ensuring adequate protein through sources like tofu, tempeh, lentils, and nuts to maintain muscle mass and assist with glucose regulation. Include healthy fats from avocados, seeds, and olive oil for heart health, and monitor portion sizes to support weight management, which is crucial in type 2 diabetes management.
For Diabetes Mellitus Dm
Vegetarian
Day 1
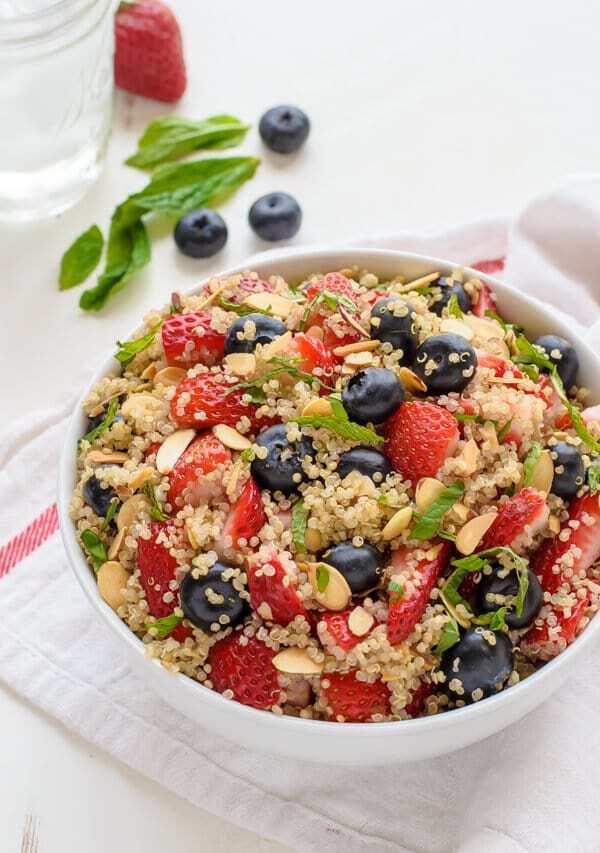
