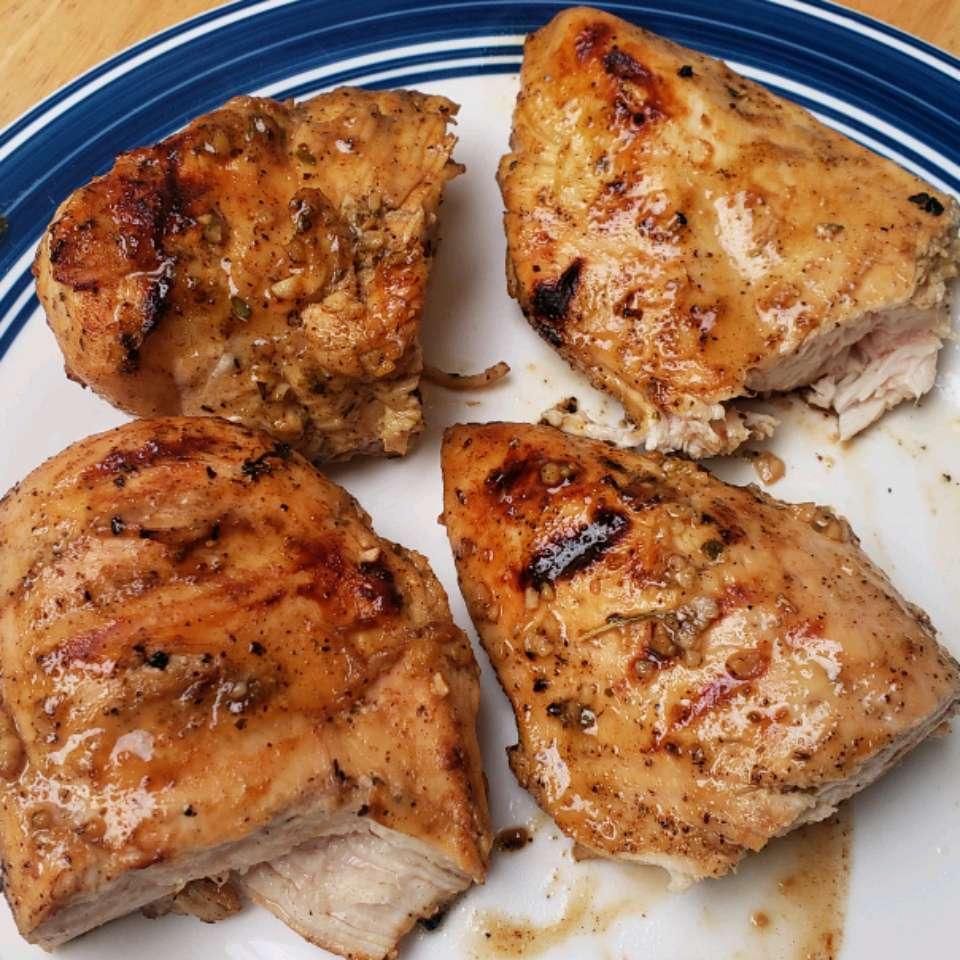
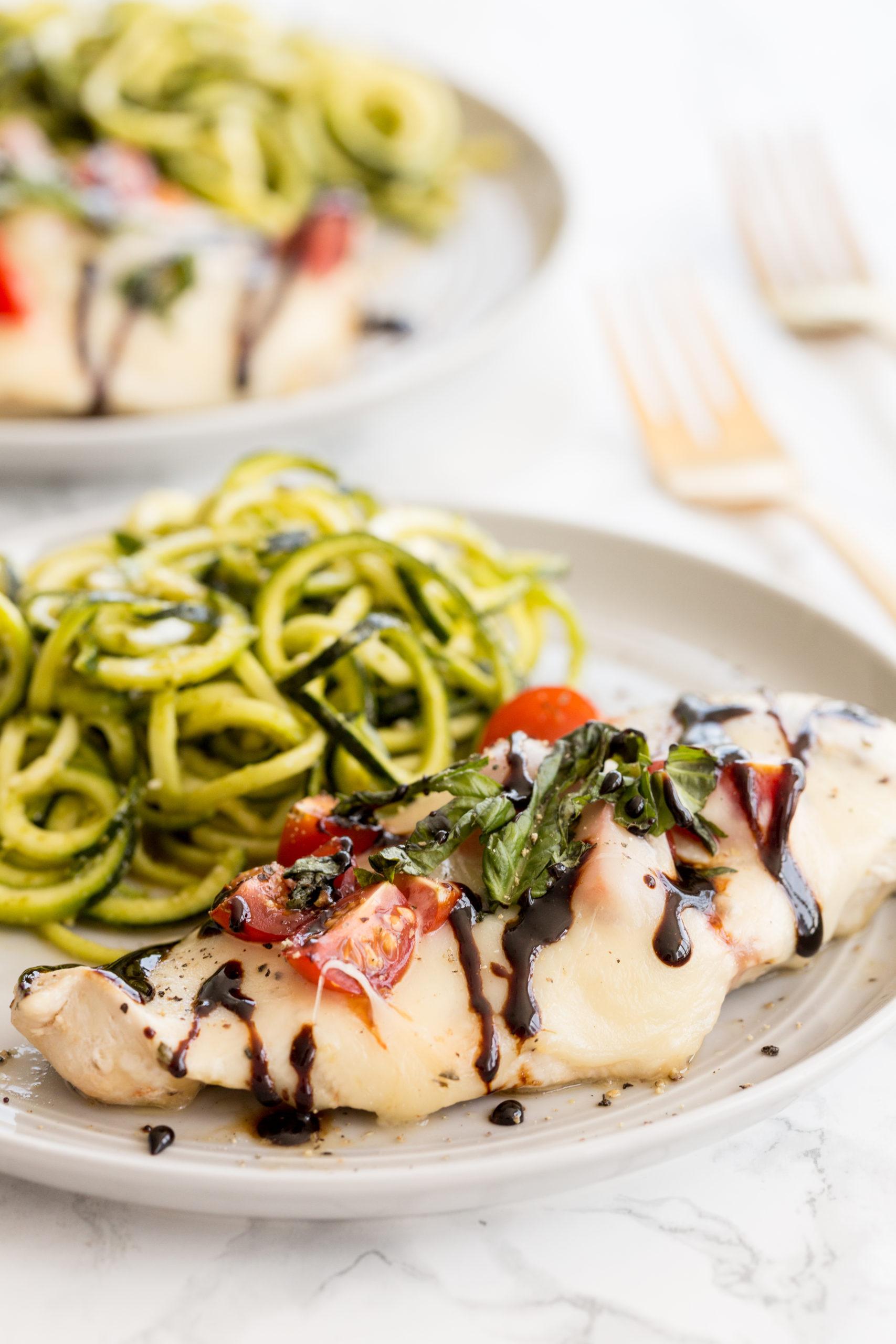
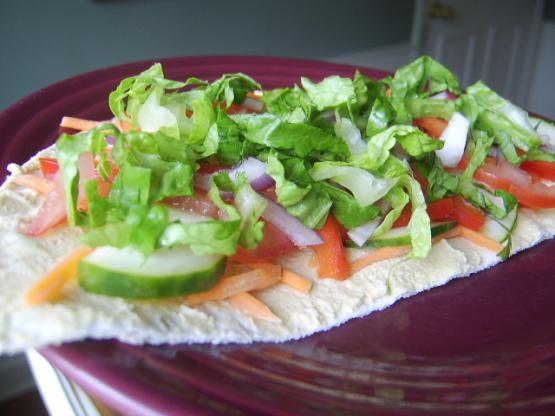
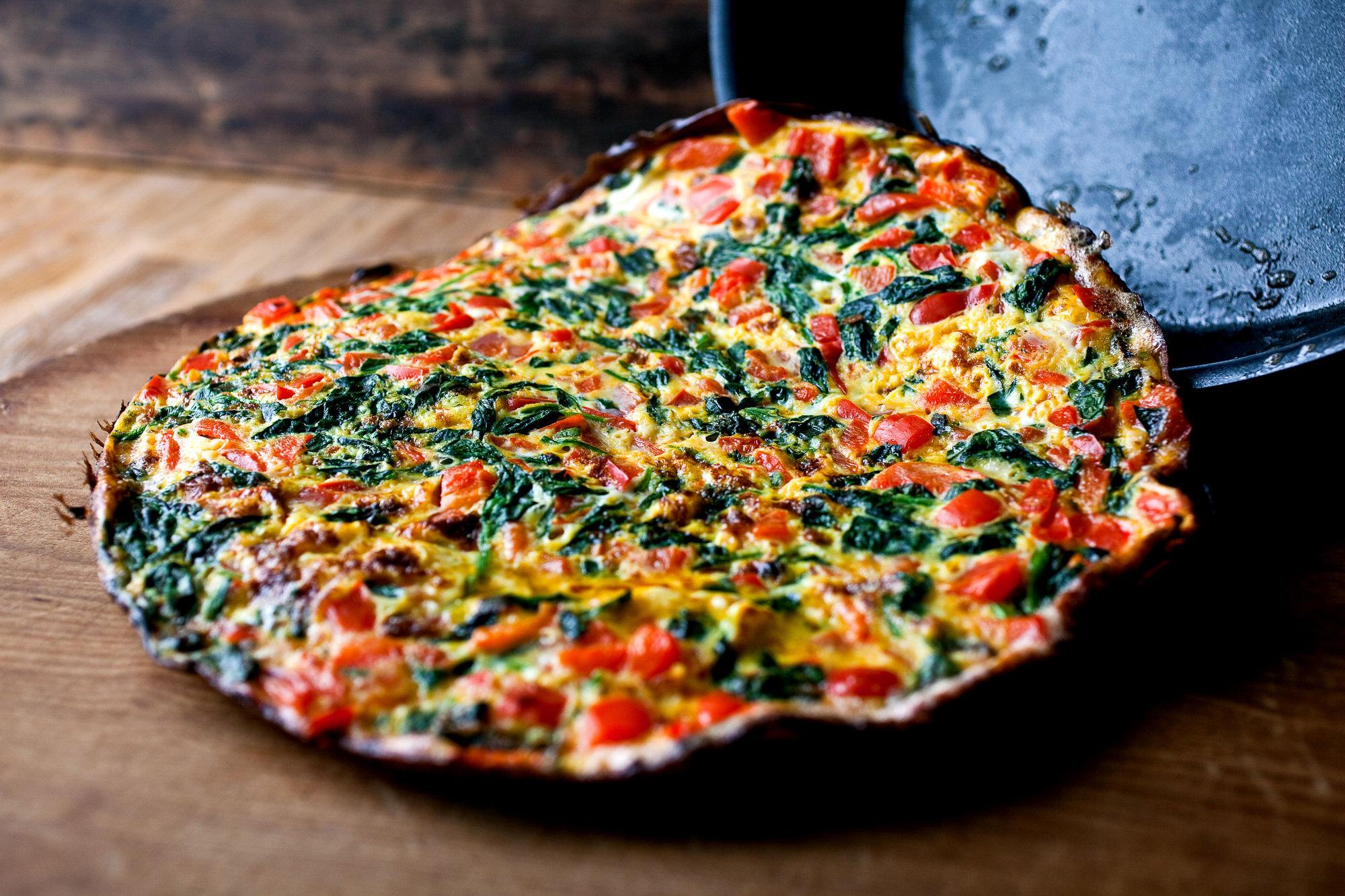
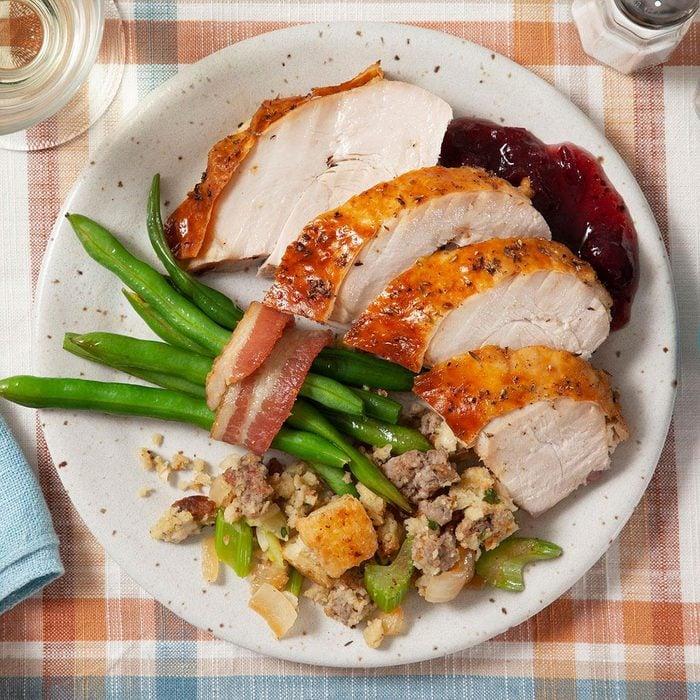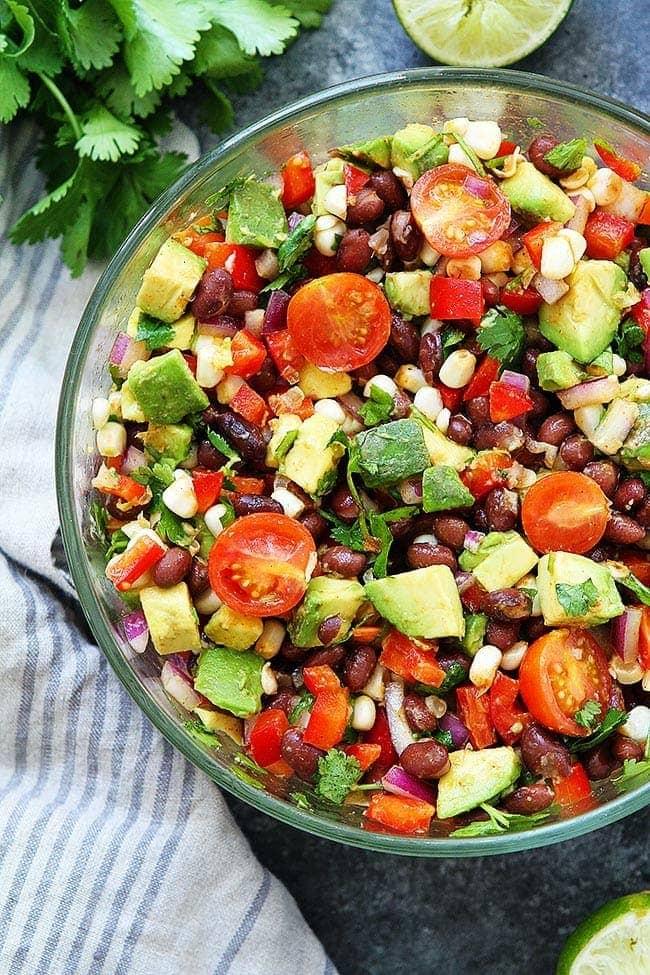Pick your health conditions
and see that we got you covered!
Filter by
Health conditions
Diet type

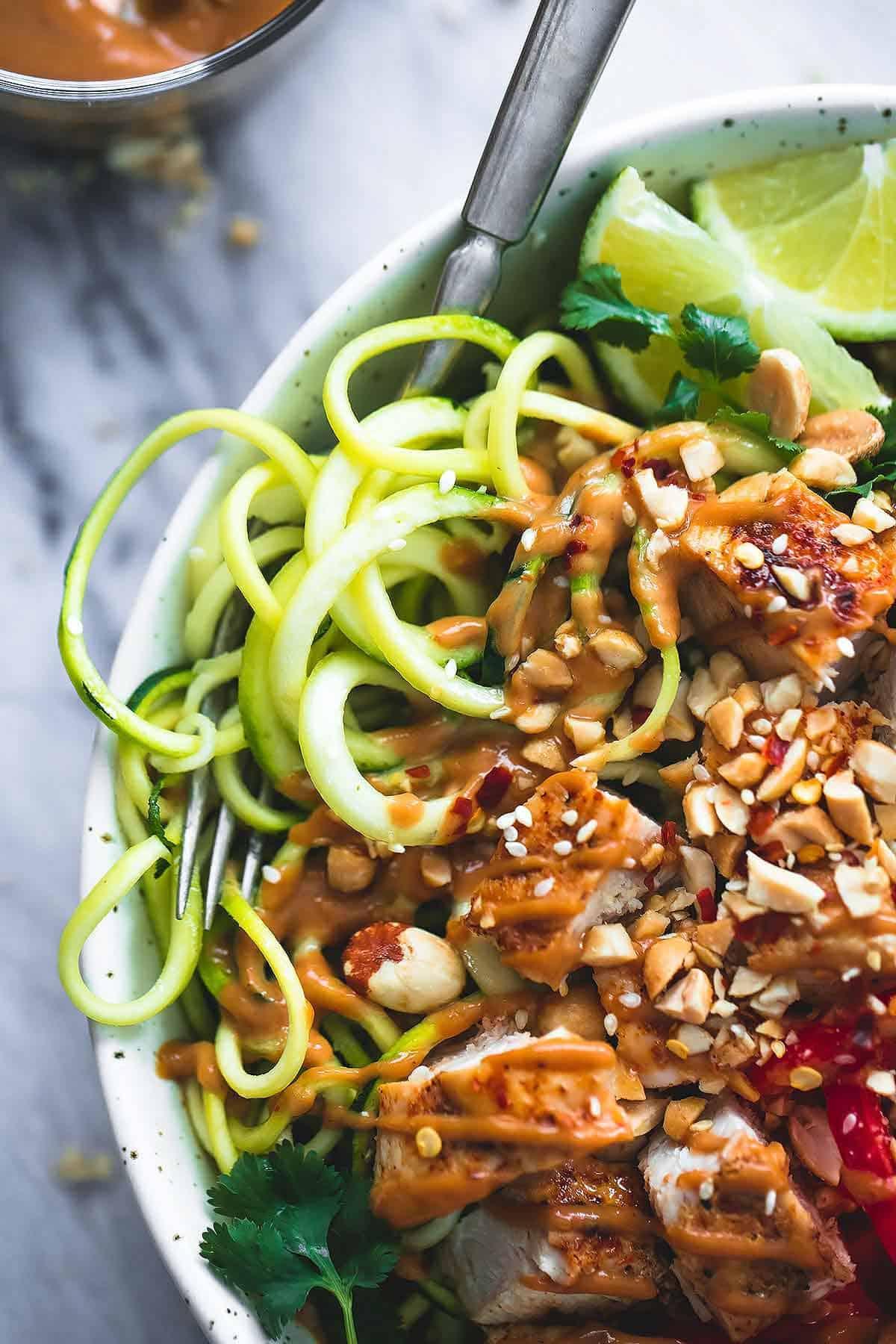
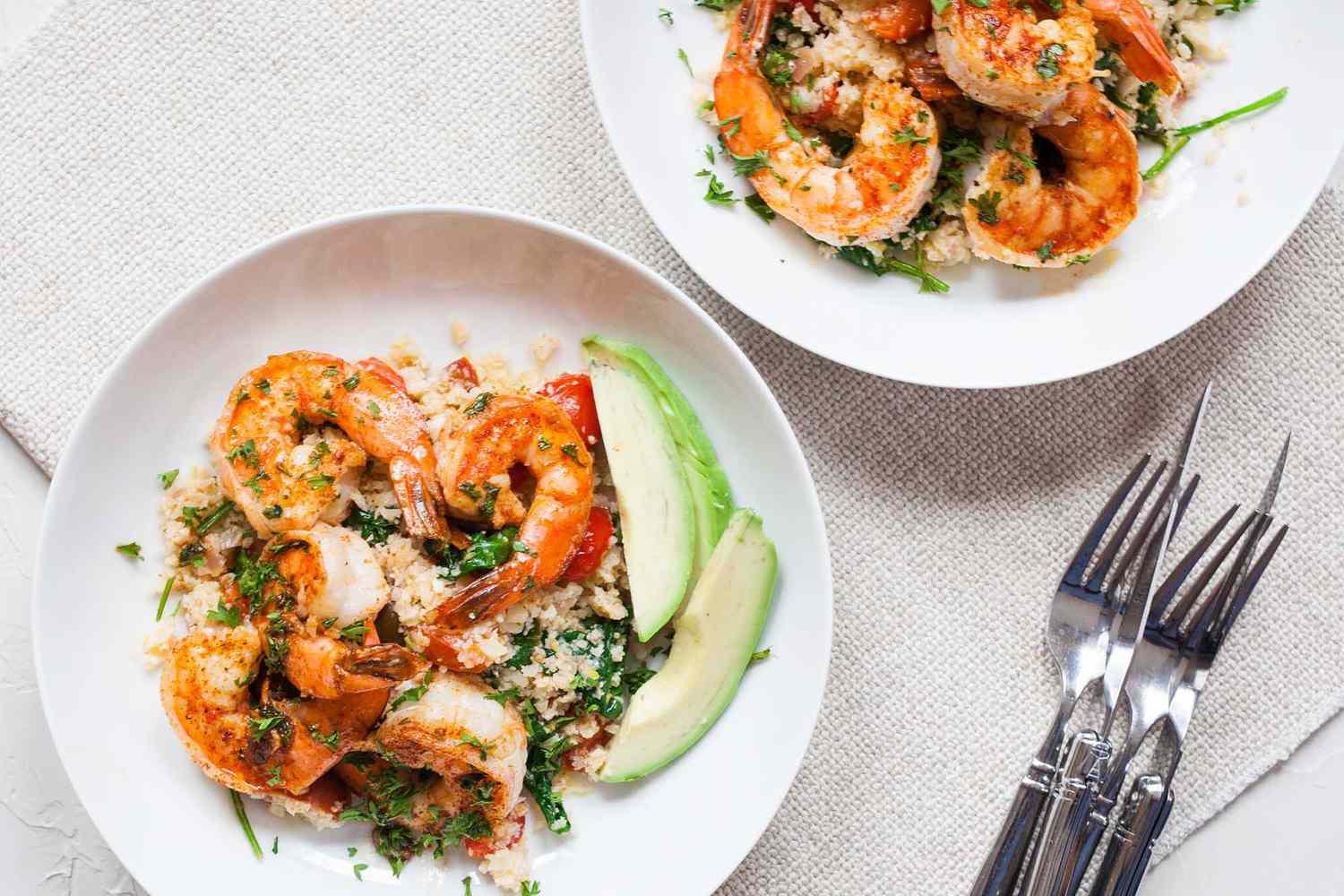
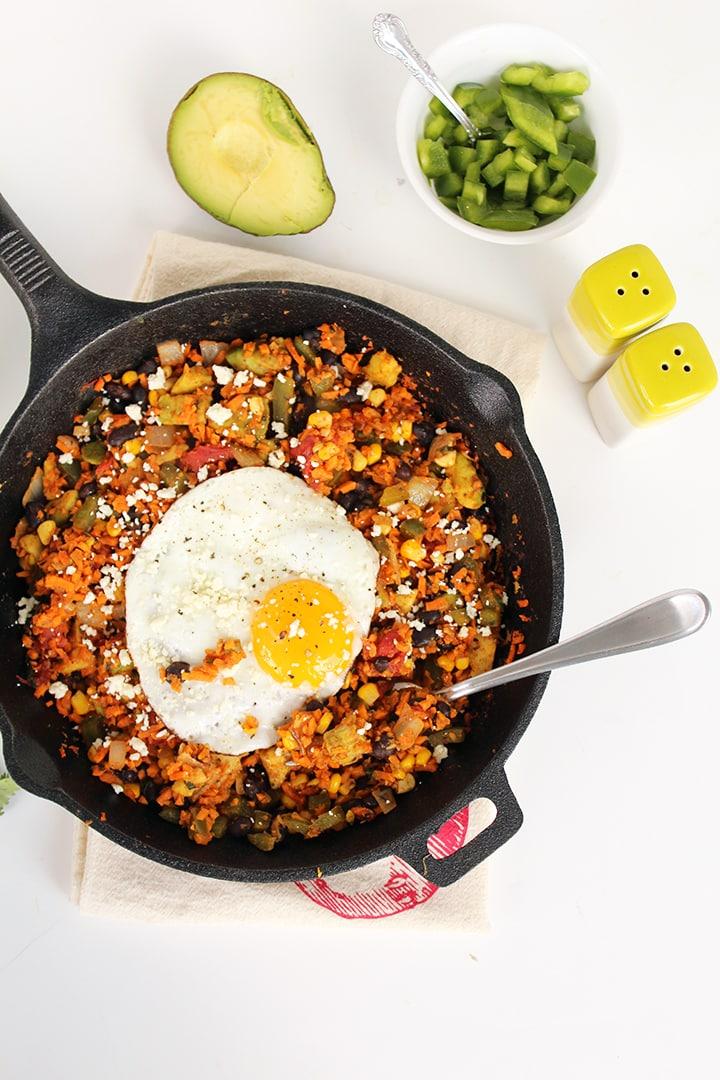
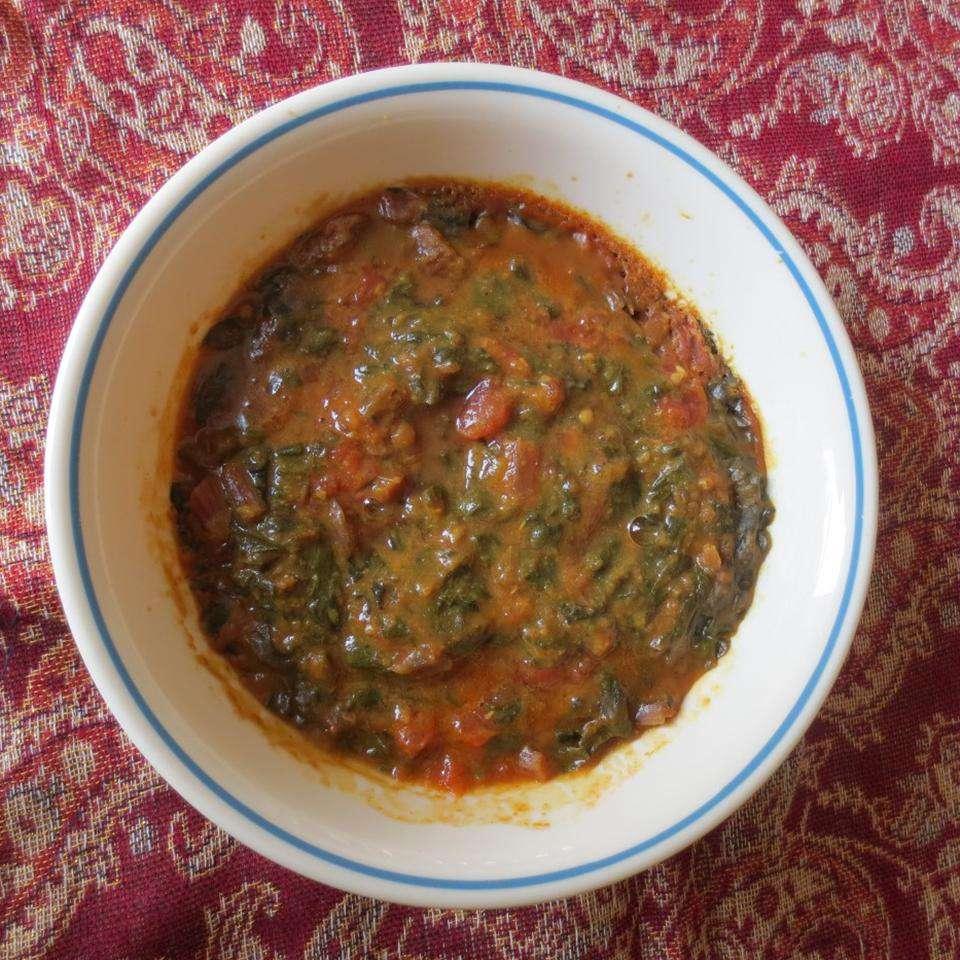
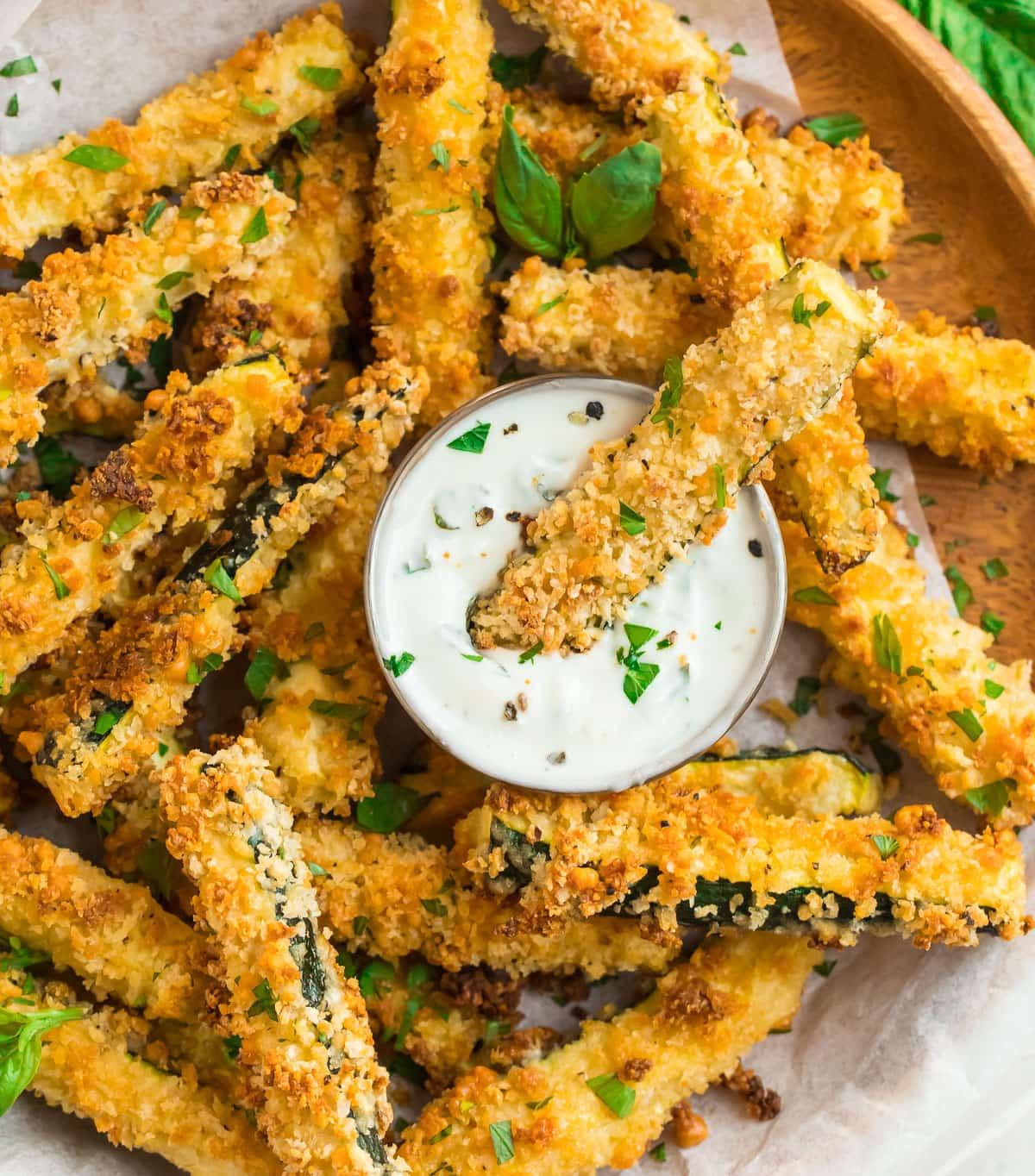
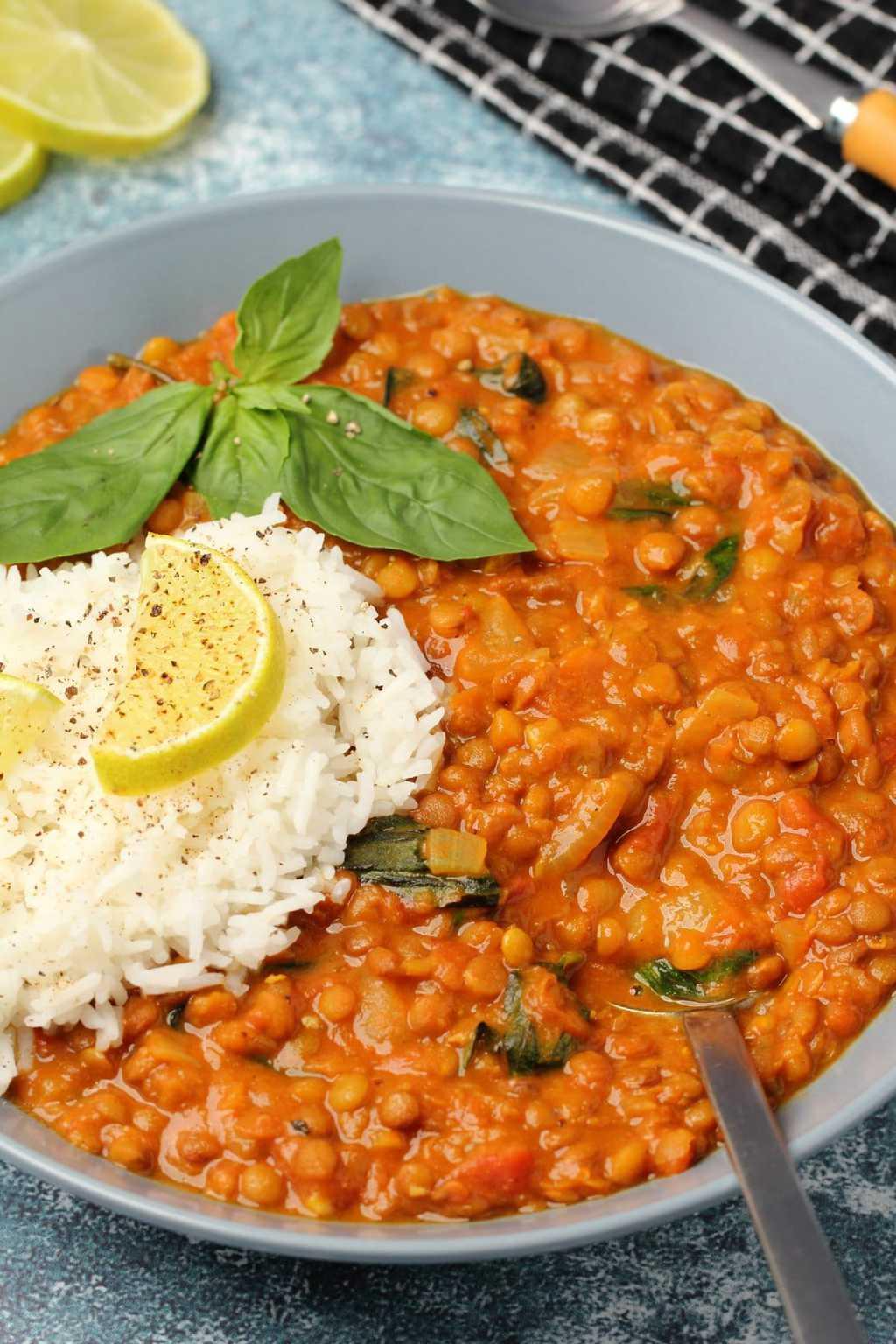
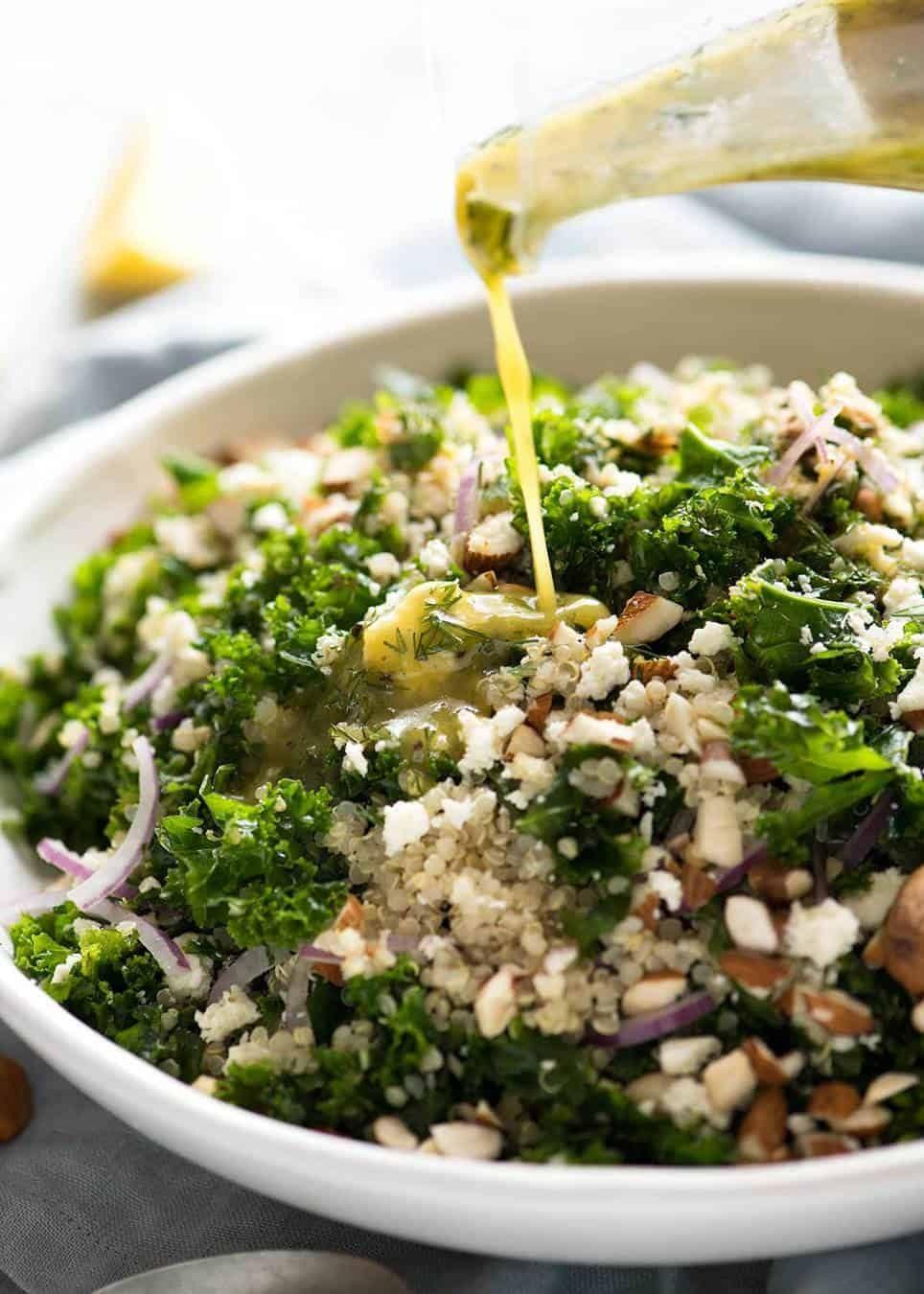
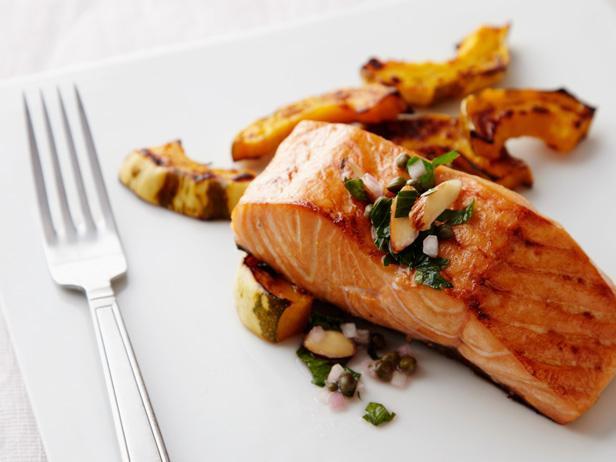
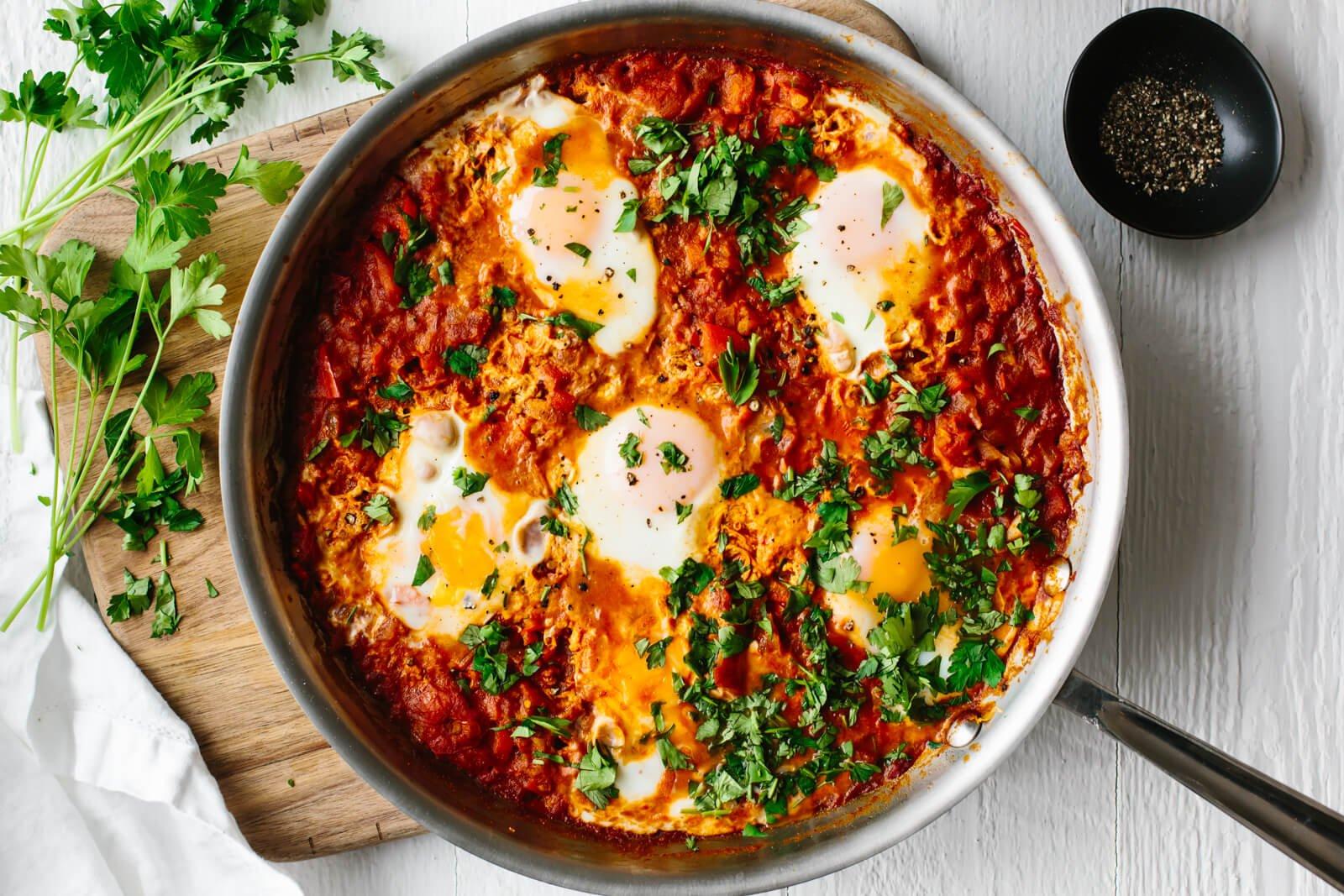