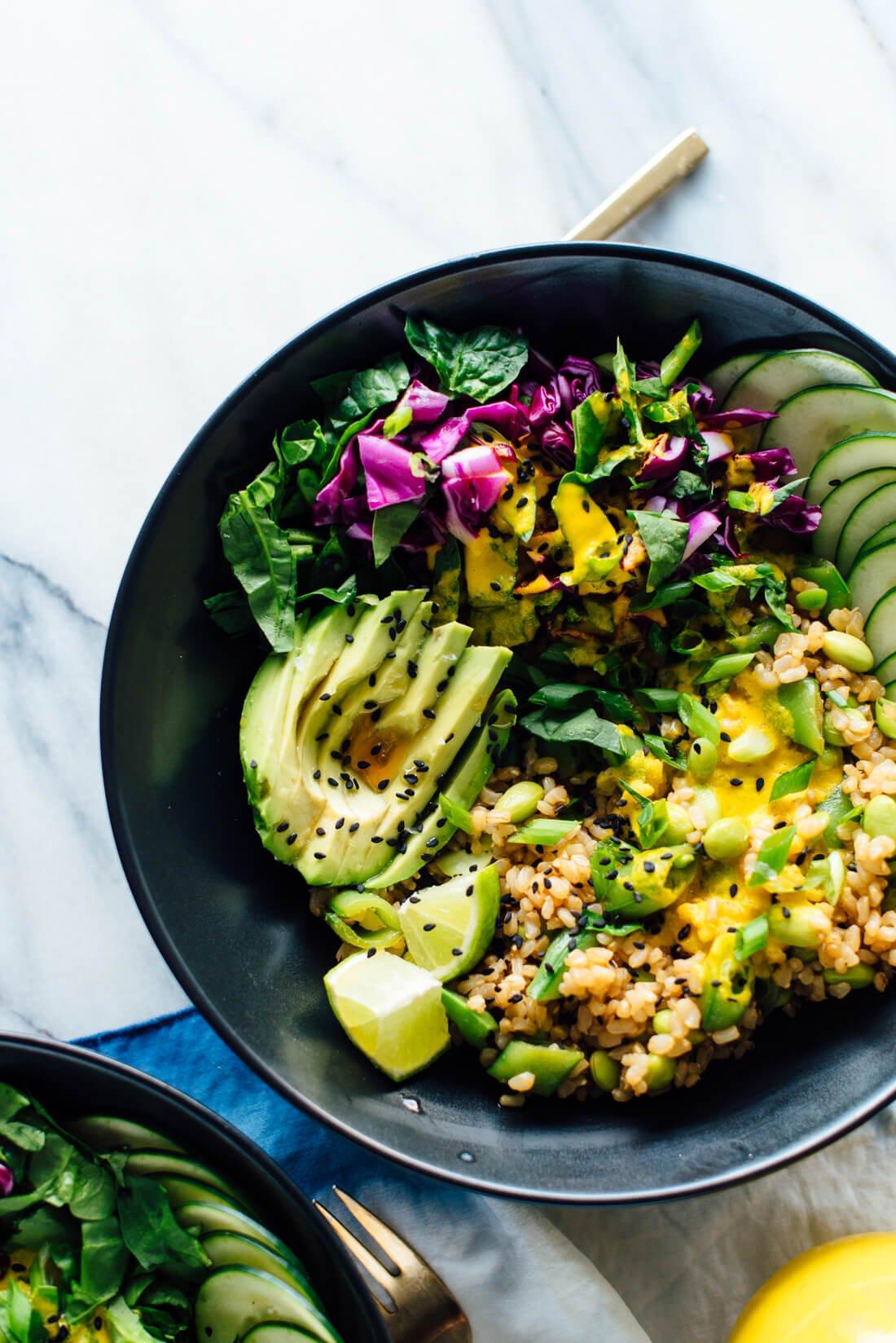
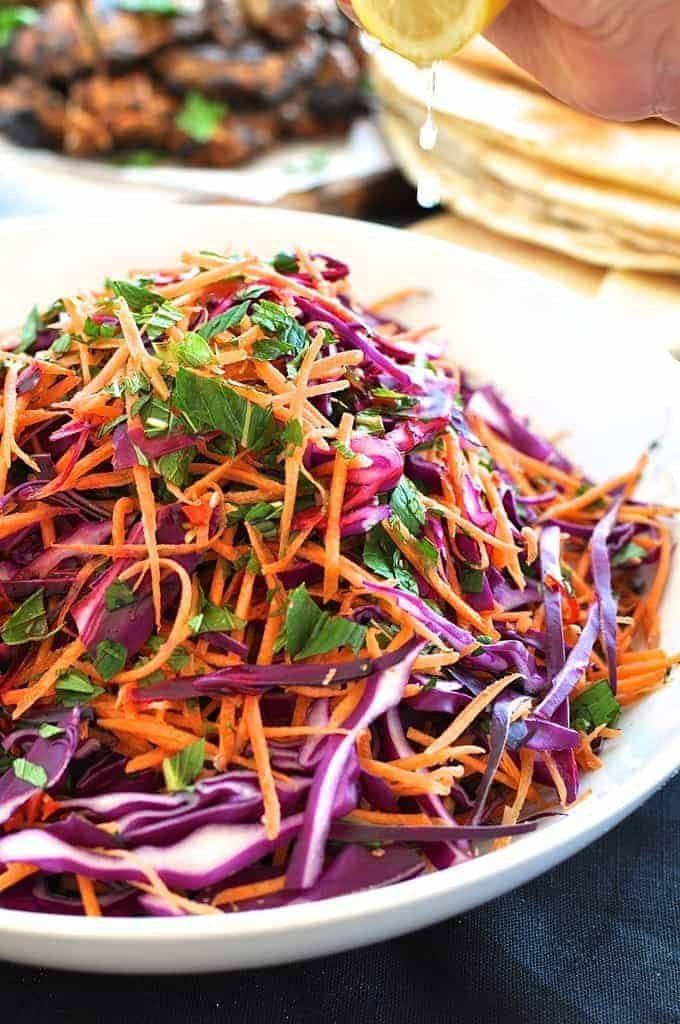
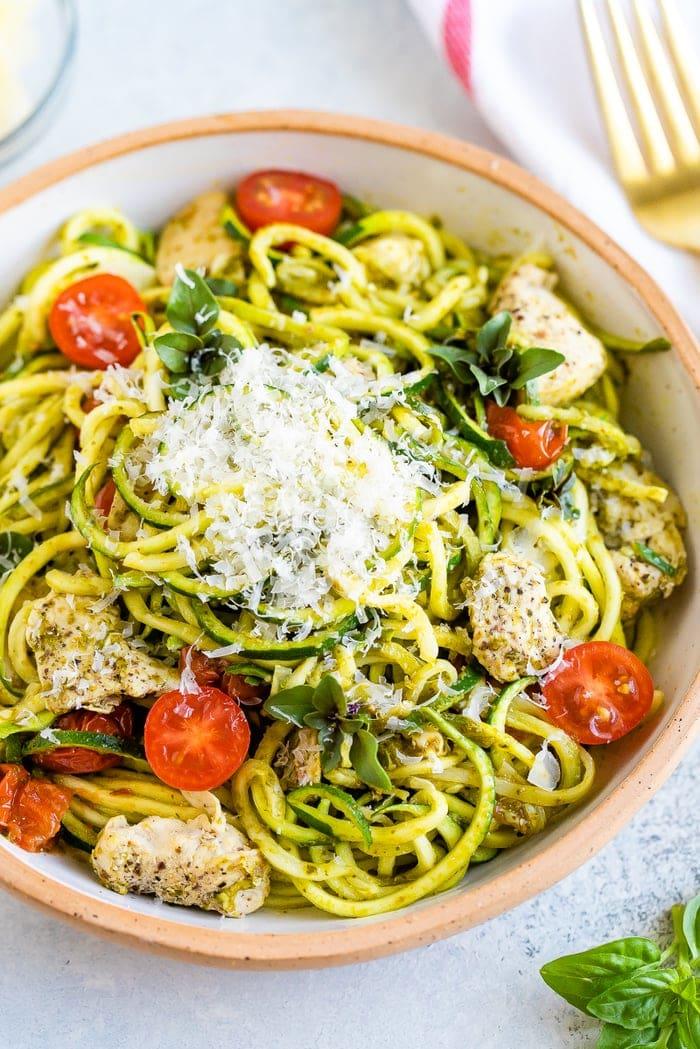
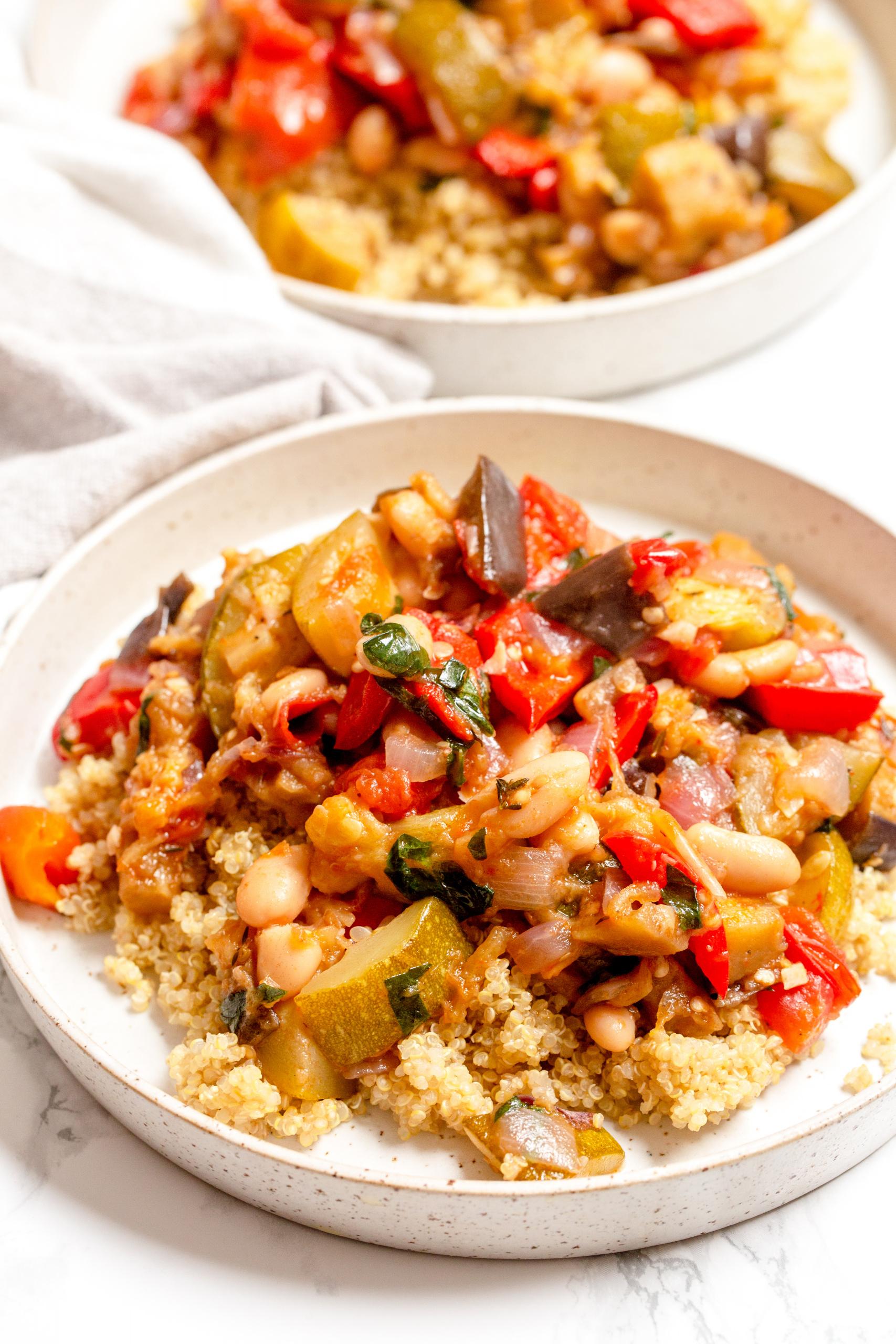
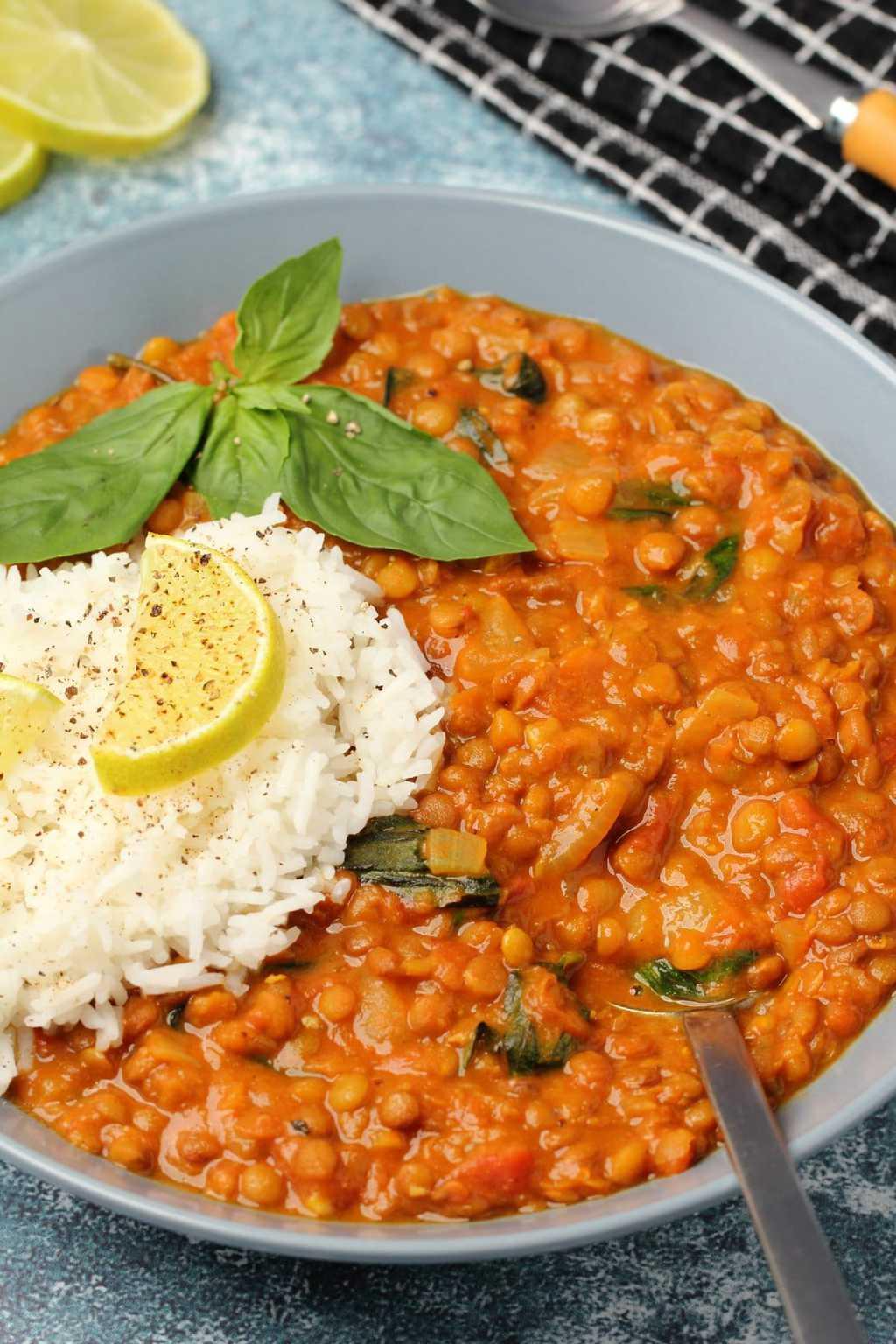
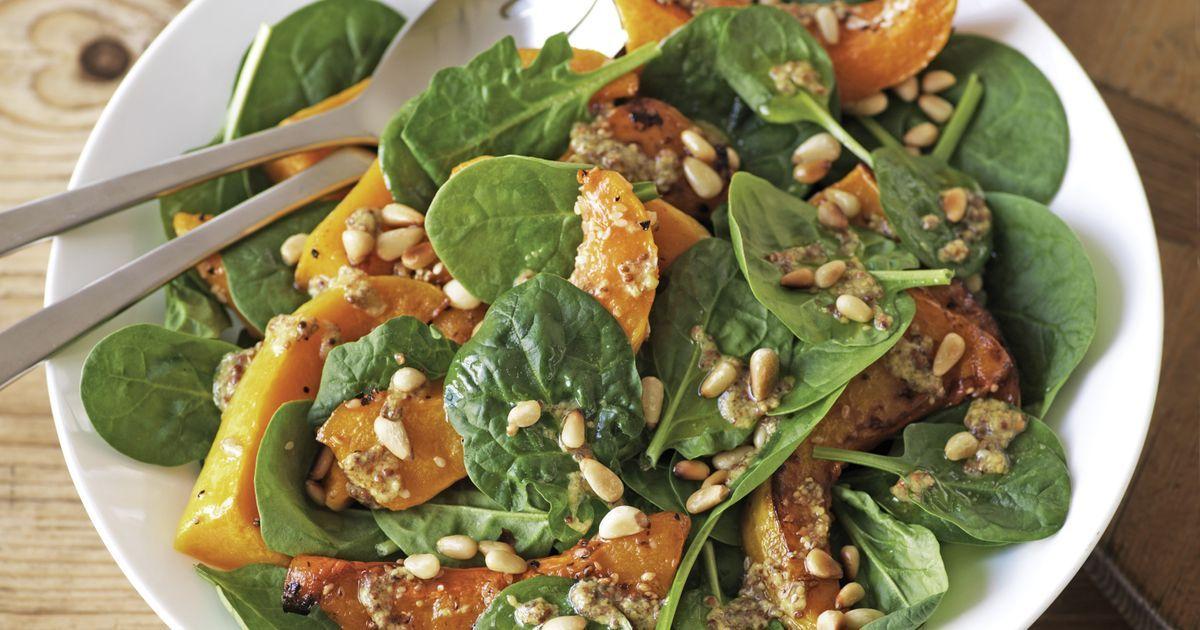
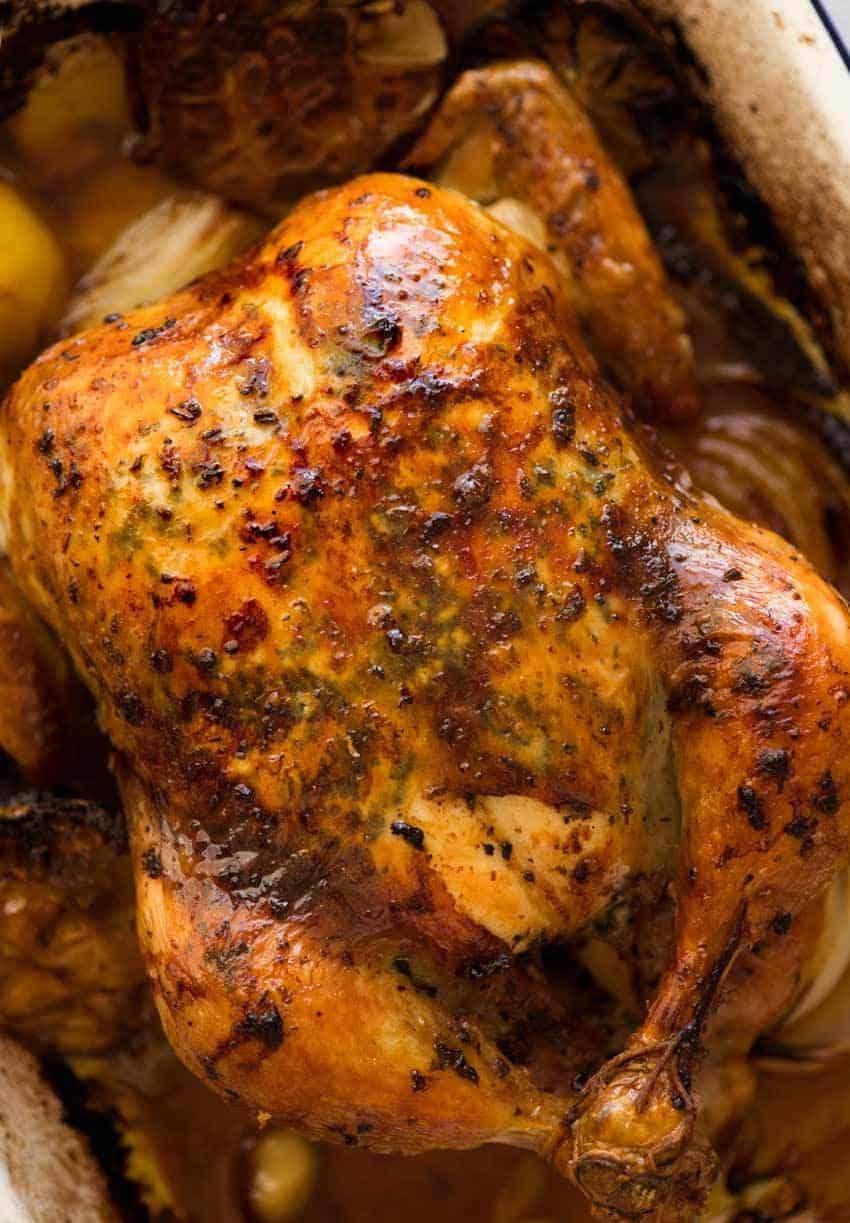
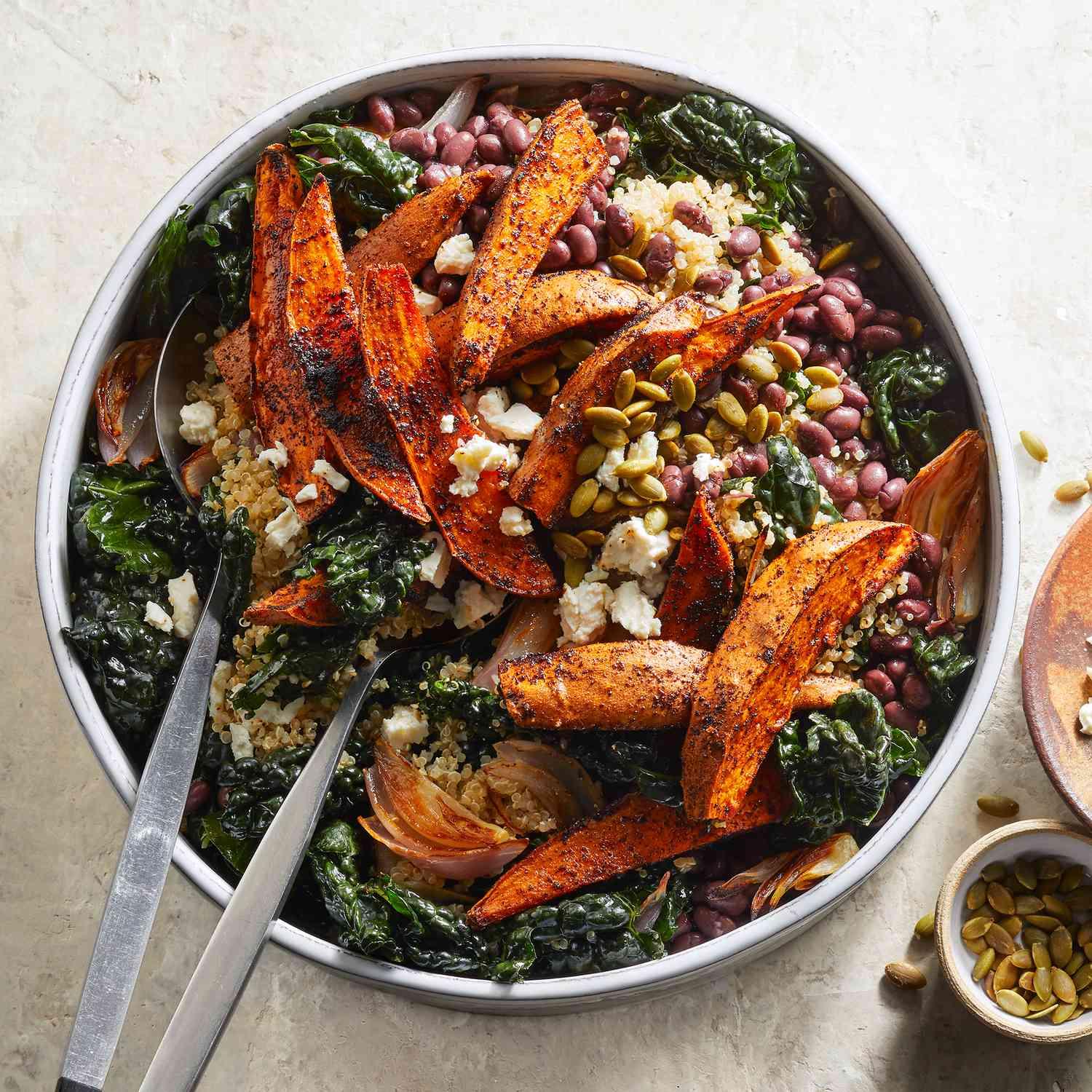
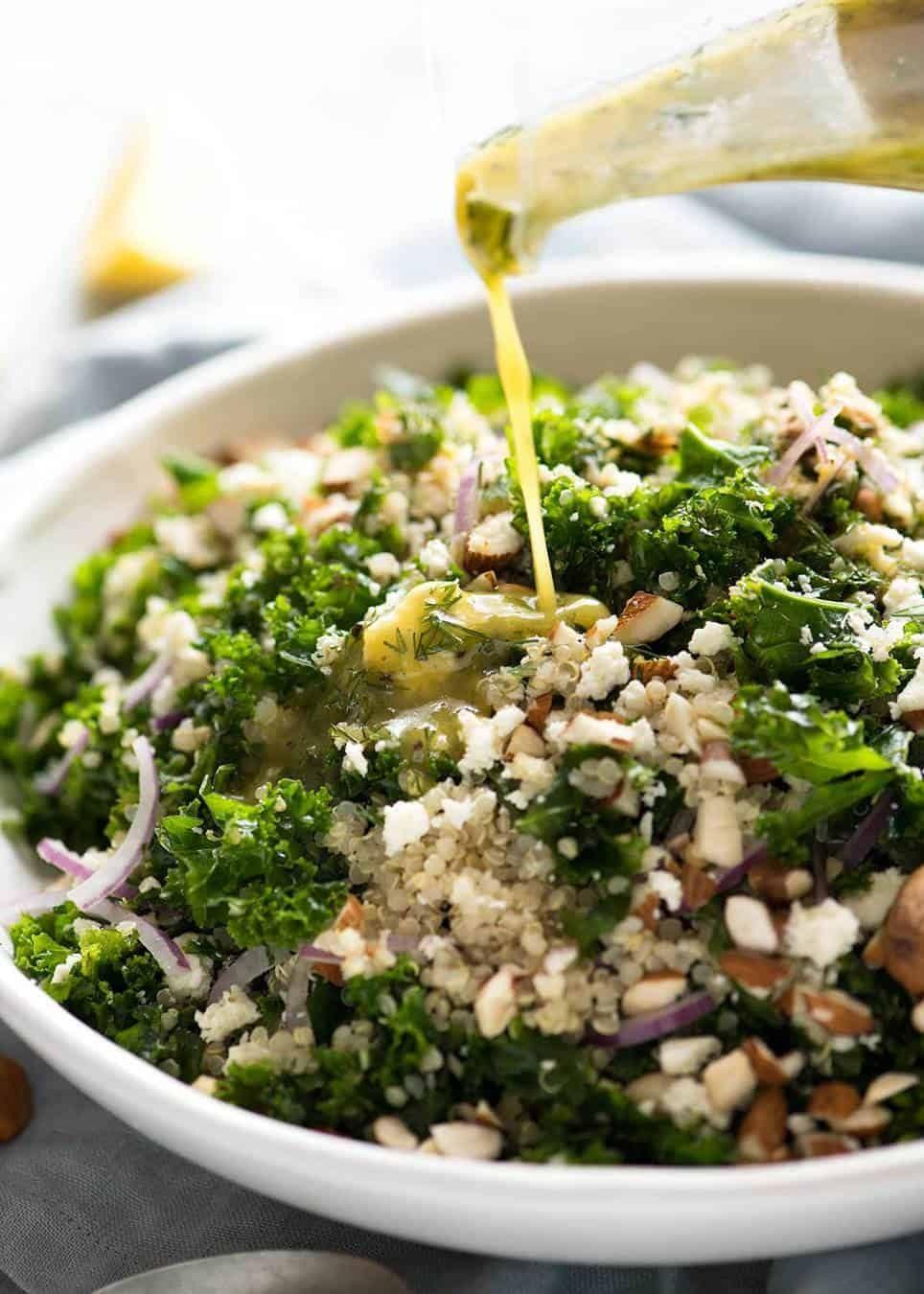
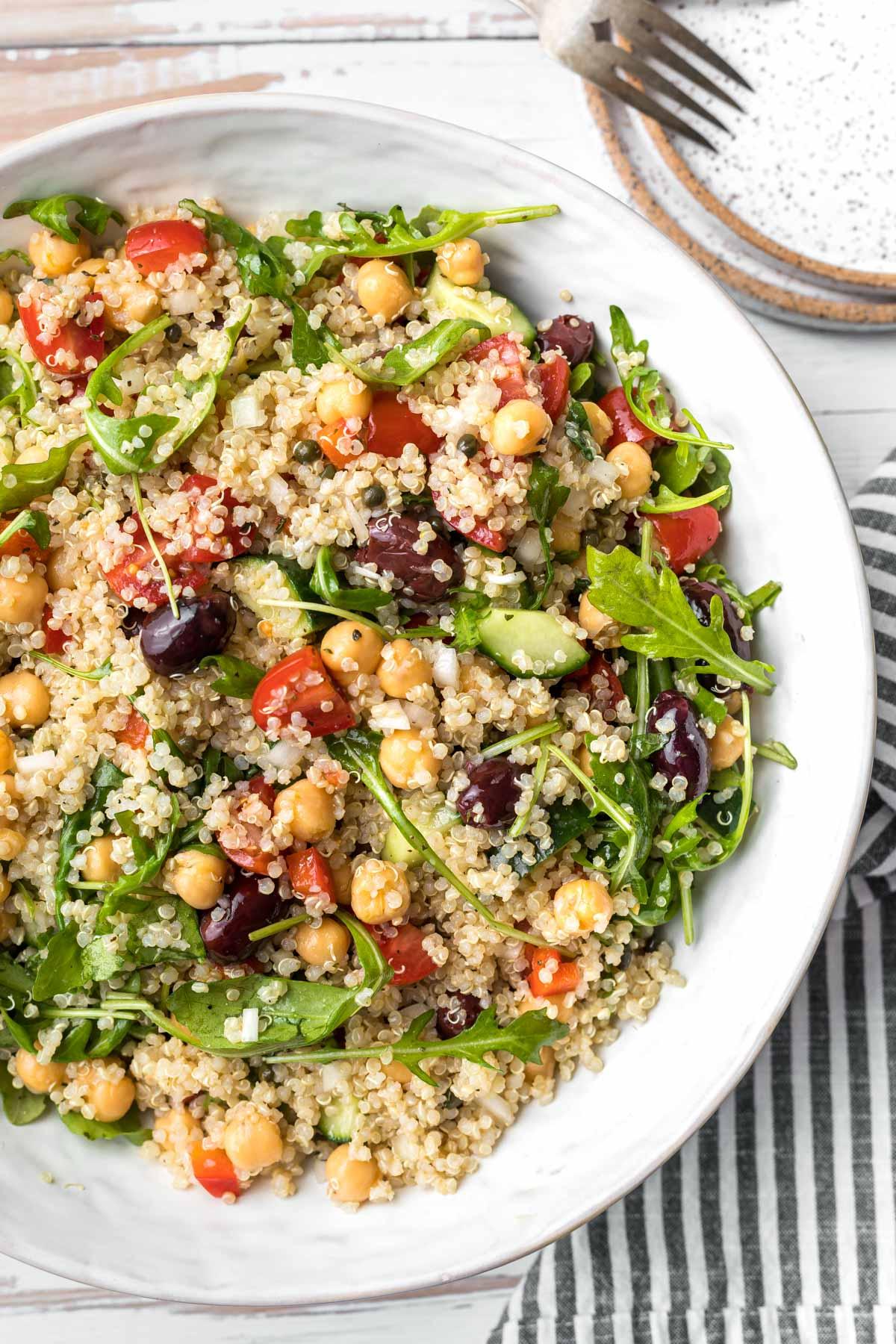
Focus on high fiber, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to improve weight management and reduce insulin resistance. Include healthy fats from sources like olive oil, nuts, and fish to support heart health and manage cholesterol levels. Limit added sugars, refined carbs, and processed meats to mitigate inflammation and decrease the risk of further metabolic complications.