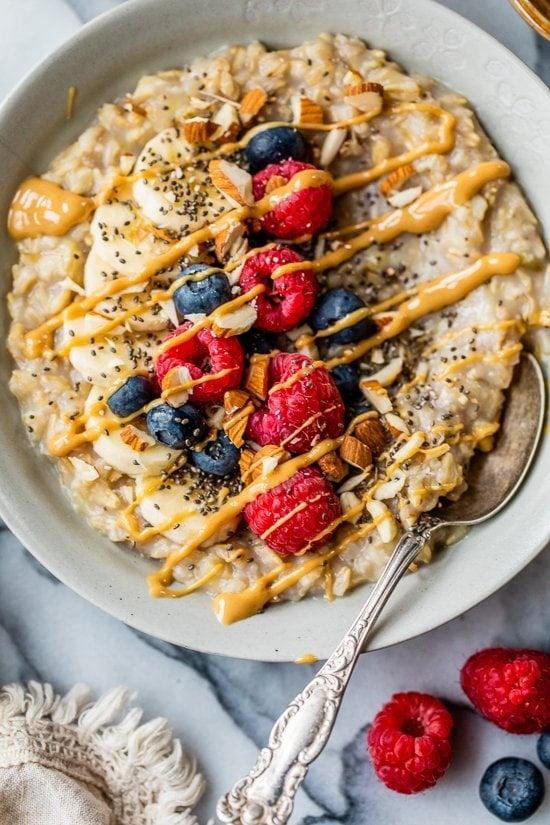
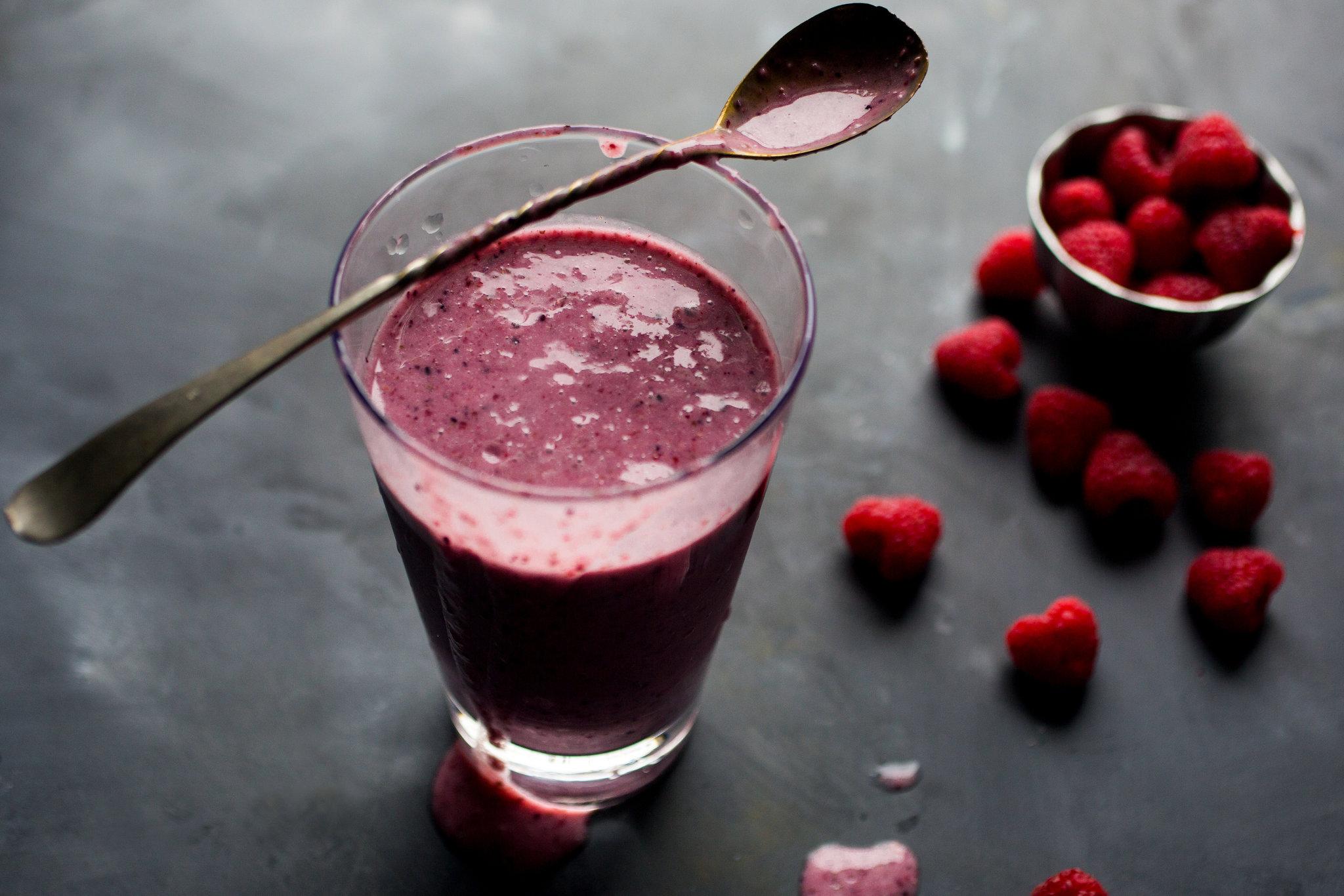
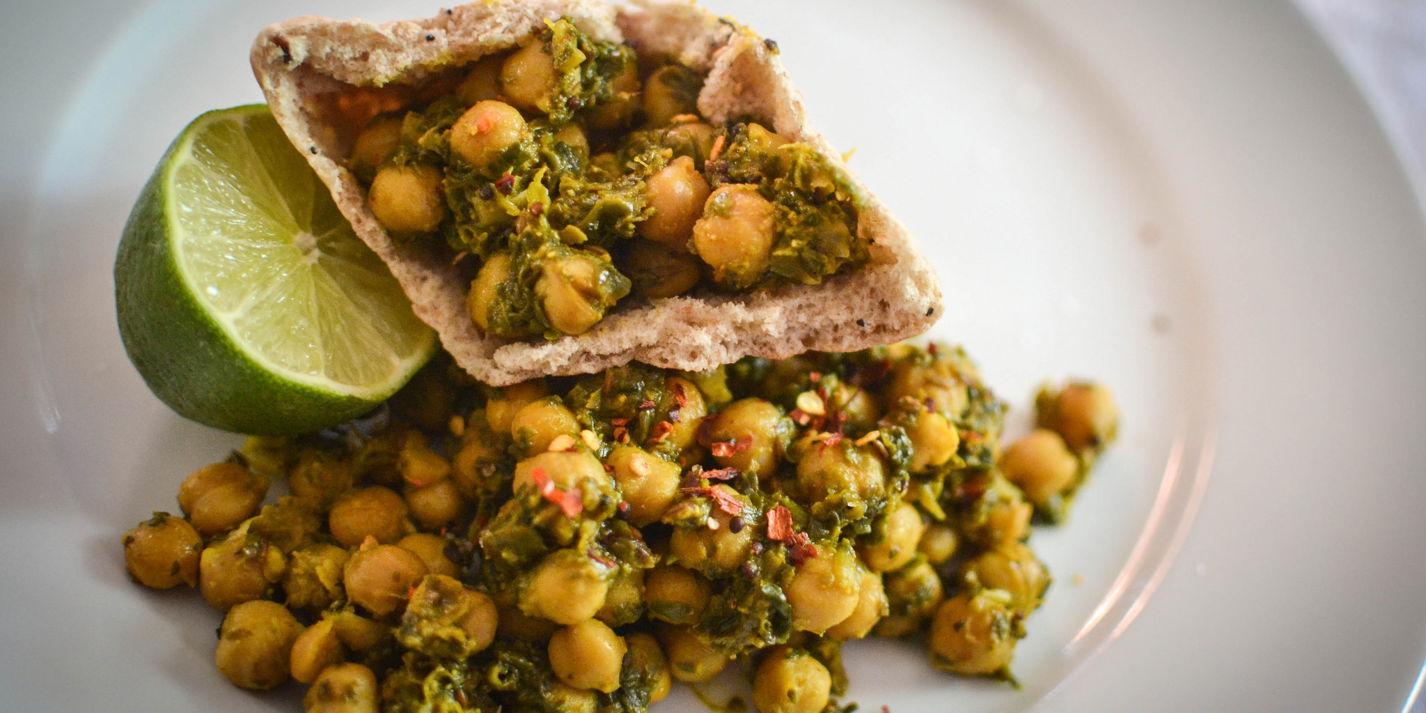
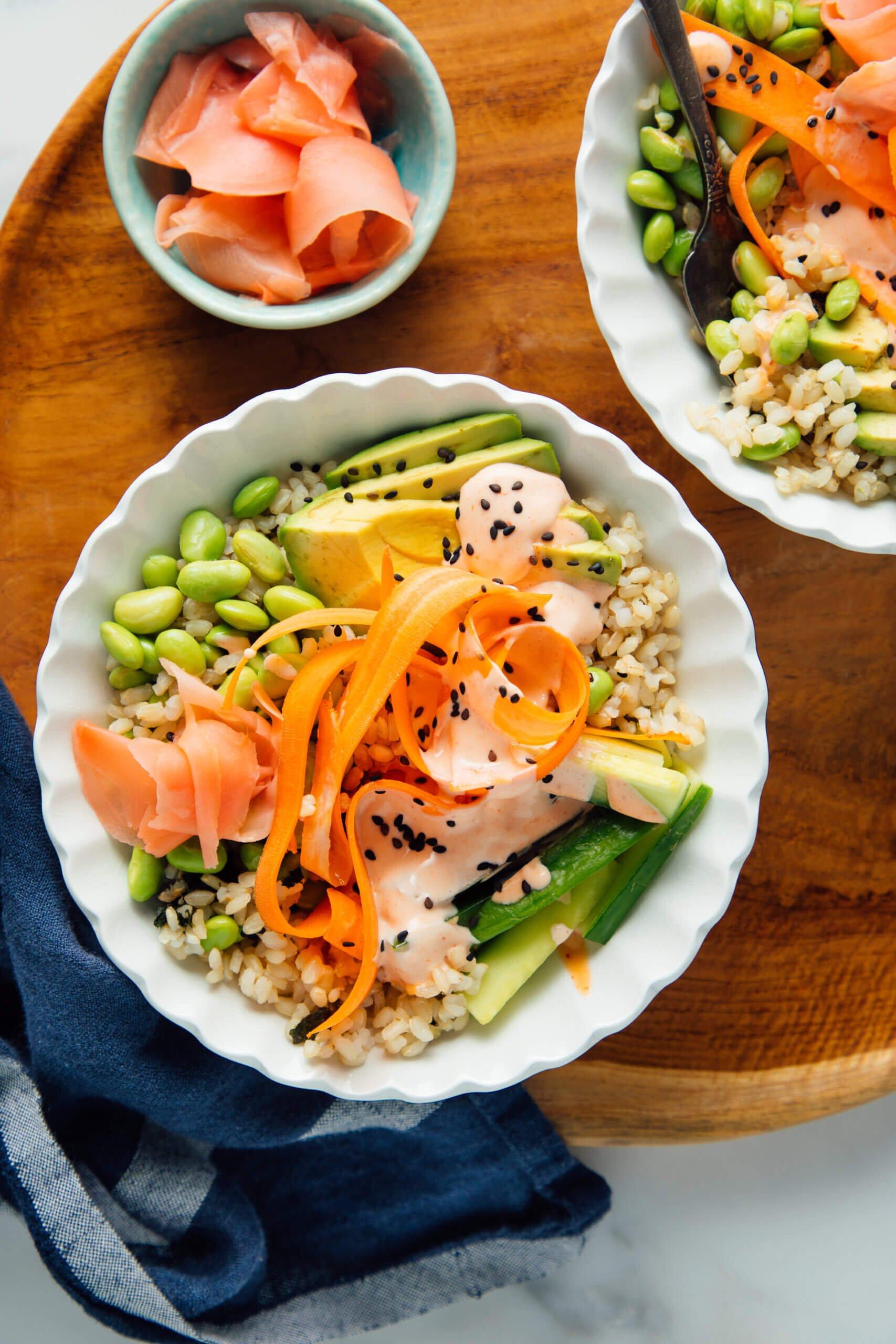
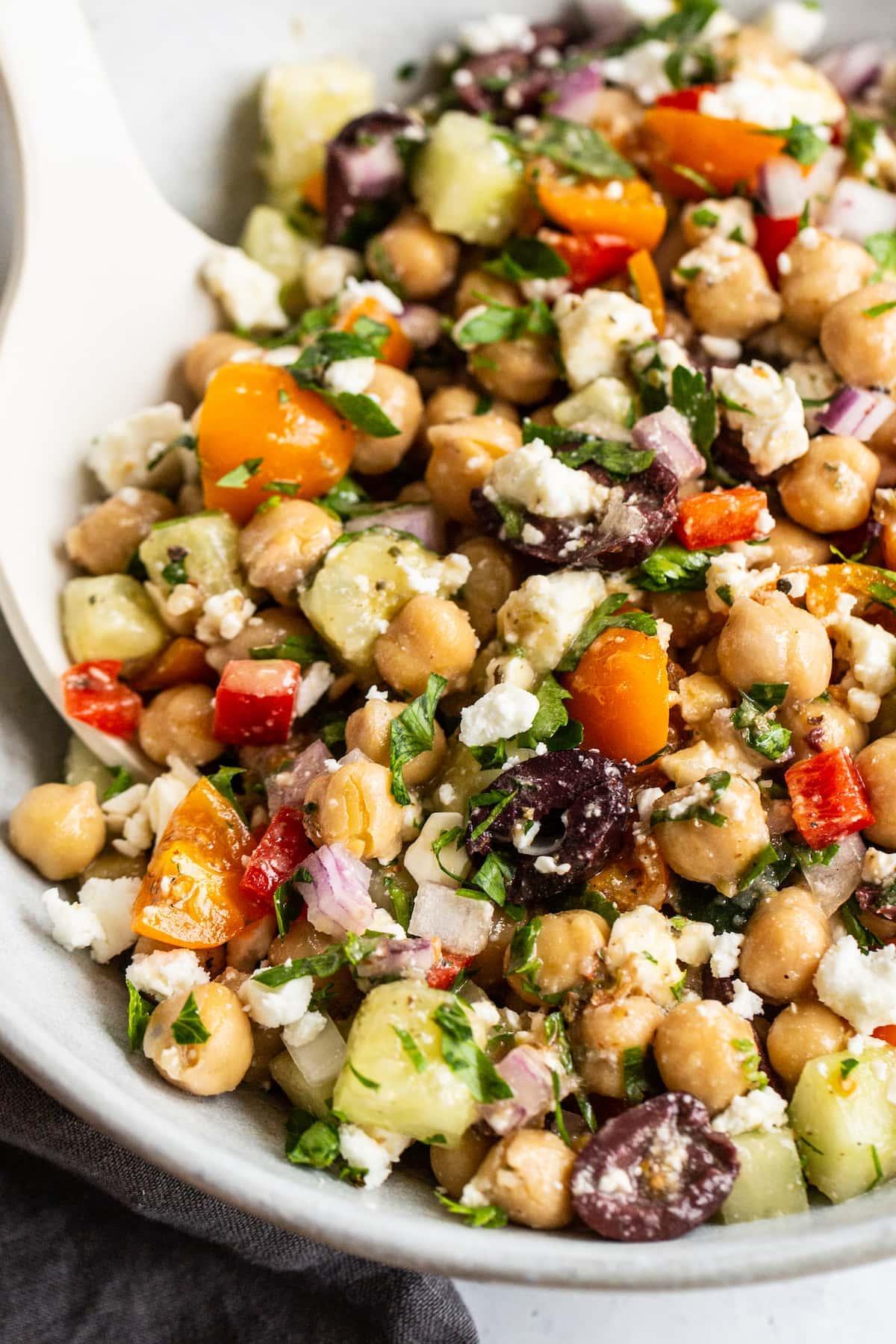
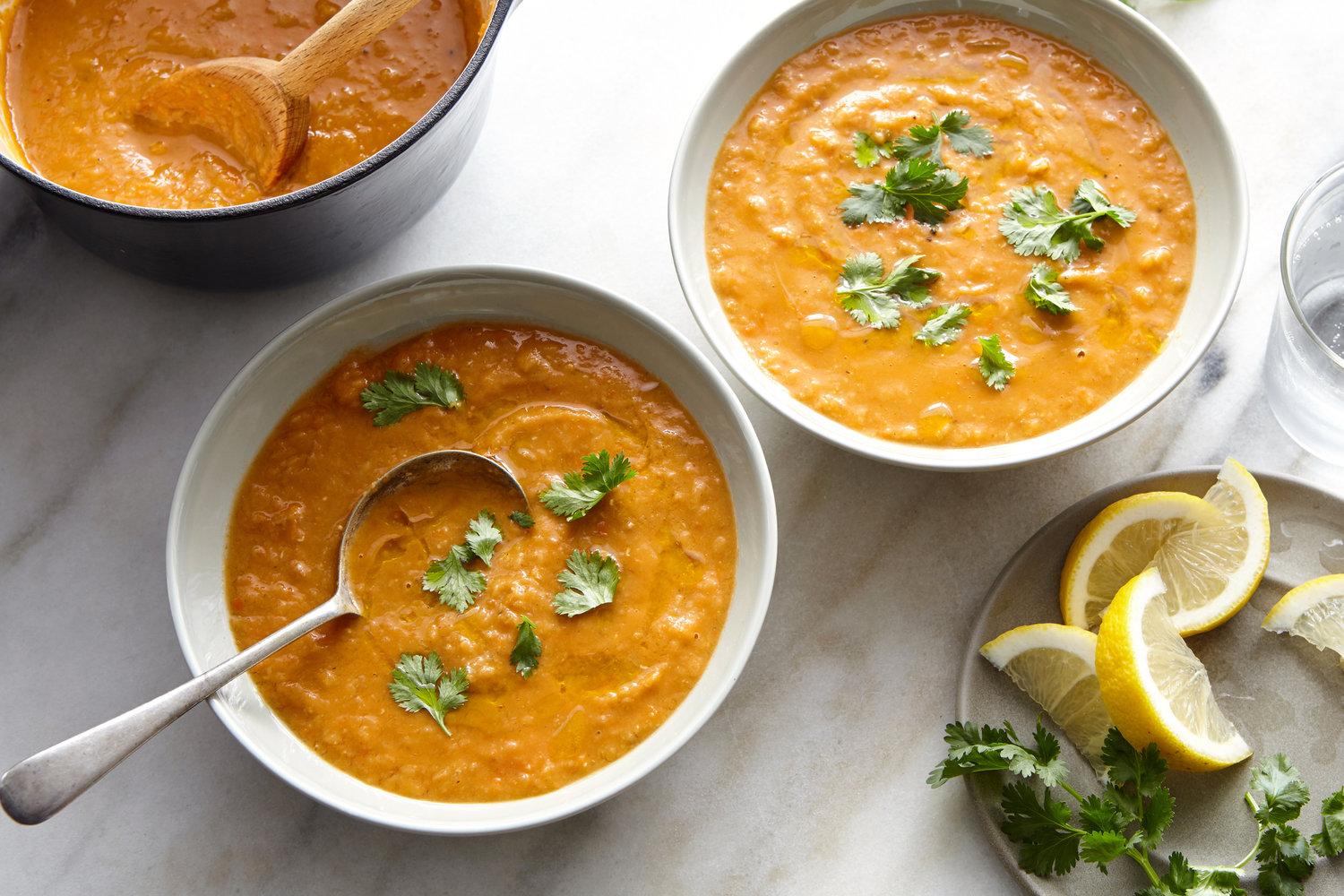
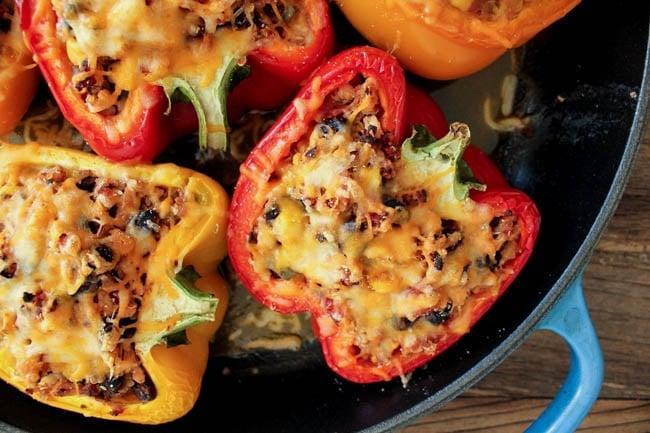
Focus on low-glycemic index foods that release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, minimizing blood sugar spikes and improving glycemic control. Balance carbohydrates with adequate protein and healthy fats to stabilize blood sugar levels and provide sustained energy. Include consistent meal timings and portion control to help regulate insulin dosing and maintain a stable metabolic response.
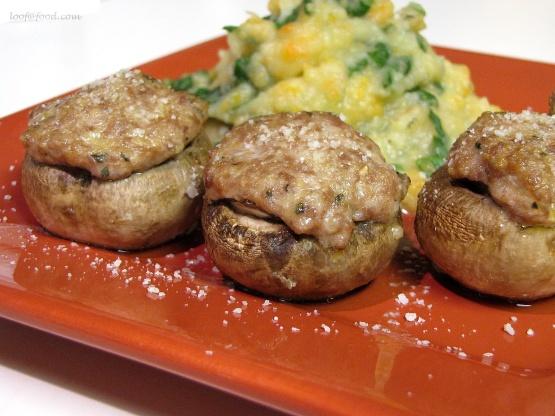
For Diabetes Type 1 Juvenile Insulindependent
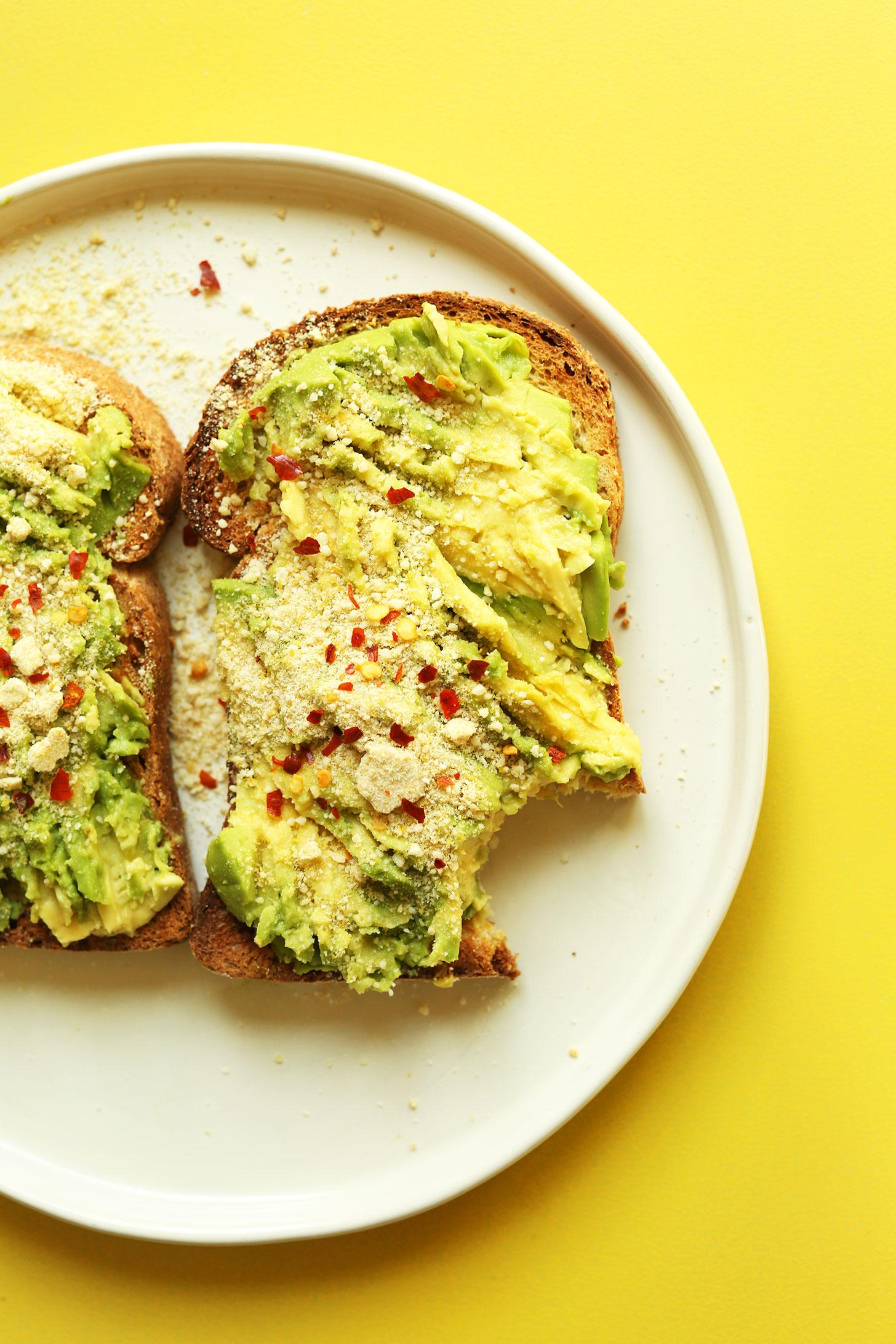
Low Glycemic
Day 1
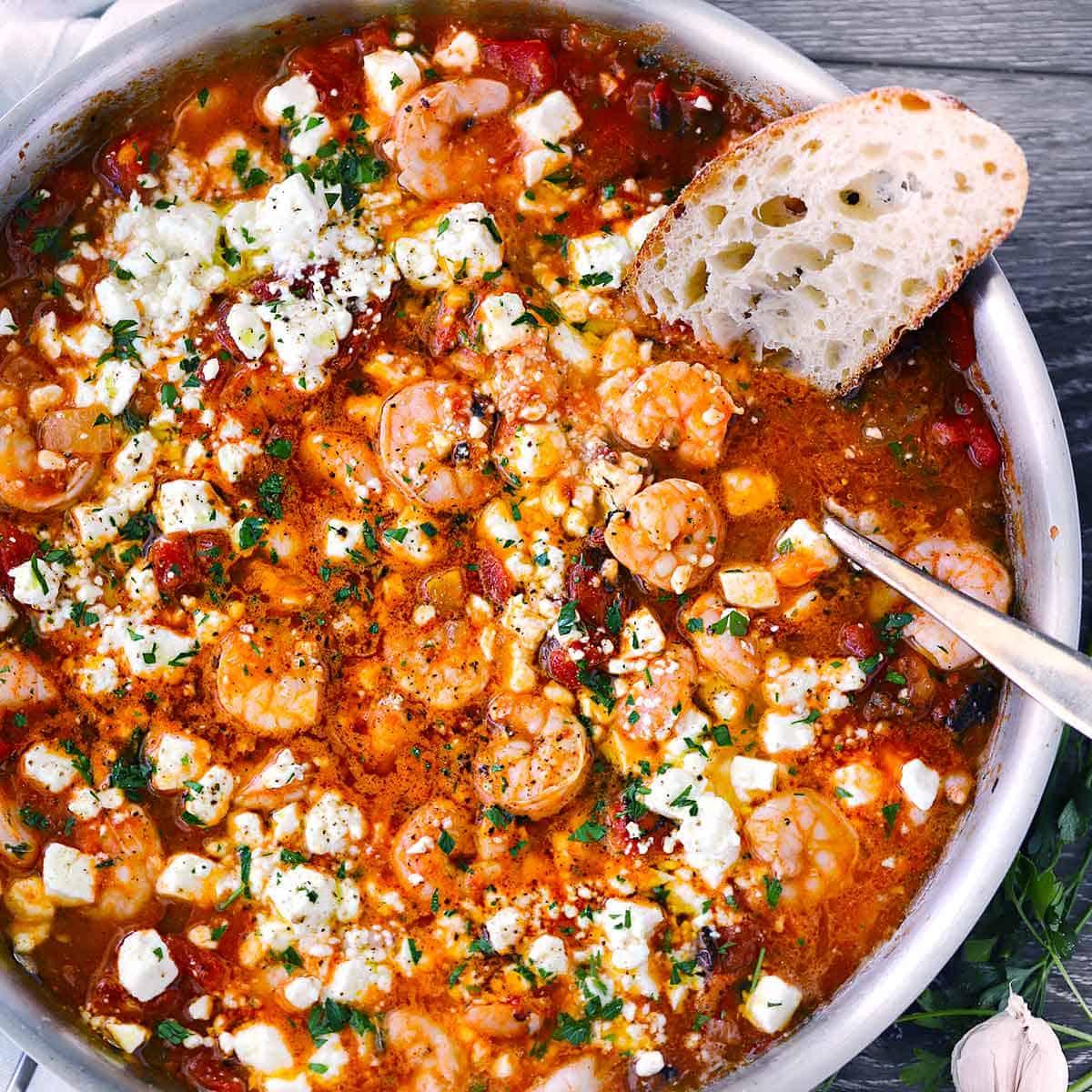