For Metabolic Syndrome
Mediterranean
Day 1
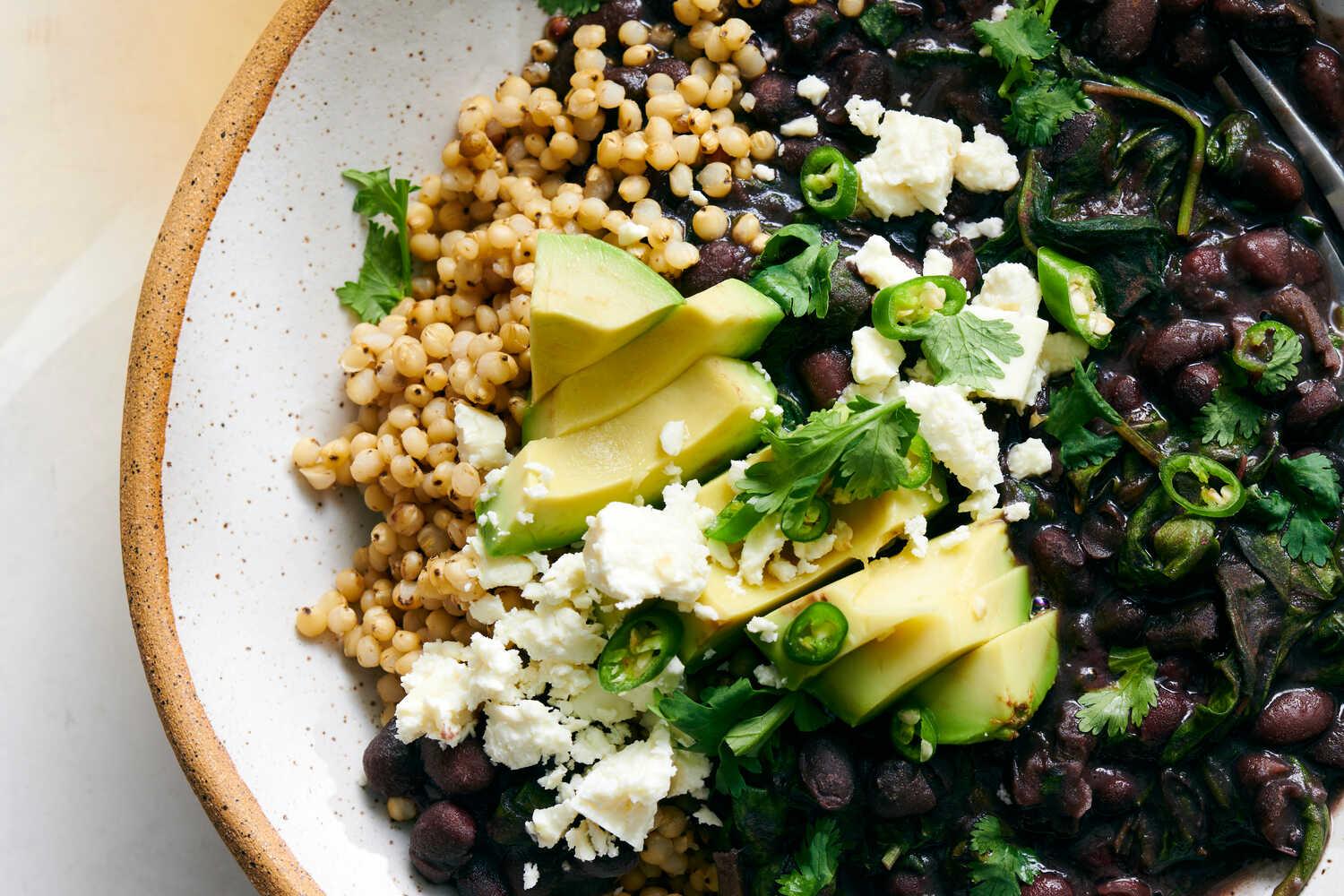
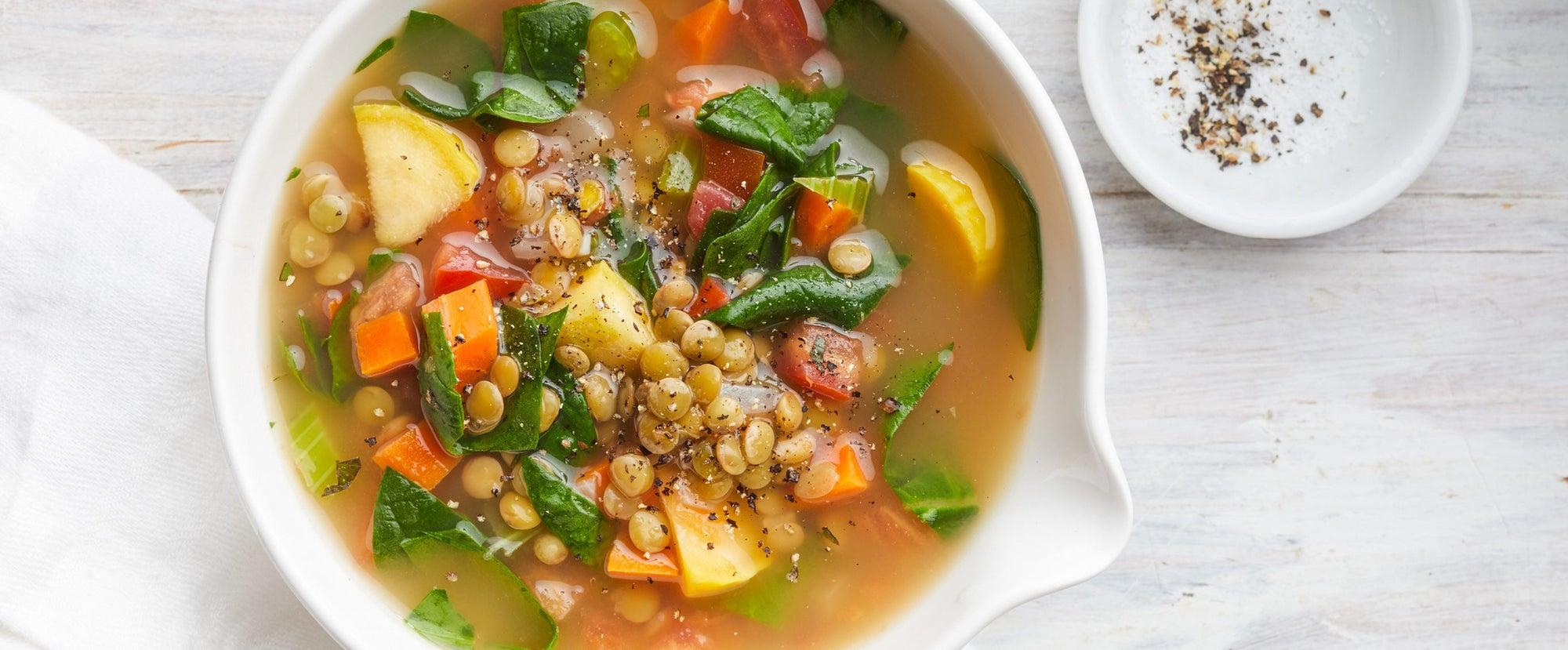
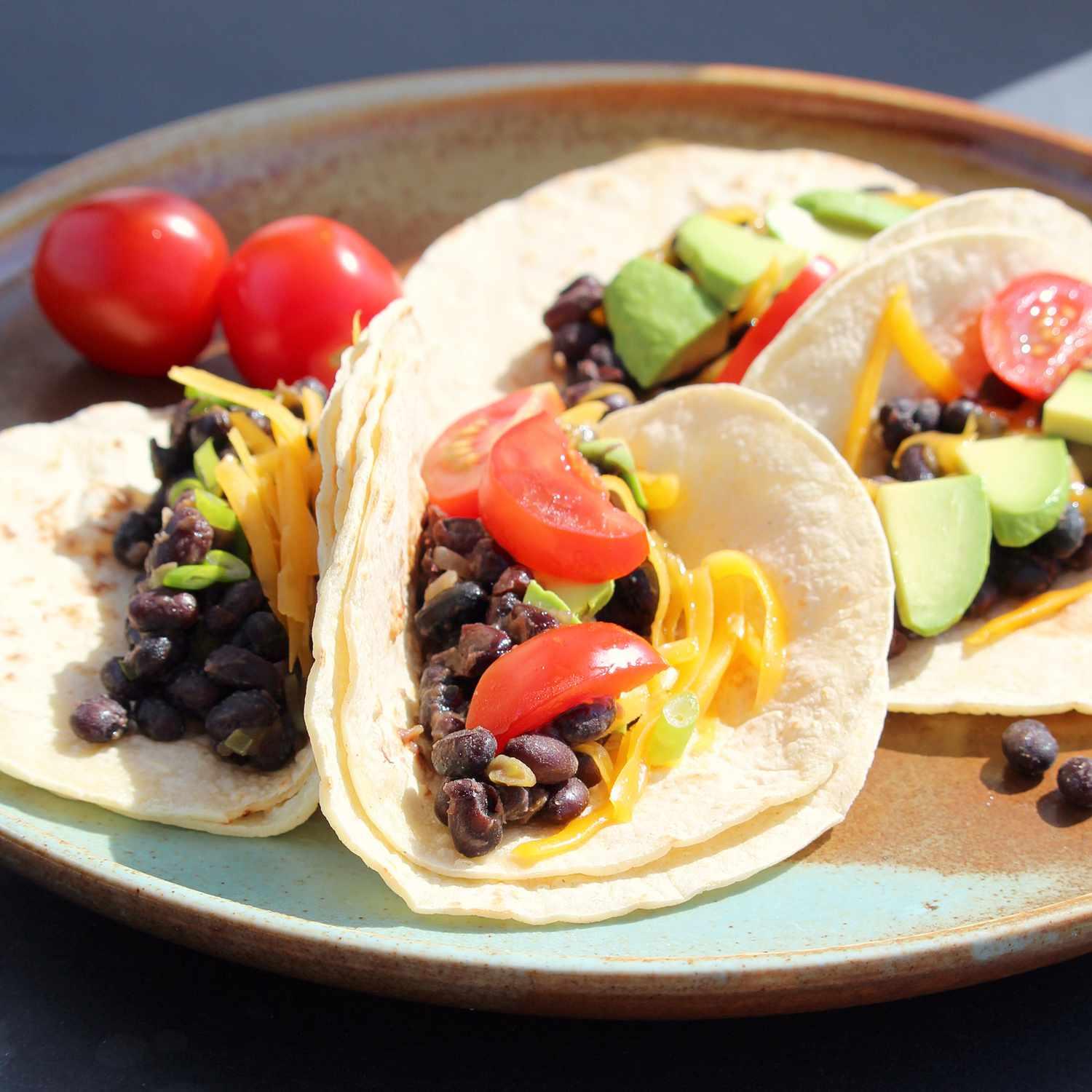
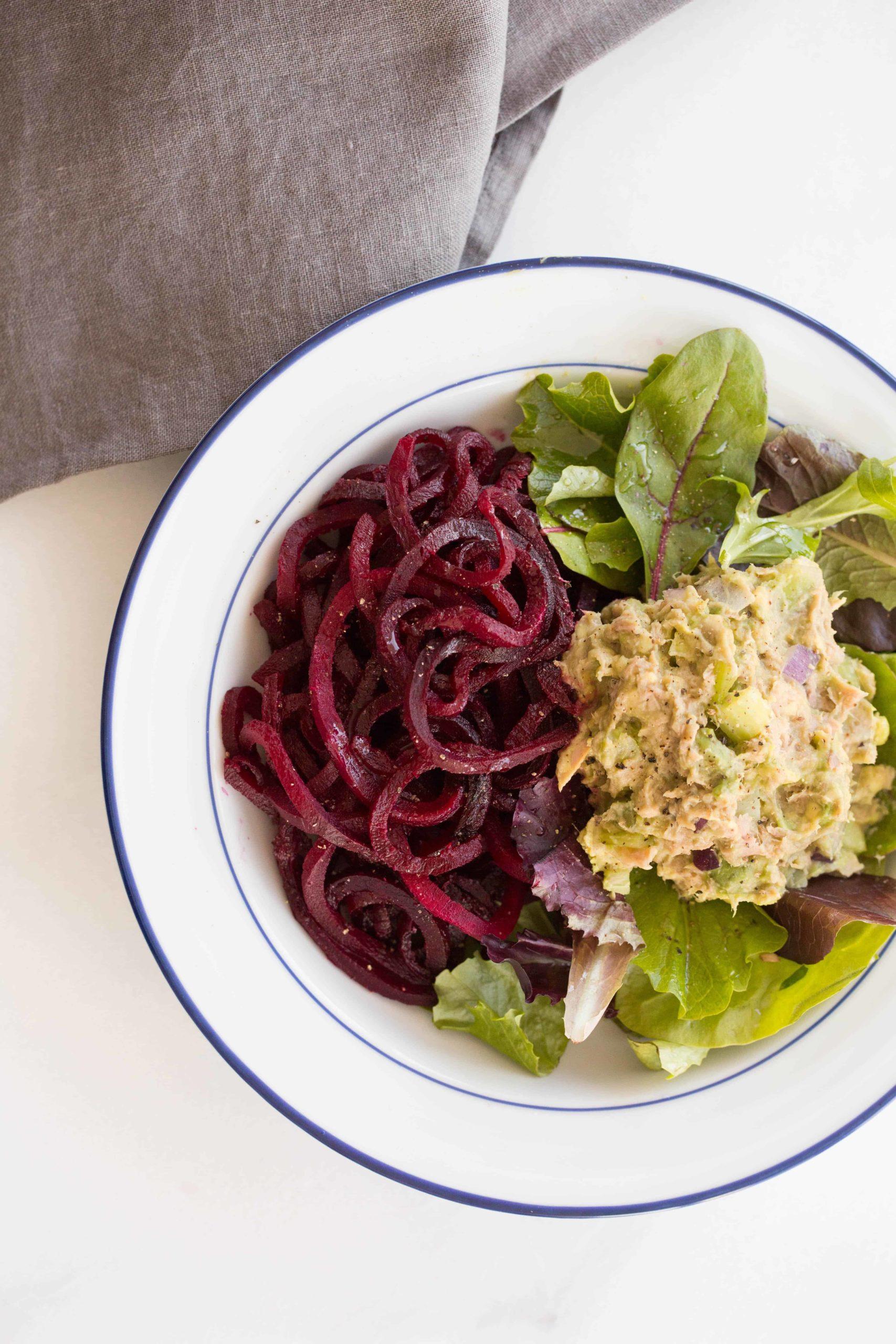
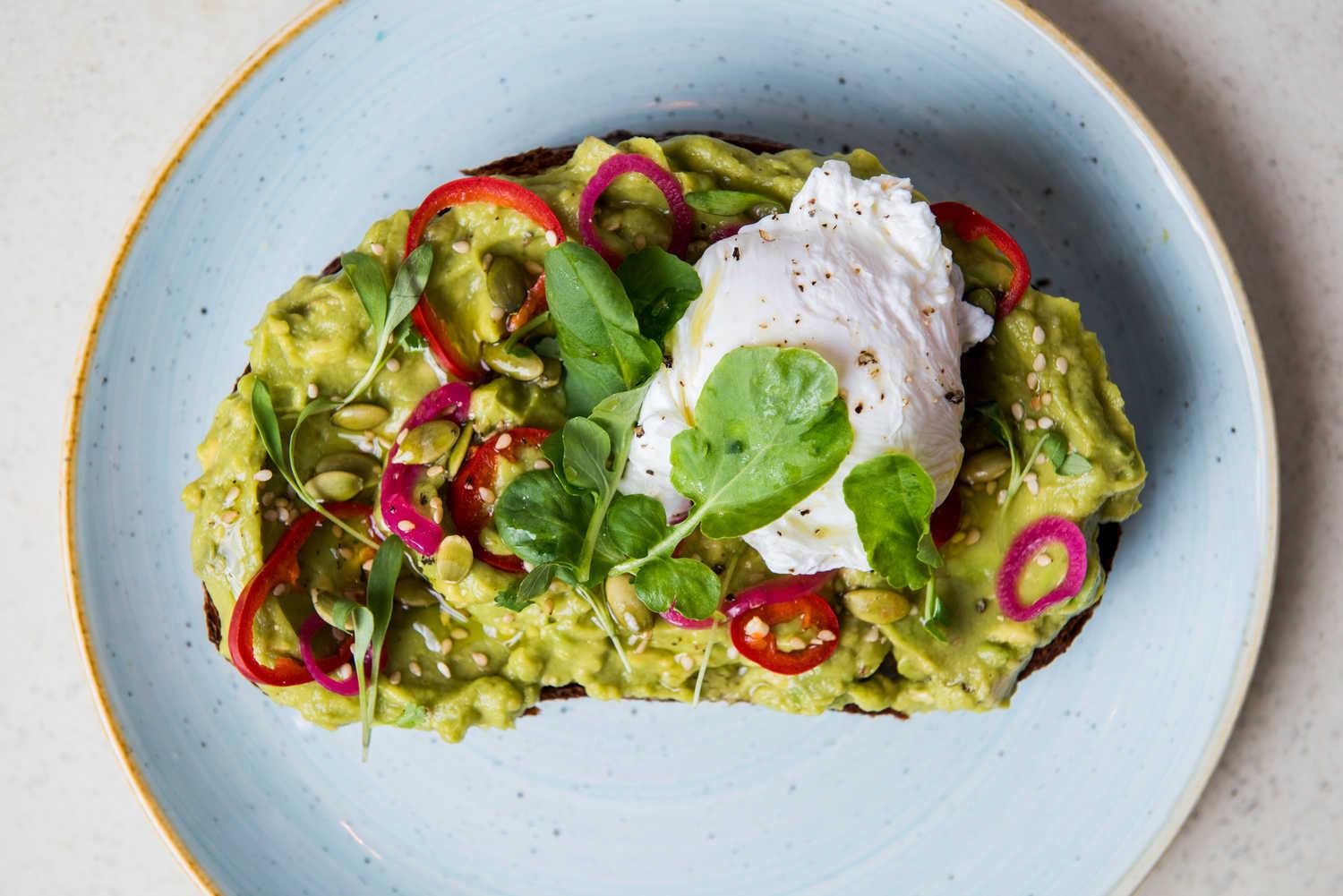
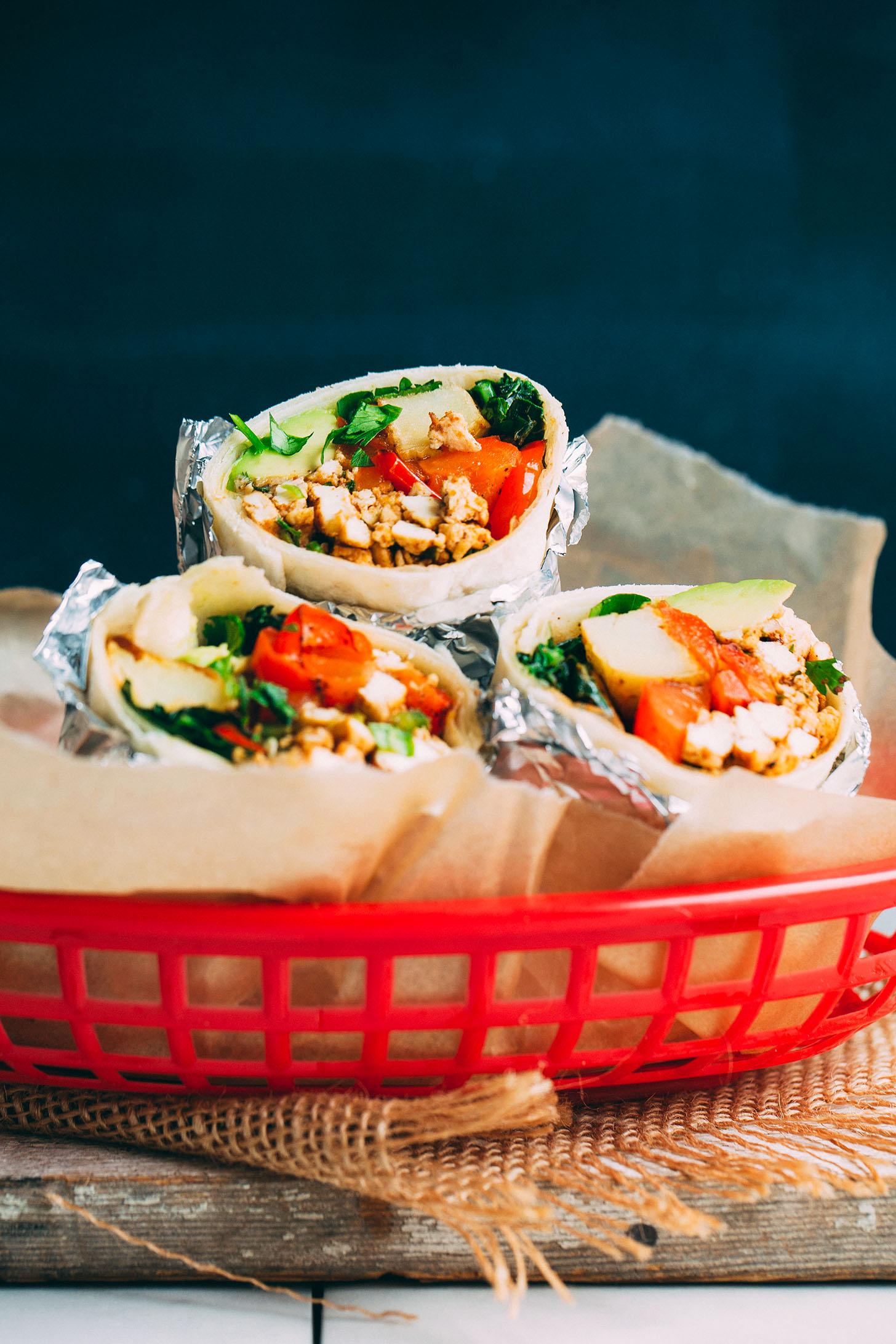
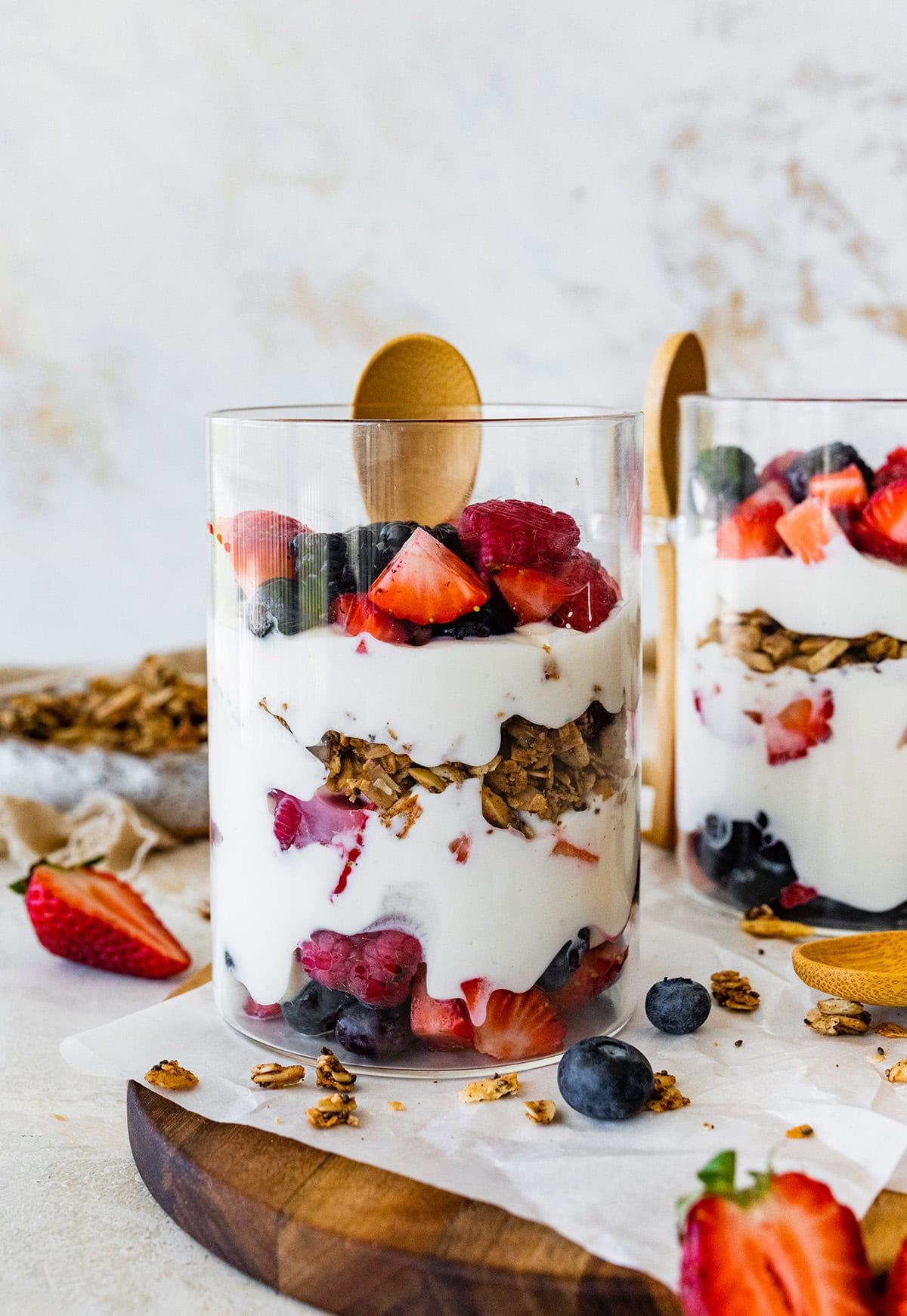
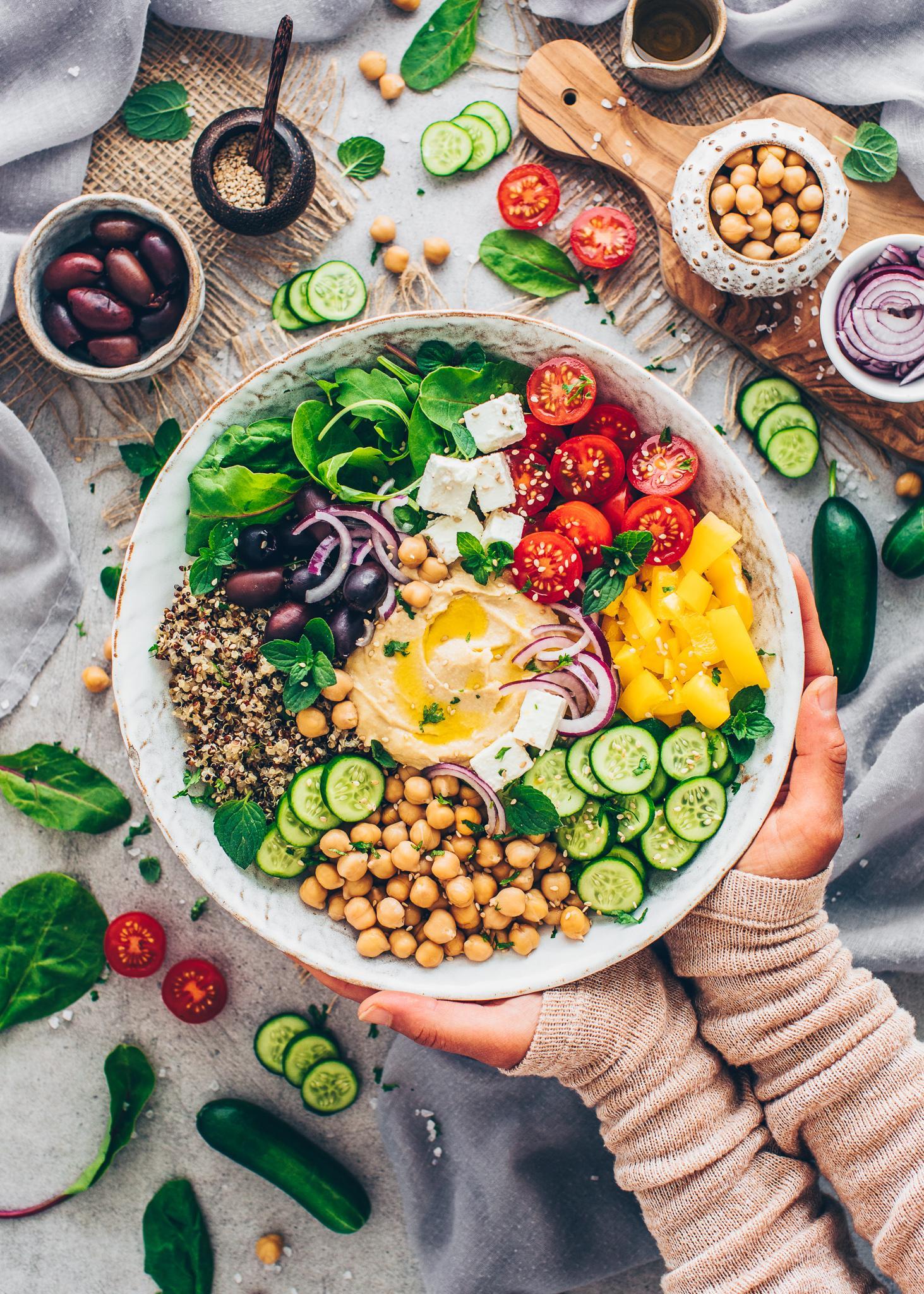
A low-FODMAP meal plan limits foods high in certain fermentable carbs to reduce bloating, gas, and bowel irregularities associated with IBS. The plan focuses on non-trigger foods, incorporating easily digestible fruits, vegetables, proteins, and grains, and avoids onions, garlic, beans, wheat, and lactose. It's typically implemented in phases, starting with elimination of high-FODMAP foods, followed by gradual reintroduction to identify personal triggers.
For Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Low Fodmap
Day 1


AI recipes for Crohn's Disease & Gluten Free
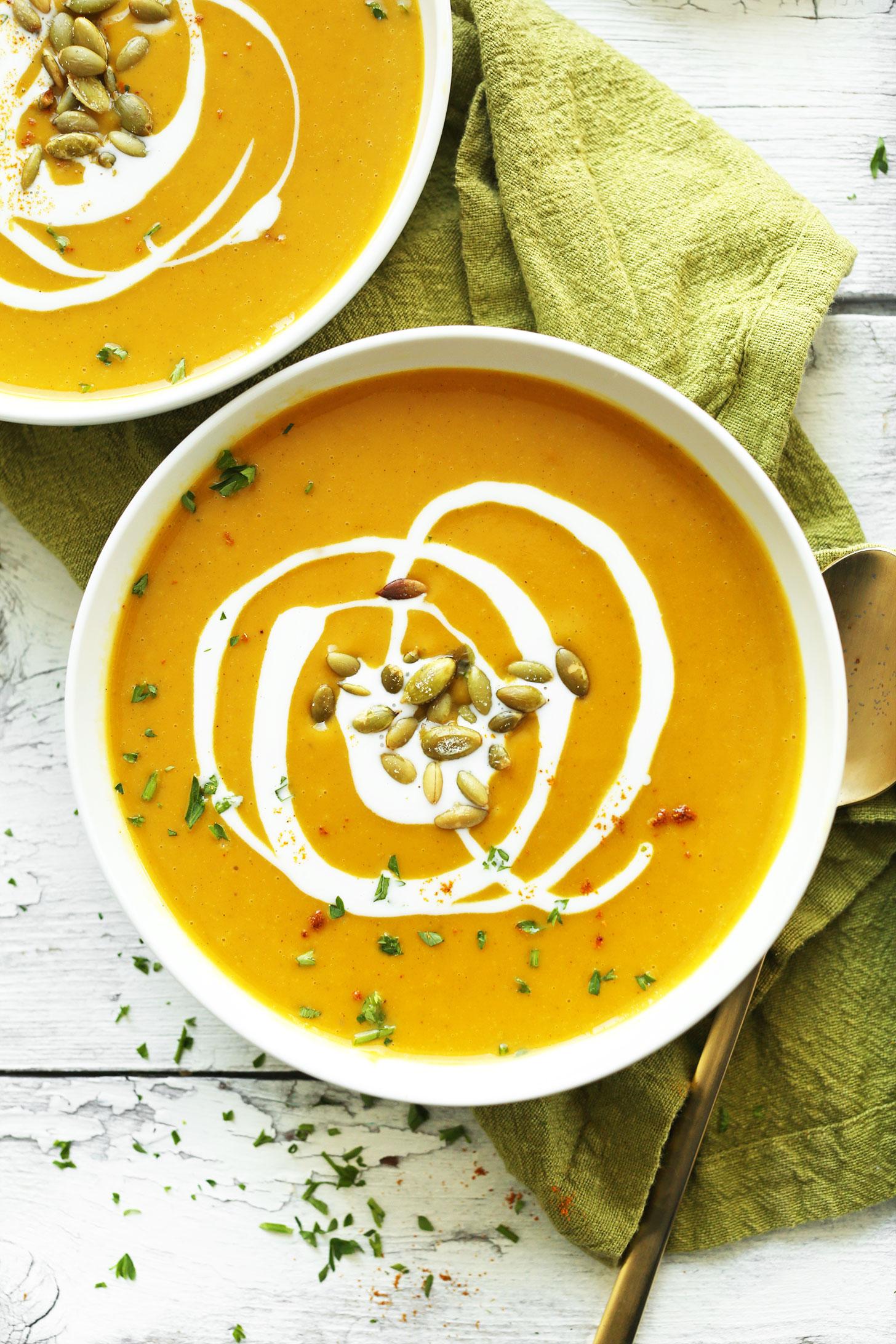