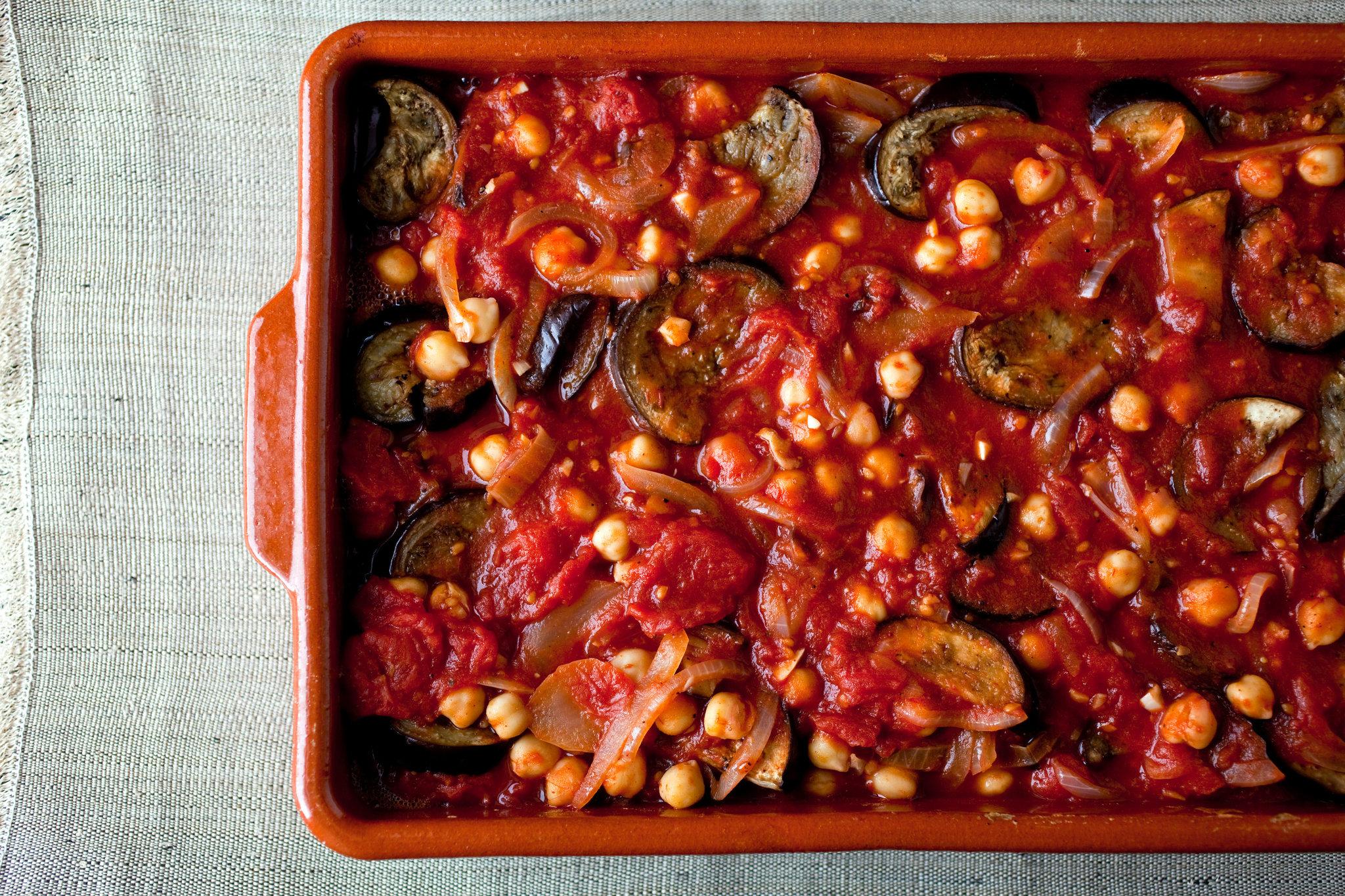
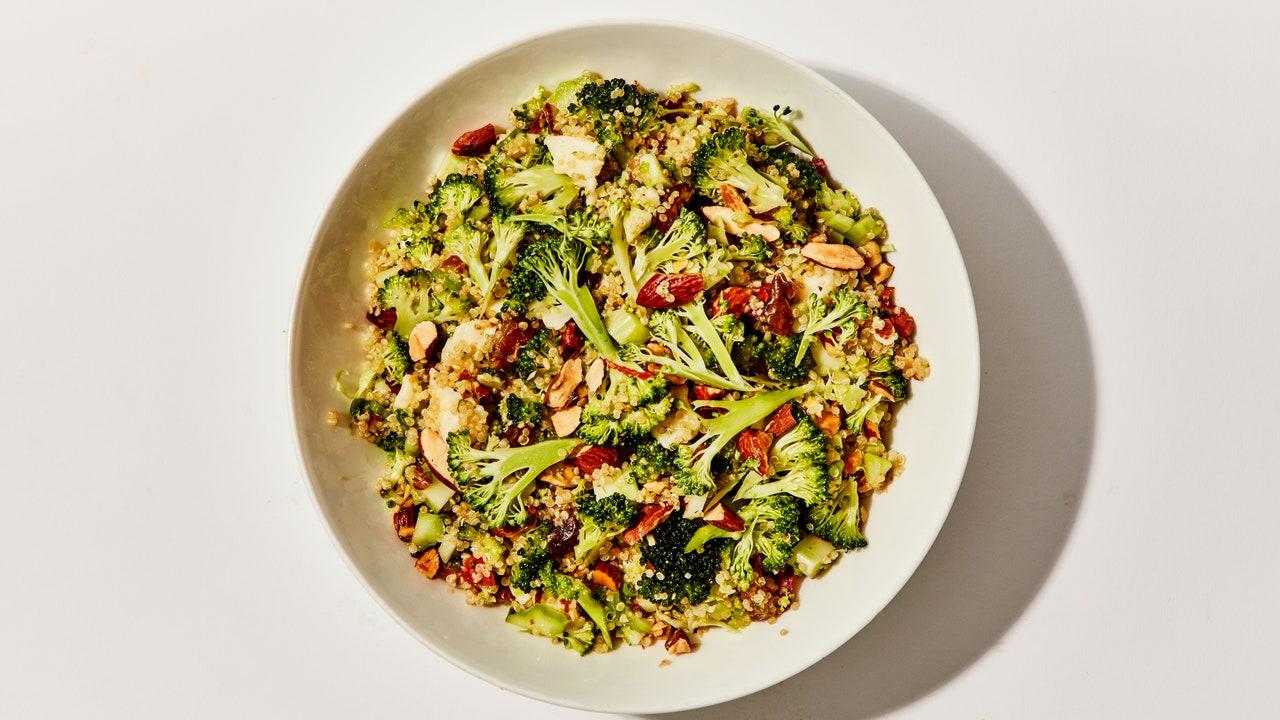
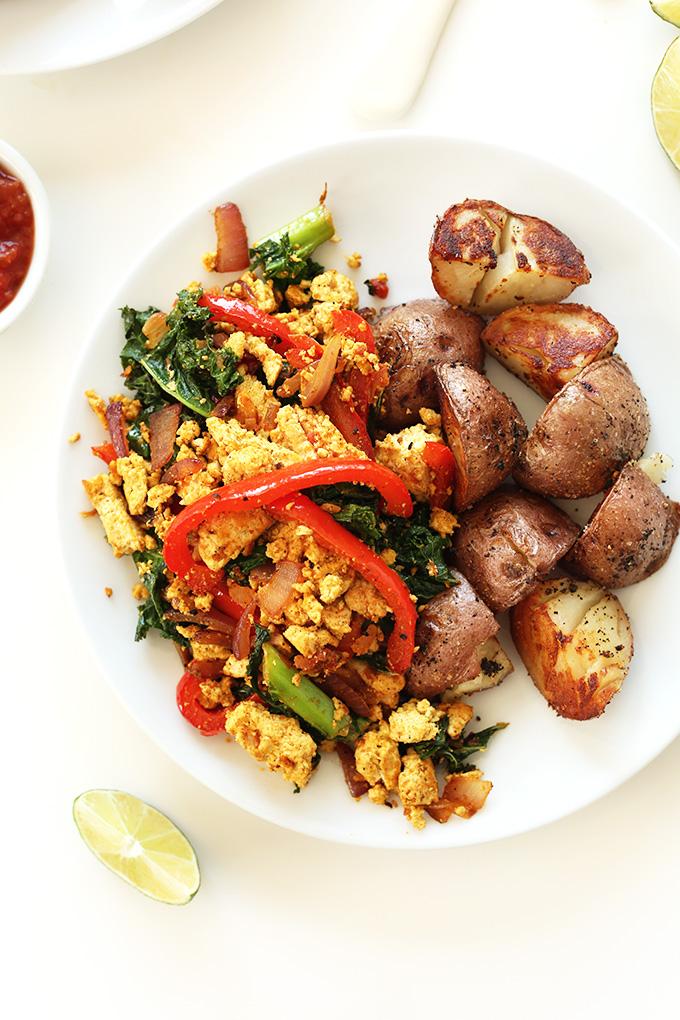
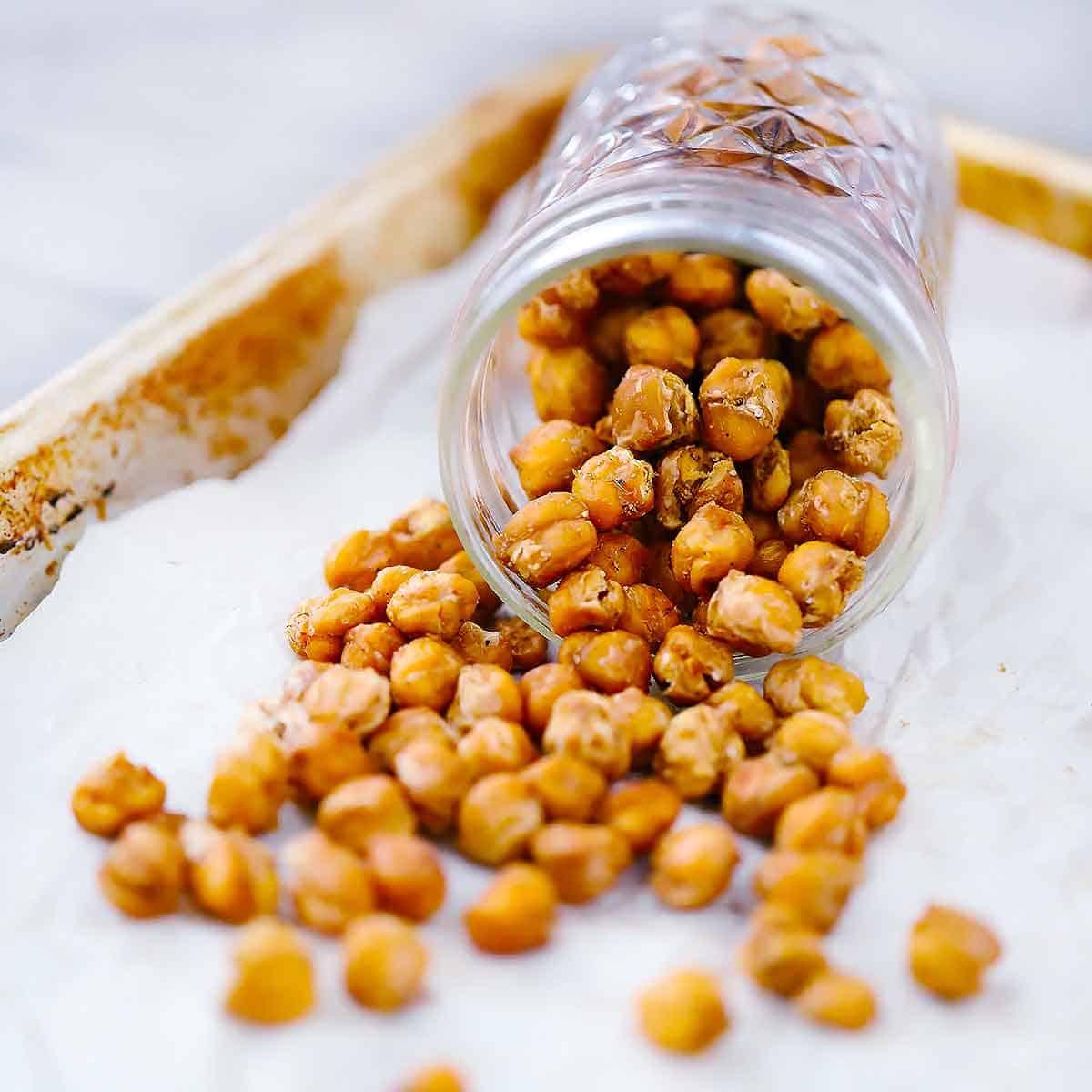
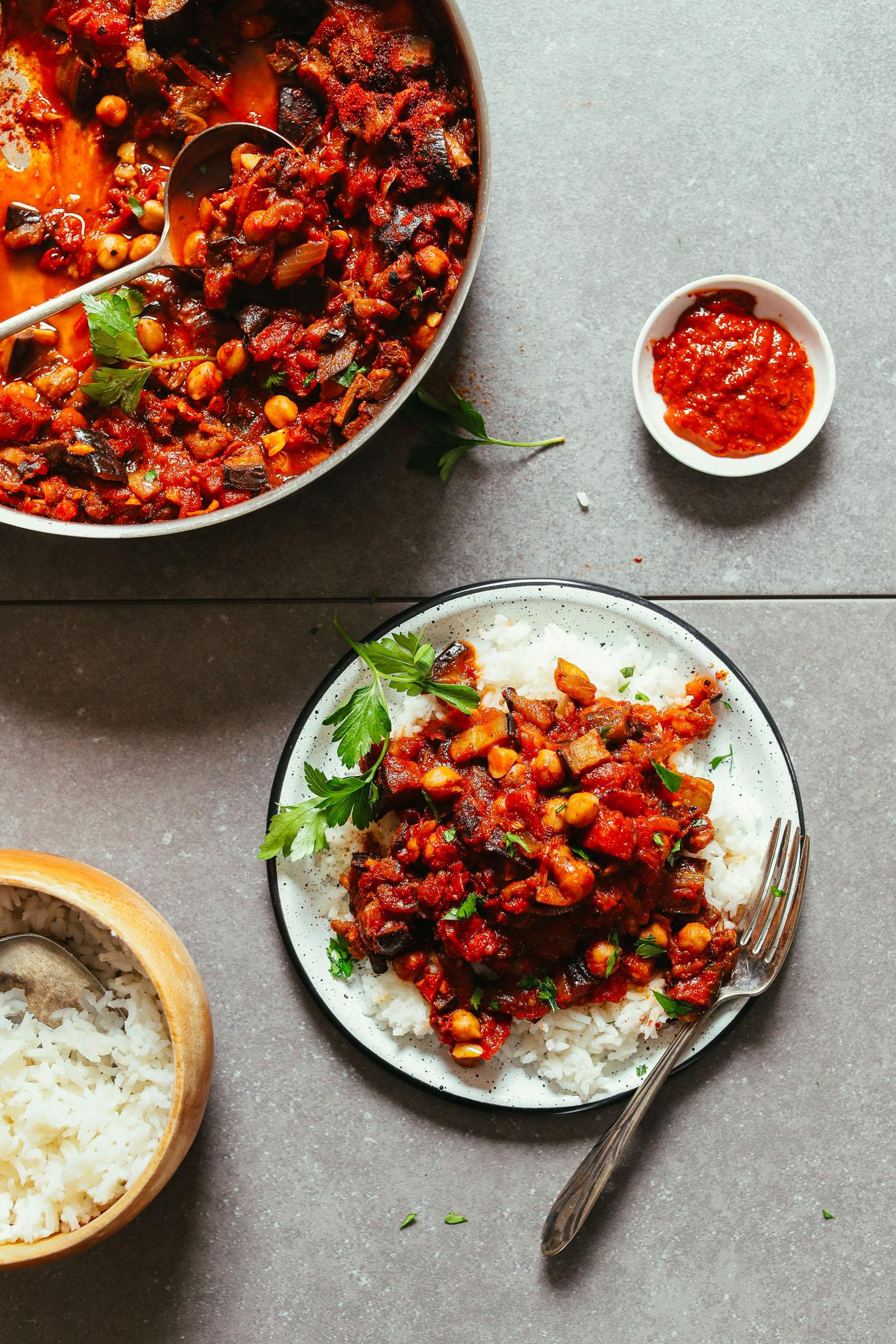
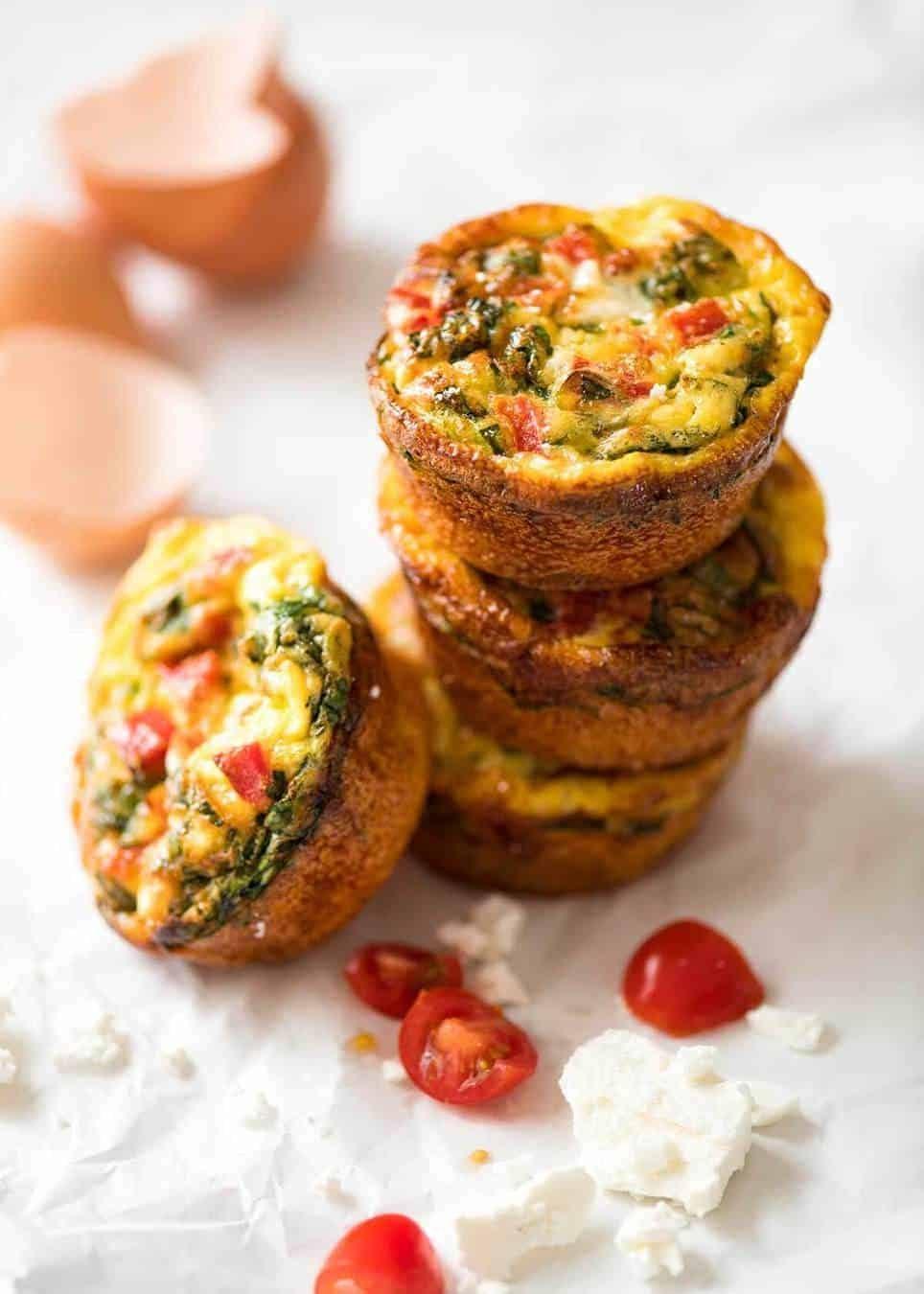
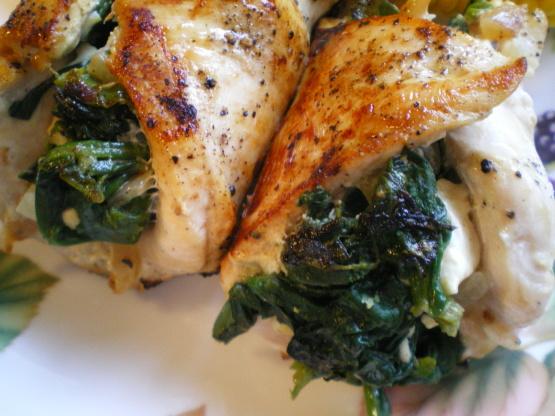
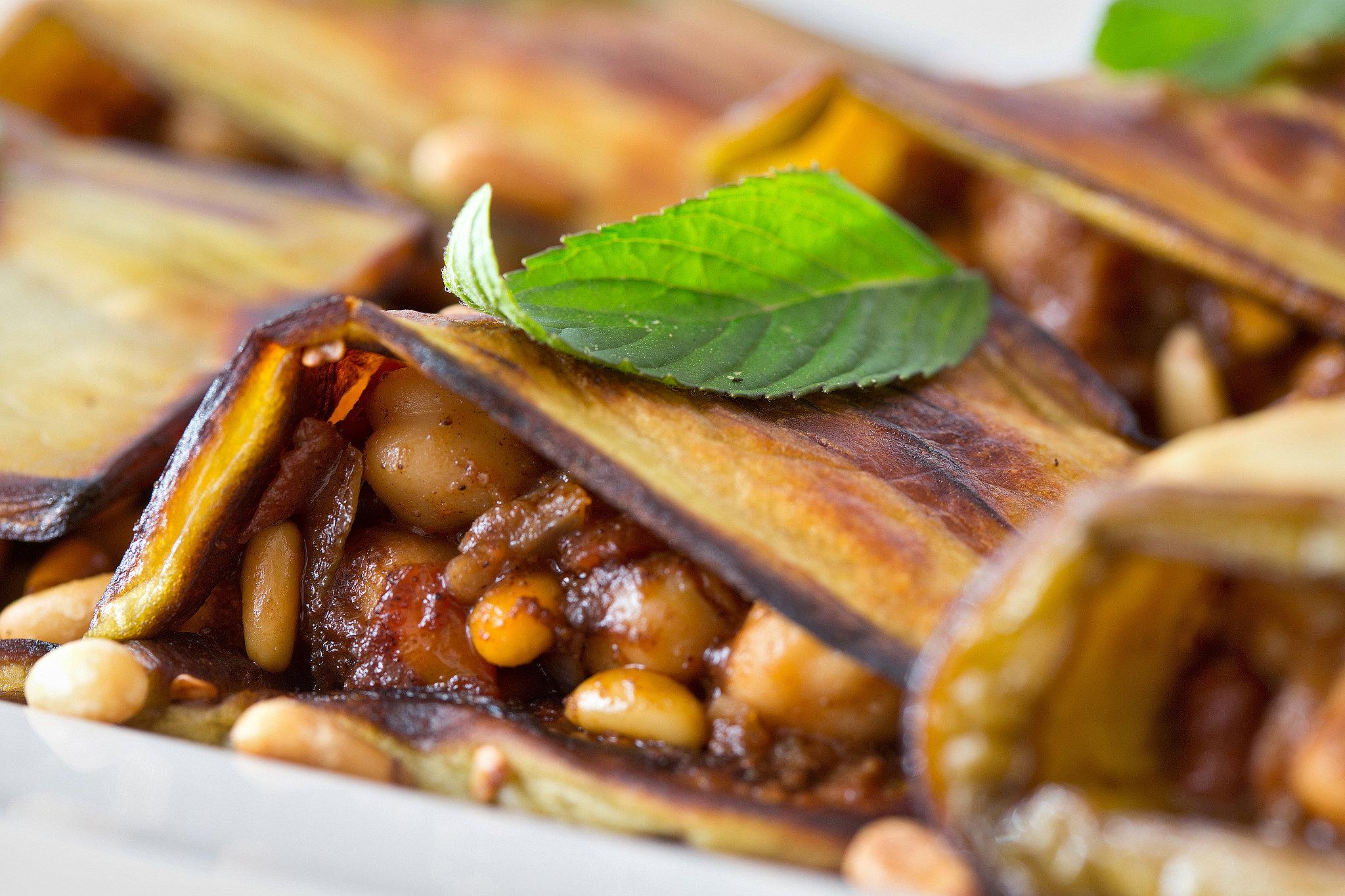
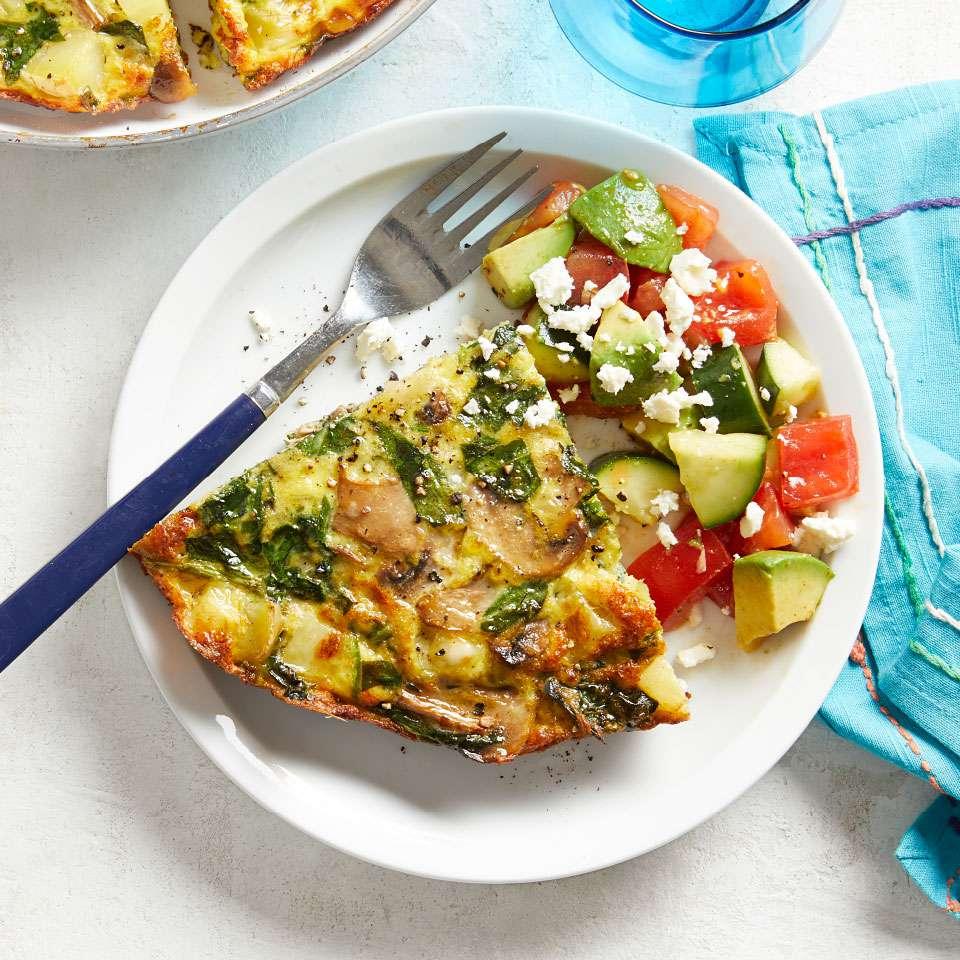
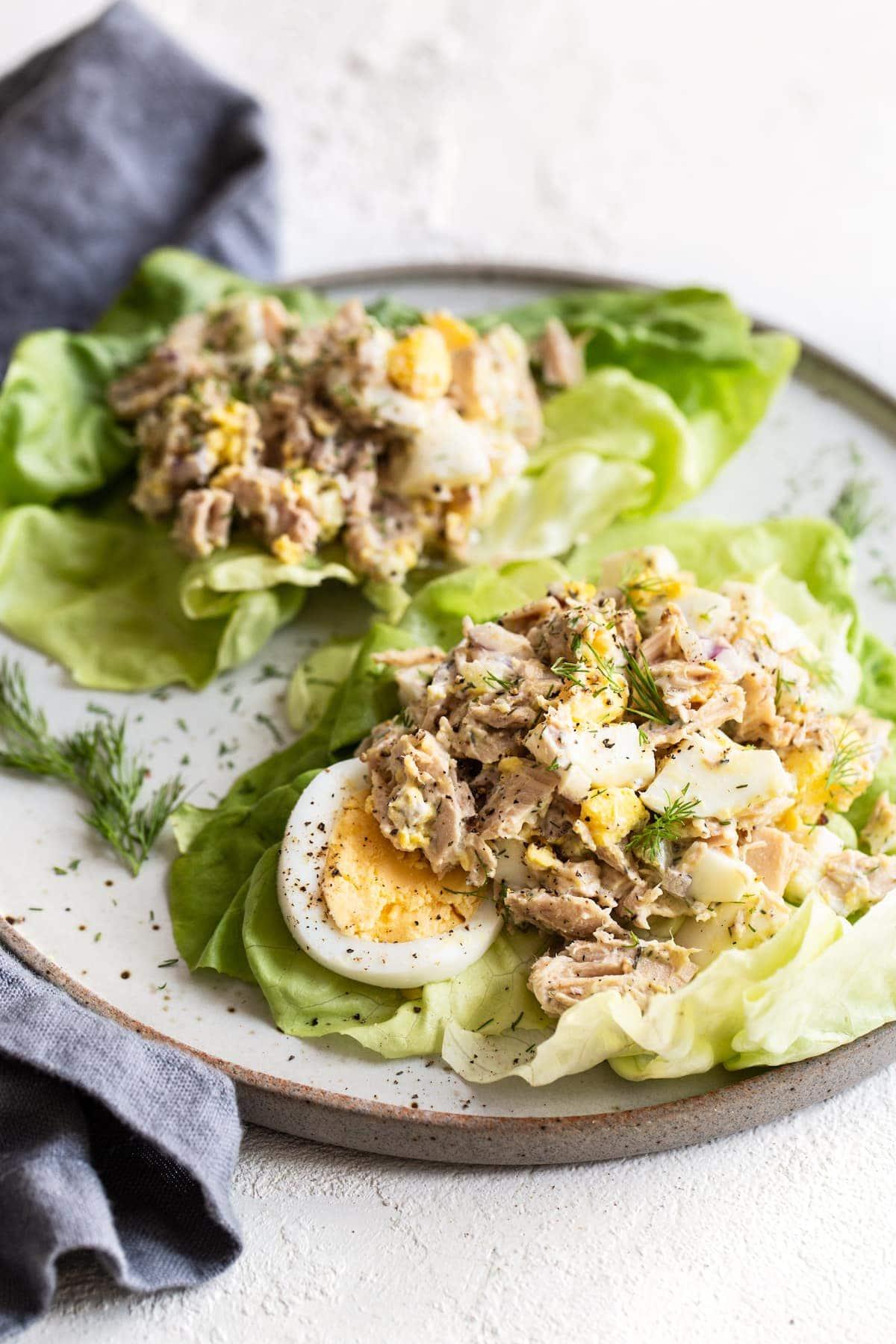
Focuses on high-fiber foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes to help control blood sugar levels. Includes healthy fats from sources such as olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish to support heart health and manage insulin resistance. Limits processed foods, refined sugars, and red meats, emphasizing lean proteins and plant-based meals to maintain a balanced diet and support weight management.