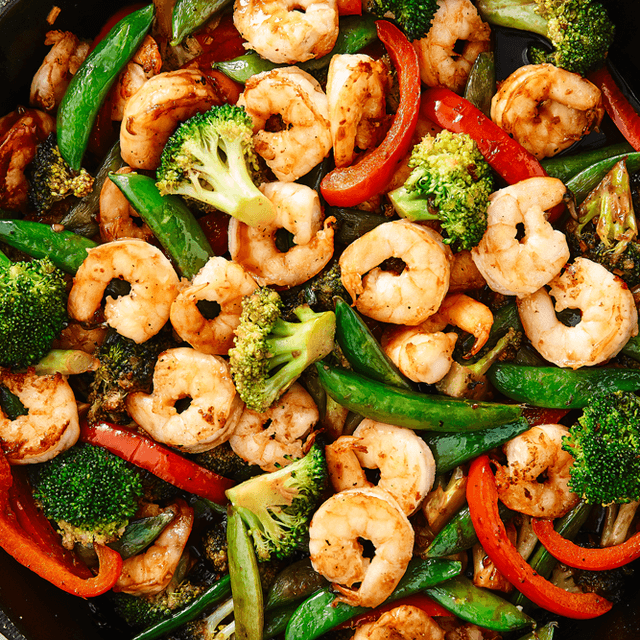
Focuses on high-fiber foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes to help control blood sugar levels. Includes healthy fats from sources such as olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish to support heart health and manage insulin resistance. Limits processed foods, refined sugars, and red meats, emphasizing lean proteins and plant-based meals to maintain a balanced diet and support weight management.