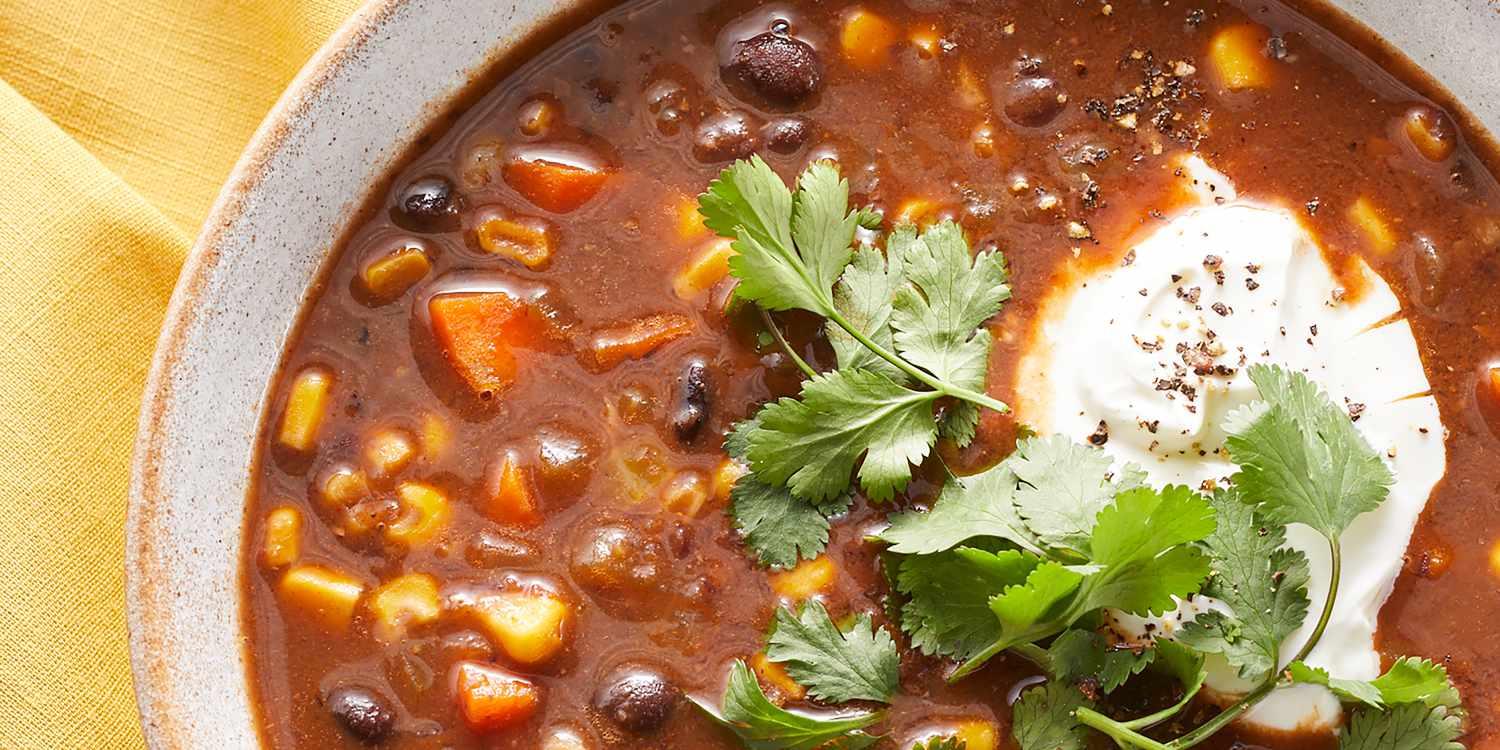
For Diabetes Mellitus Dm
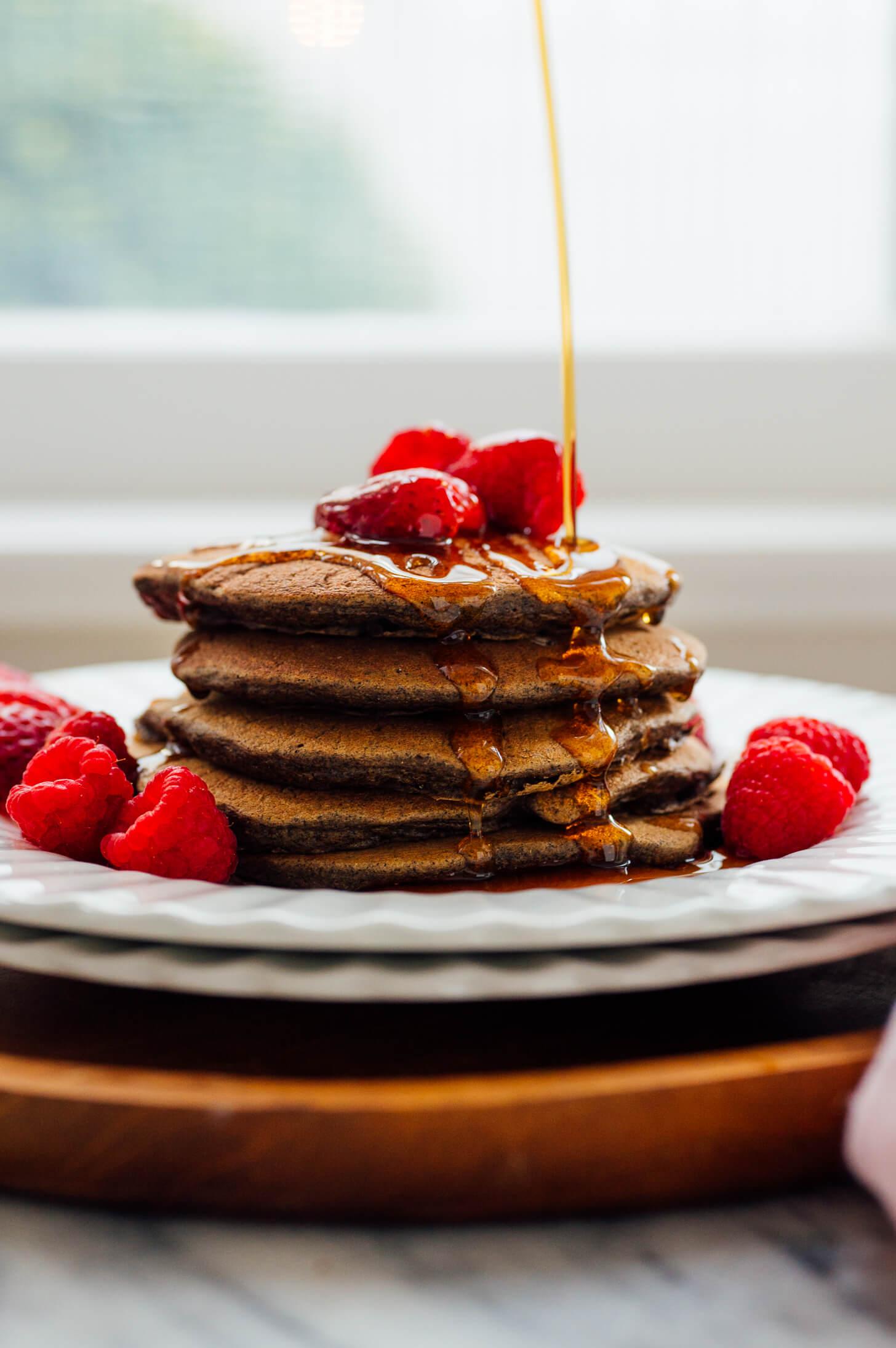
Mediterranean
Day 1
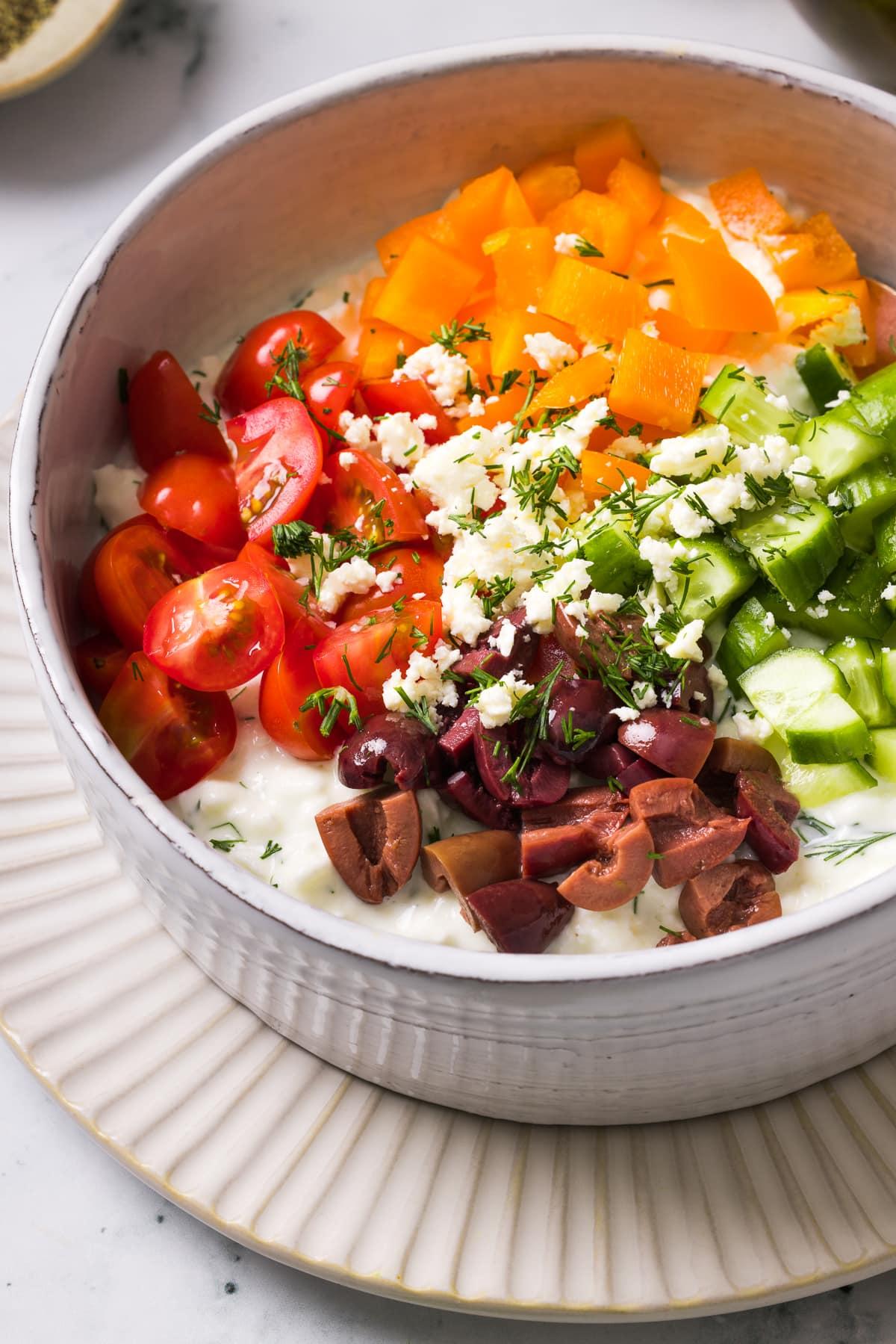
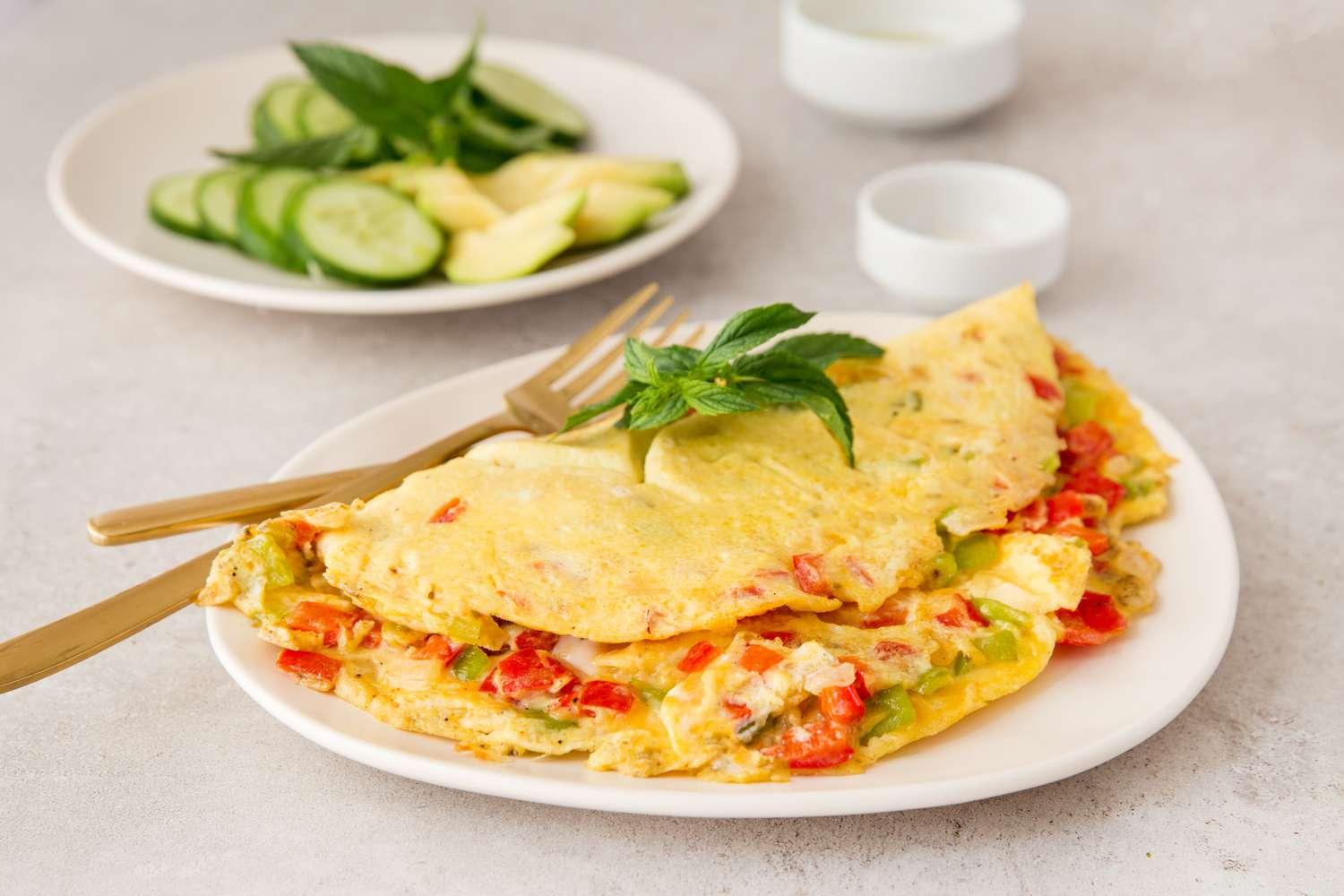
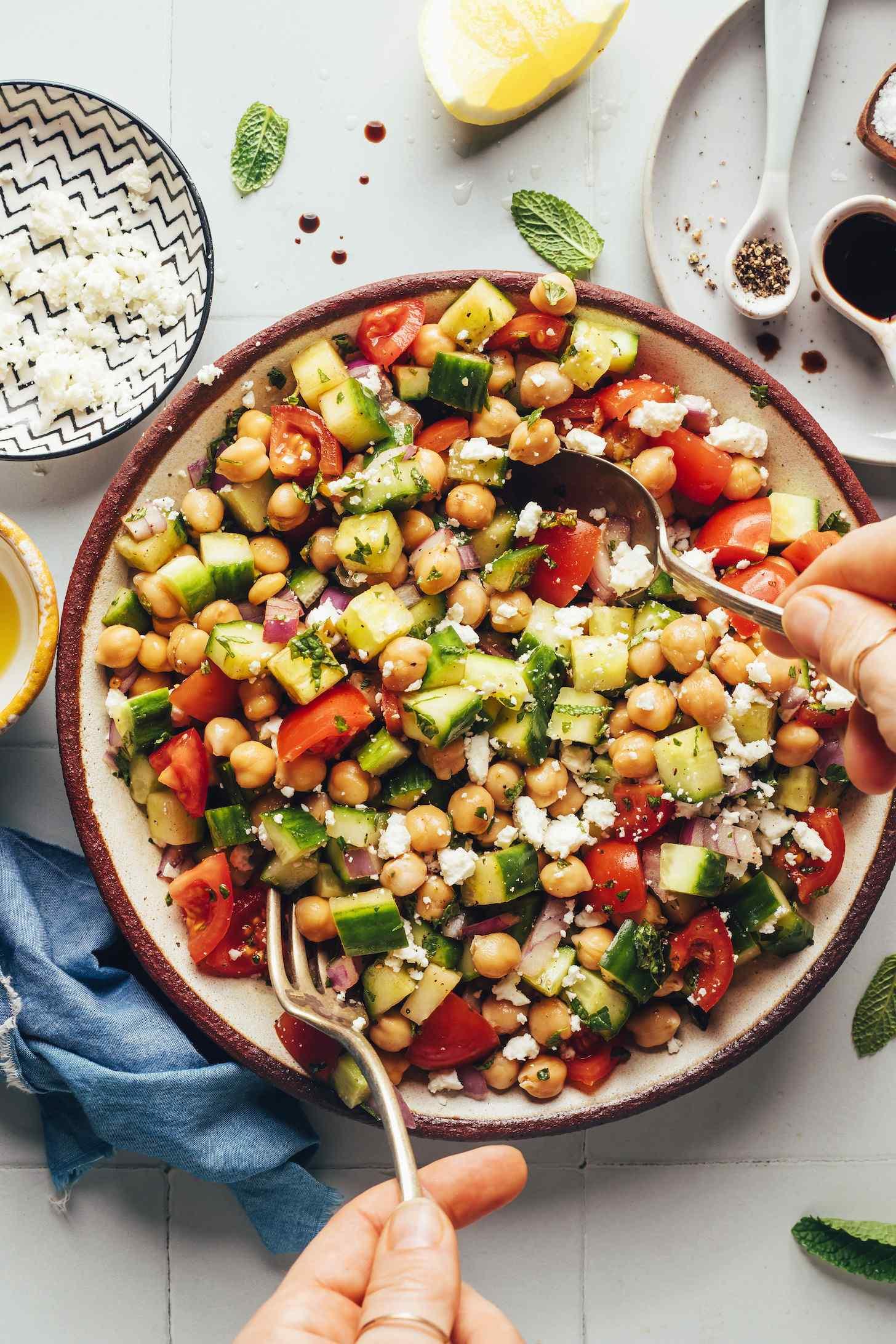
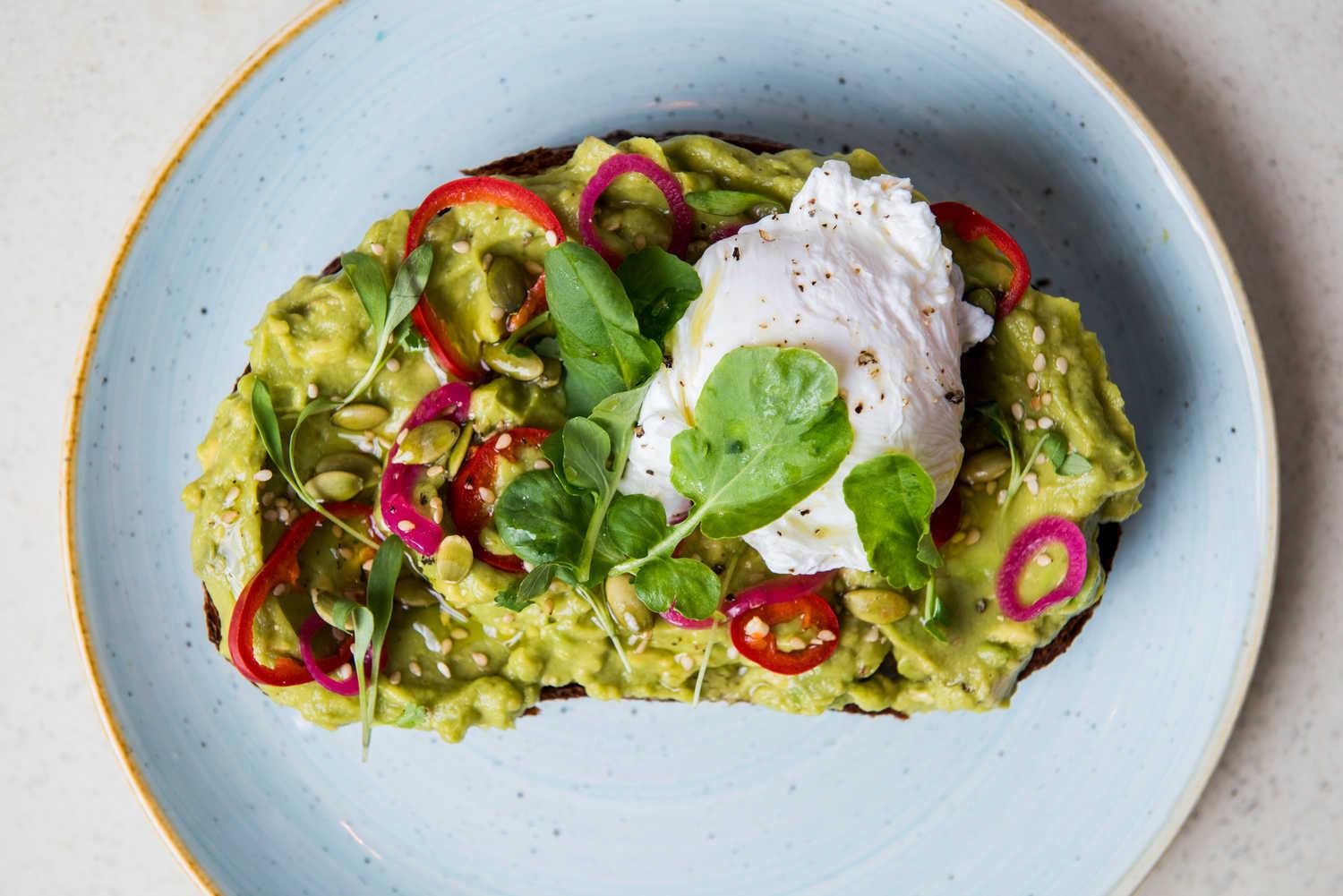