For Diabetes Mellitus Dm
Mediterranean
Day 1
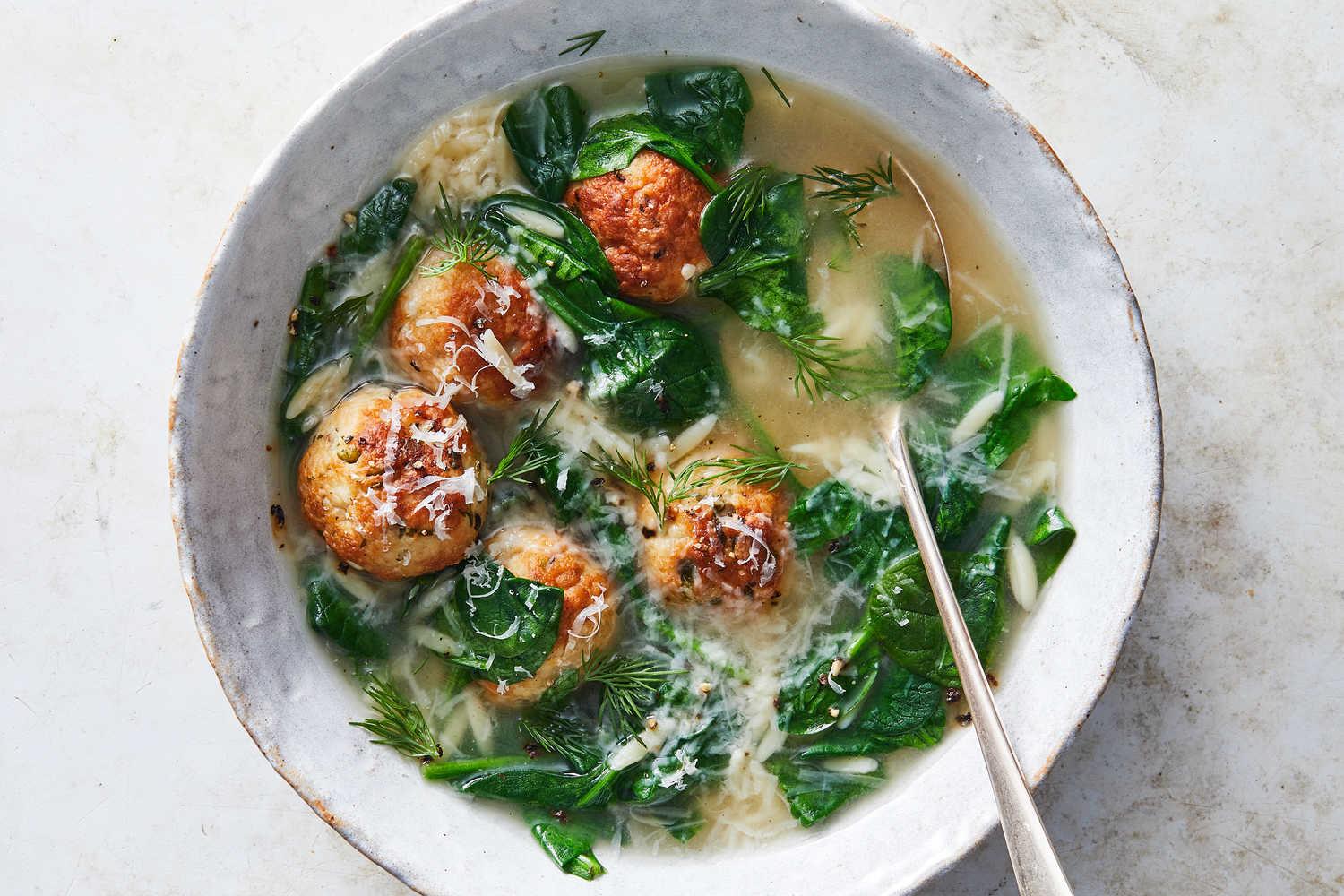
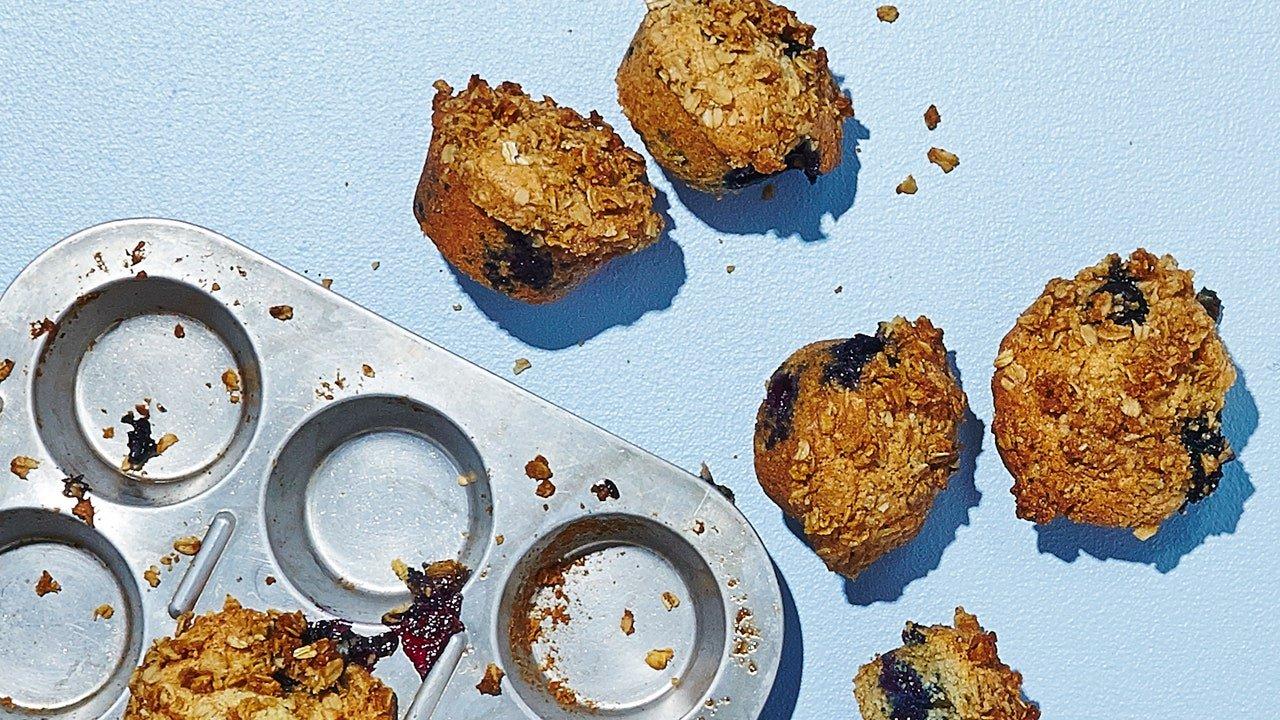
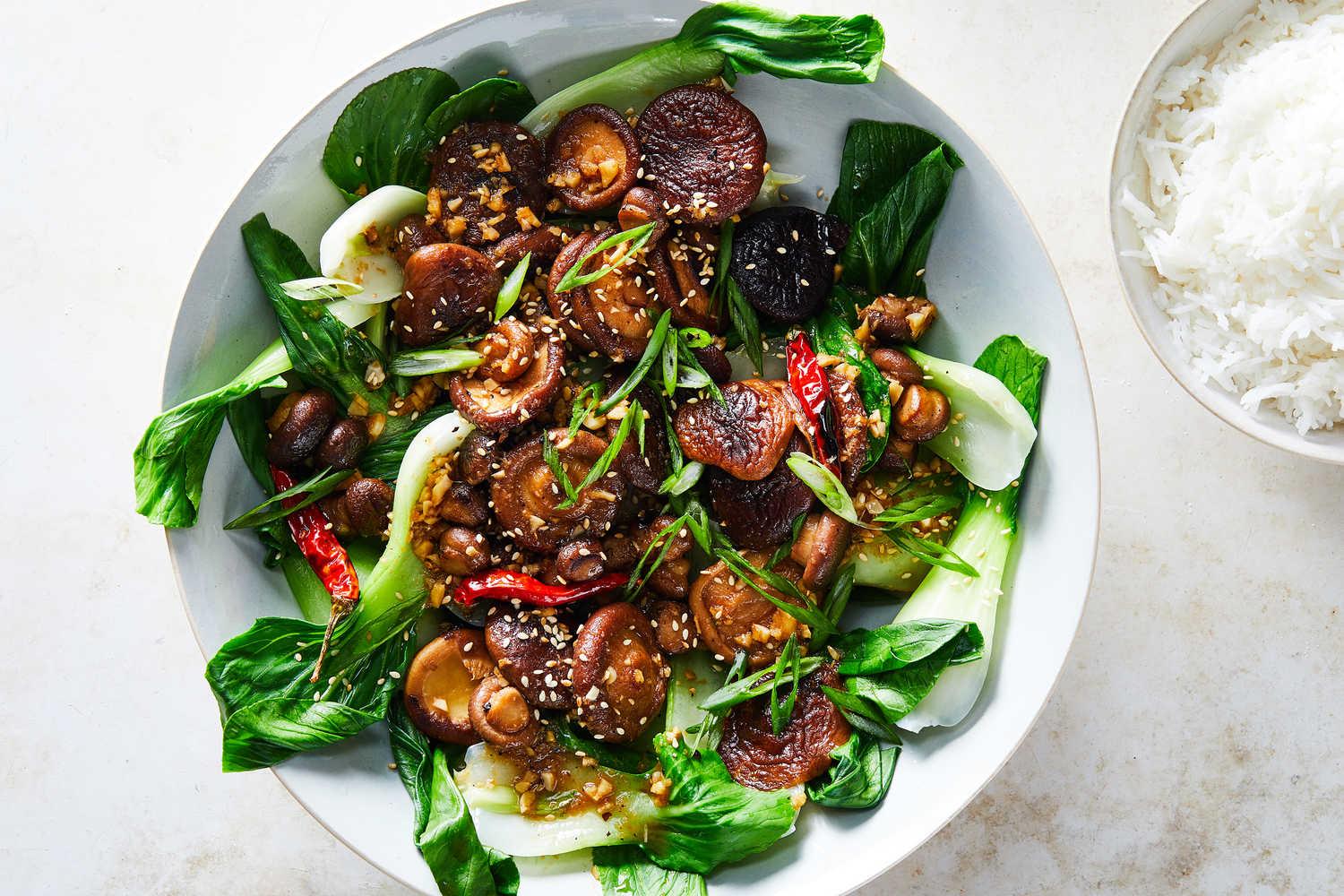
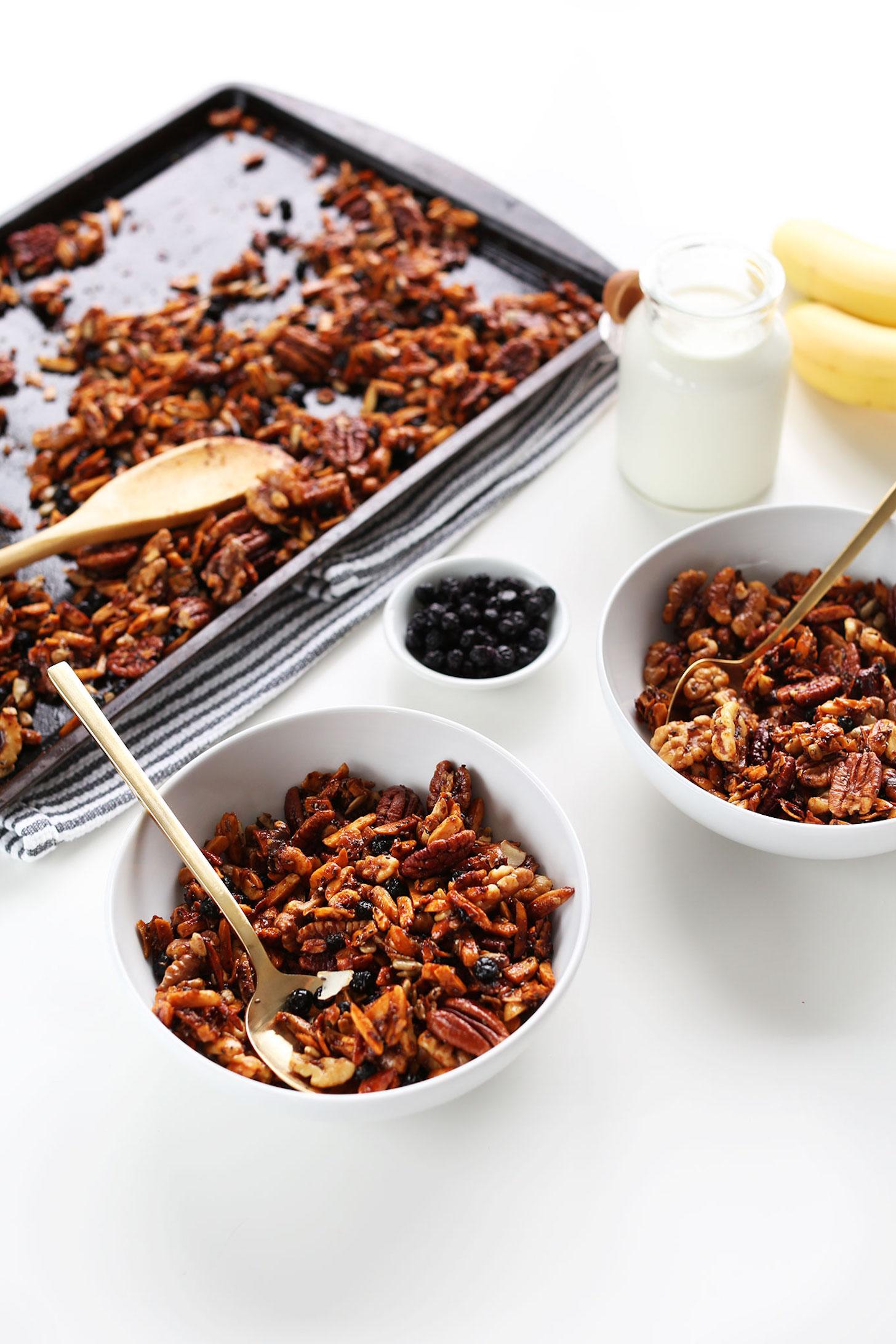
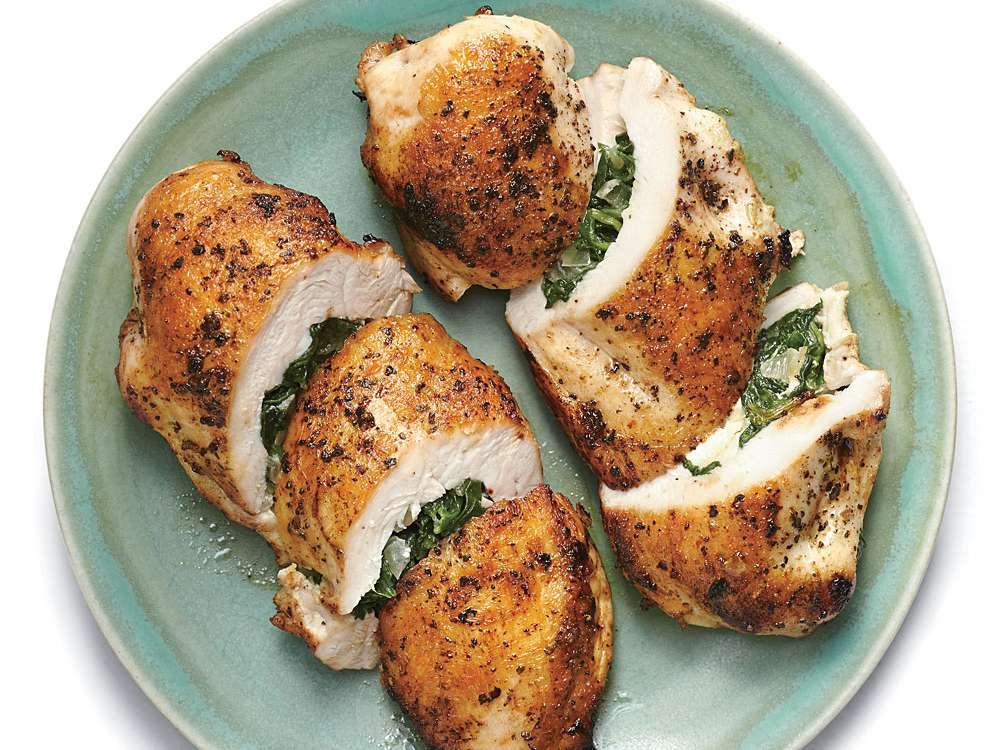
A meal plan for Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) focuses on anti-inflammatory foods such as leafy greens, fatty fish, and berries, while eliminating potential triggers like dairy, refined sugars, and processed foods. It emphasizes whole foods with high fiber content to support gut health and probiotics to maintain a healthy microbiome, which can influence inflammation levels. The meal plan may also include foods rich in zinc and vitamin A to support skin health and encourage the avoidance of nightshades and yeast-containing foods, as some individuals with HS might be sensitive to these.
For Hidradenitis
Anti Inflammatory
Day 1
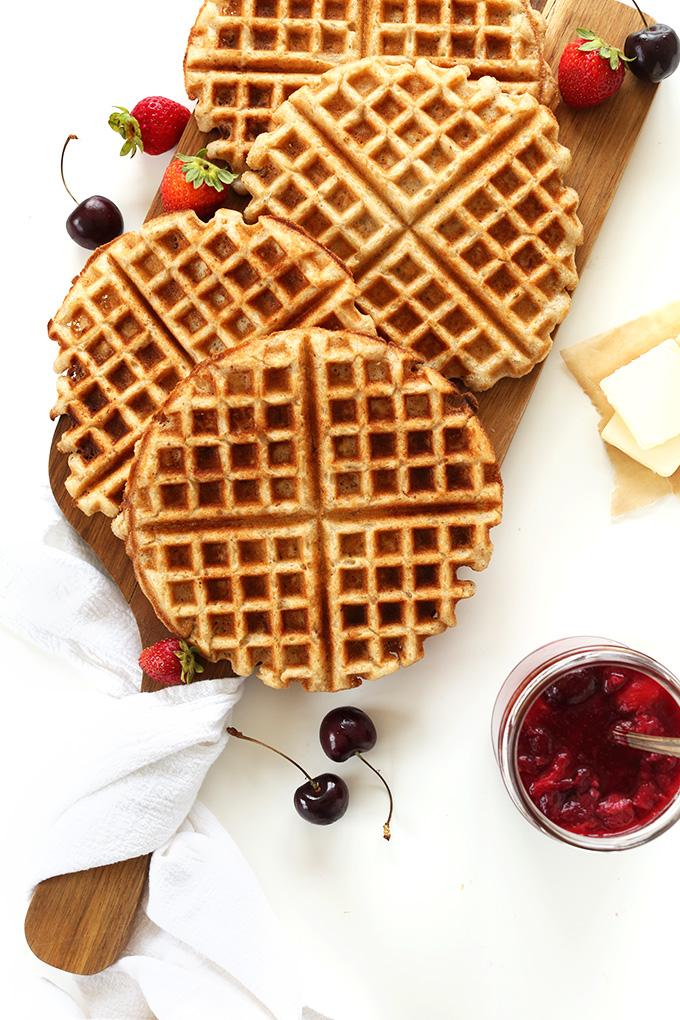
Anti-inflammatory foods: The meal plan features foods that reduce inflammation, like leafy greens, fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, known to help alleviate back pain symptoms. Adequate calcium and vitamin D: Includes dairy products, fortified foods, or leafy greens and sunlight exposure to maintain bone health and minimize the risk of osteoporosis, which can exacerbate back issues. Balanced macronutrients: Ensures a proper balance of proteins, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to support overall health and provide the energy required for daily activities and potential physical therapy exercises.
For Back Pain
Balanced
Day 1
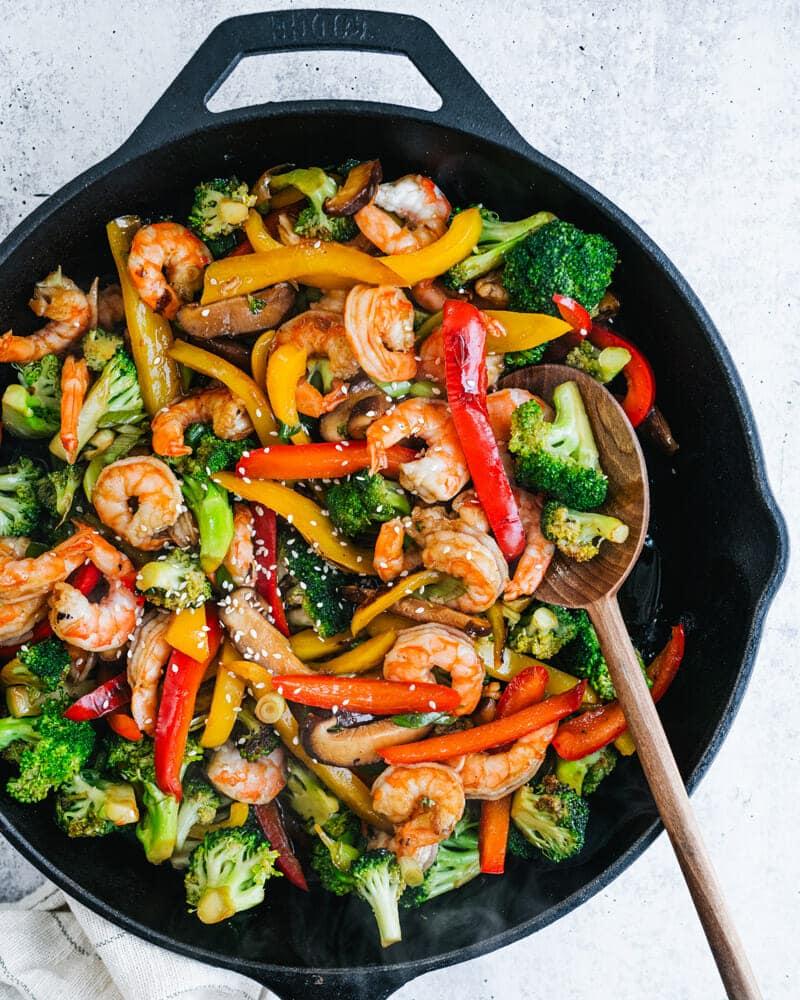
For back pain and lower_back_pain, the meal plan should include anti-inflammatory foods such as leafy greens, fatty fish (rich in omega-3), and whole grains to reduce inflammation that can exacerbate pain. For chest_pain and headache sufferers, the plan should focus on heart-healthy options like the Mediterranean diet, featuring olive oil, nuts, and lean proteins, while avoiding processed foods and excessive salt that can contribute to cardiovascular stress and trigger headaches. Pescatarian, paleo, and balanced meal plans emphasize whole foods; pescatarian includes seafood for omega-3s, paleo prioritizes lean meats and excludes grains and legumes, and a balanced plan incorporates a variety of nutrients from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
For Back Pain
For Chest Pain
For Headache
For Lower Back Pain
Balanced
Mediterranean
Pescatarian
Paleo
Day 1
A meal plan for individuals with various pains and conditions would prioritize anti-inflammatory foods (such as leafy greens, fatty fish, berries) to help reduce inflammation associated with pain symptoms and autoimmune responses. For keto followers, the plan would be low in carbs and high in healthy fats, focusing on nutrient-dense, unprocessed foods to support a state of ketosis while also considering pain management. Autoimmune protocol (AIP) users would have a plan eliminating potential trigger foods such as grains, dairy, and nightshades, while including nutrient-rich, healing foods to support gut health and reduce autoimmune flare-ups.
For Back Pain
For Abdominal Pain
For Chest Pain
For Headache
For Lower Back Pain
Keto
Autoimmune Protocol
Day 1