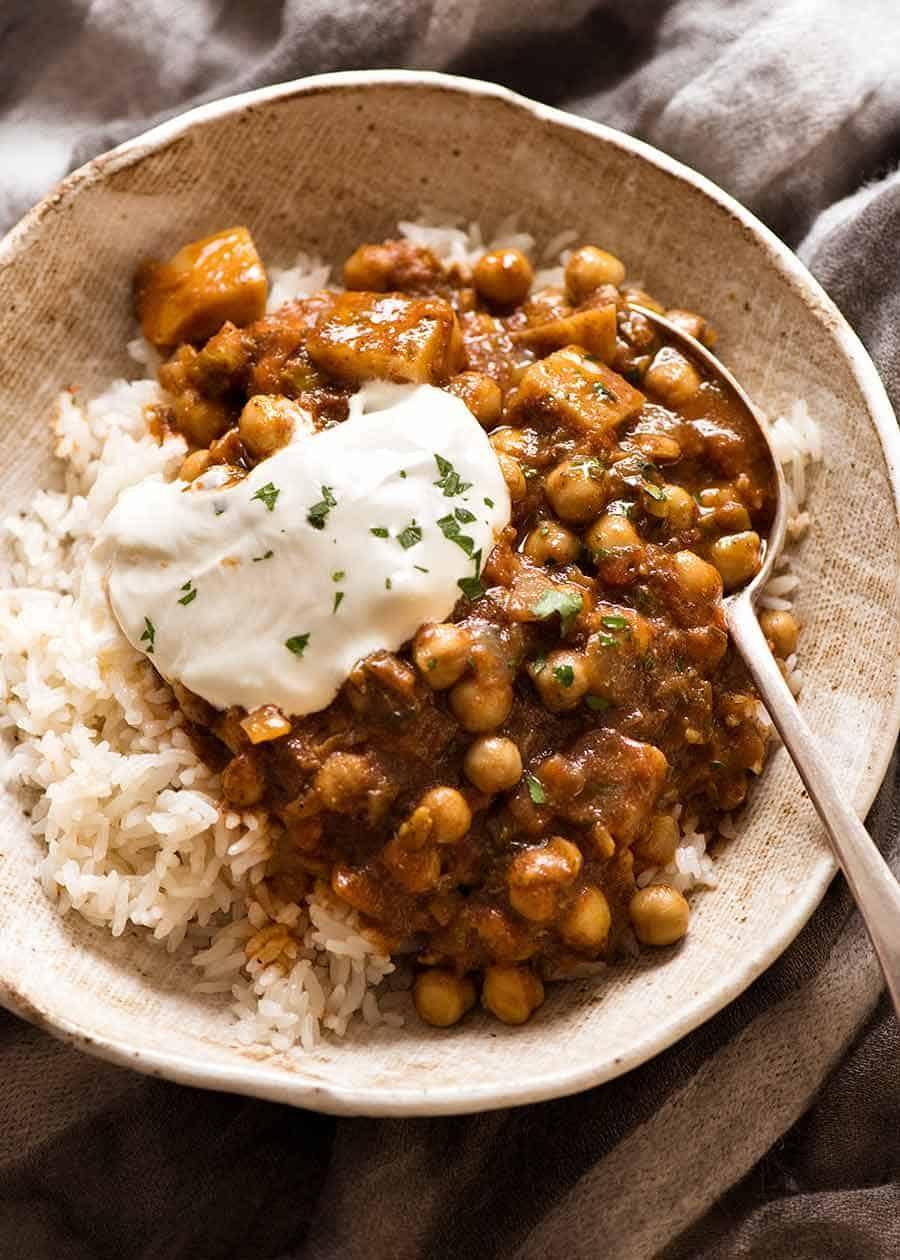
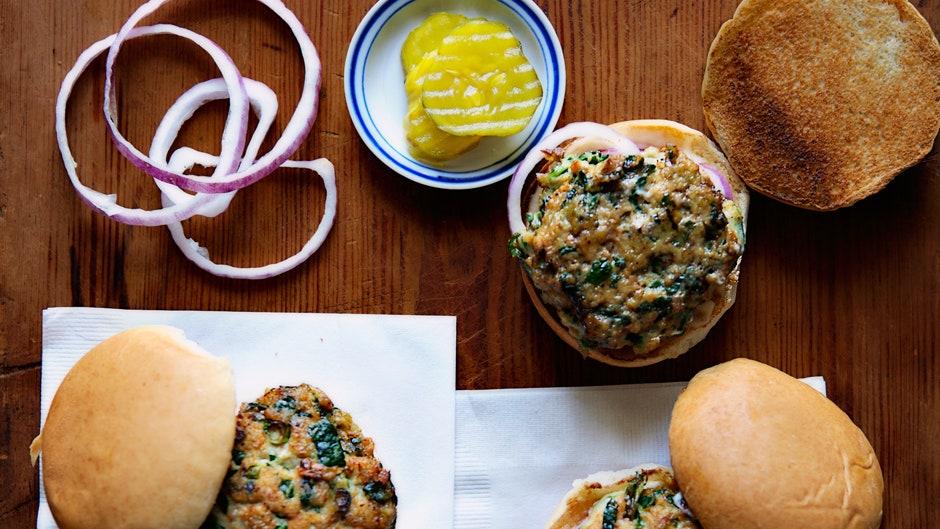
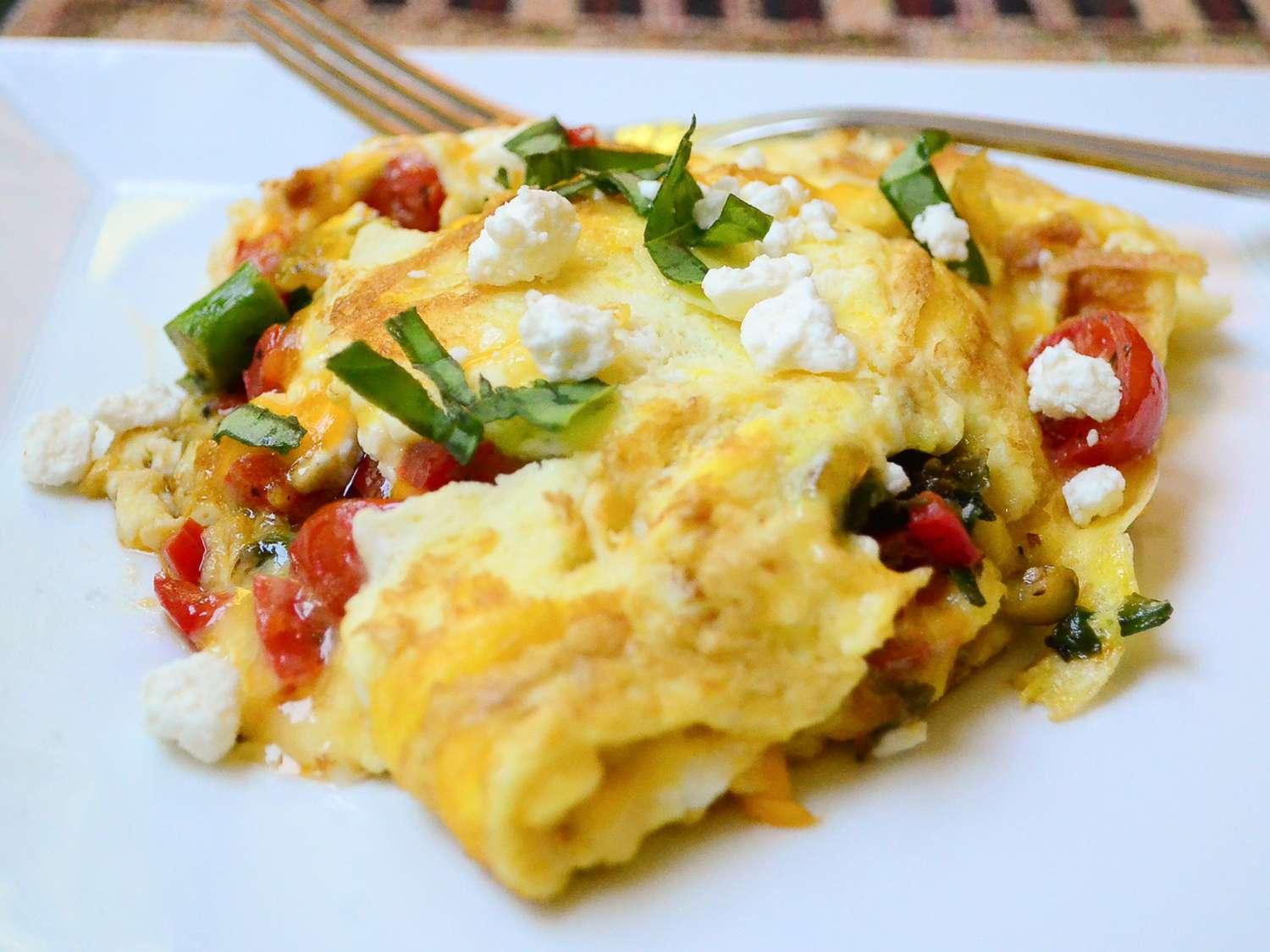
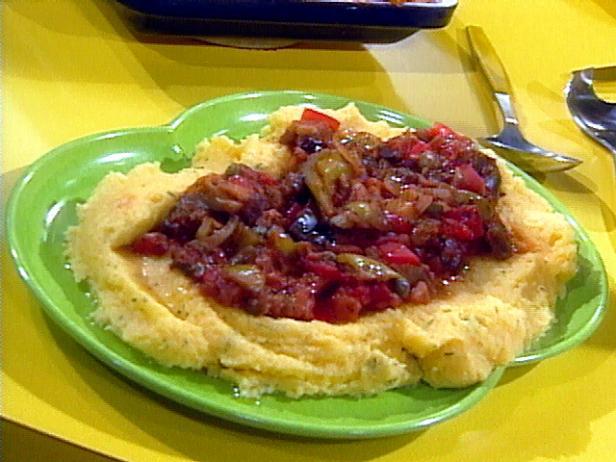
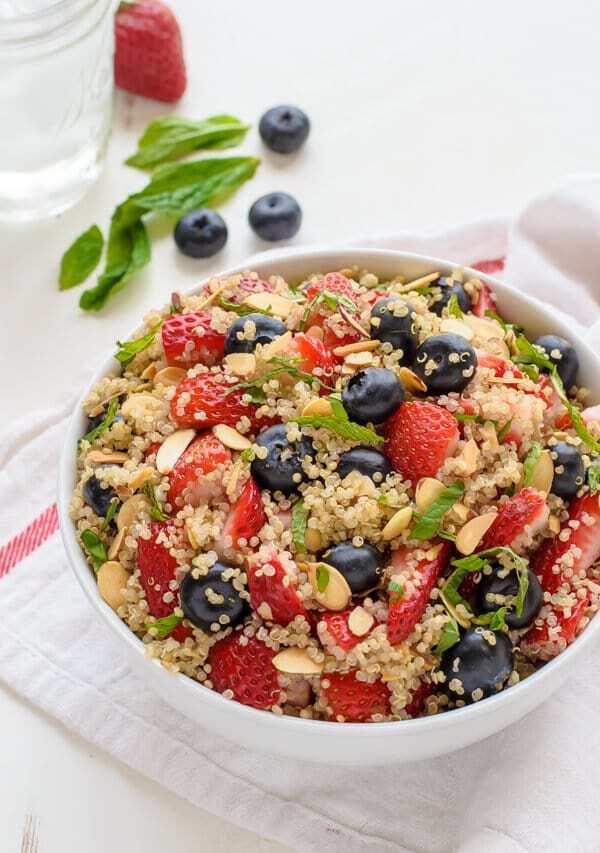
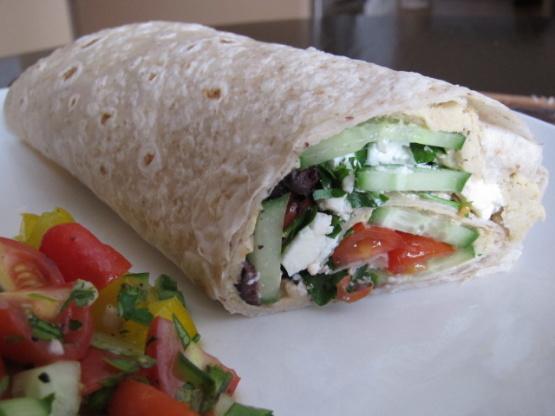
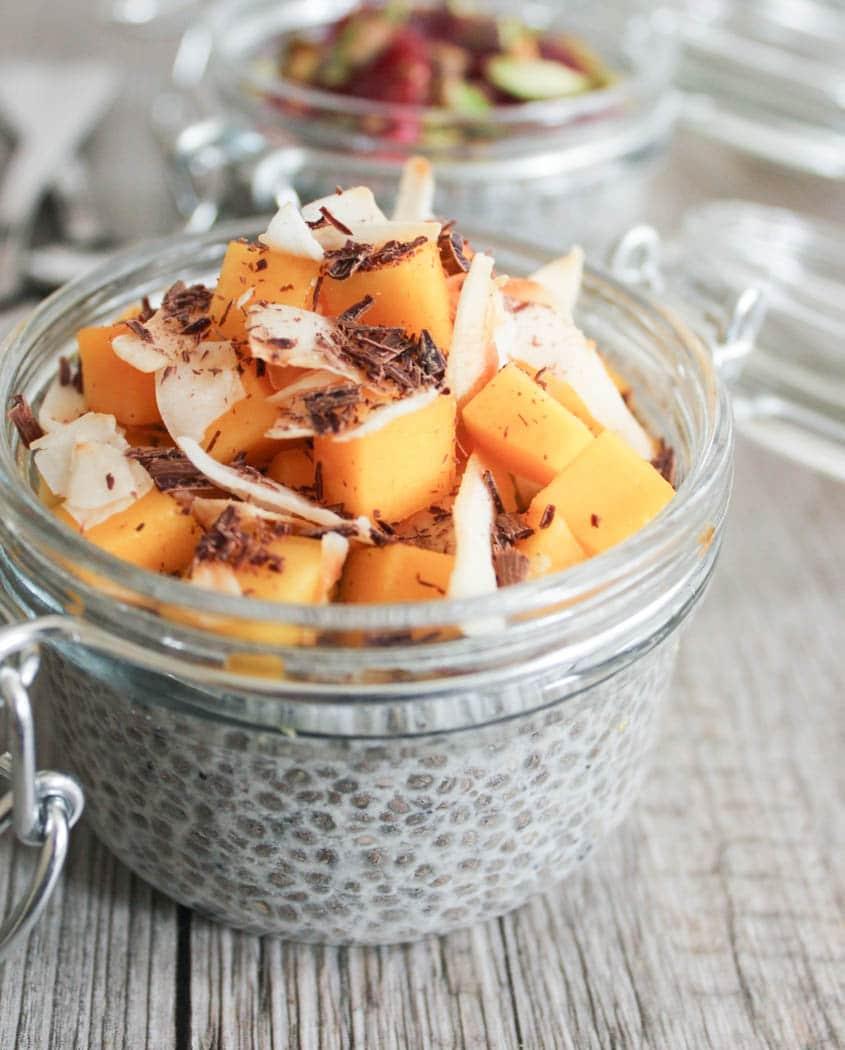
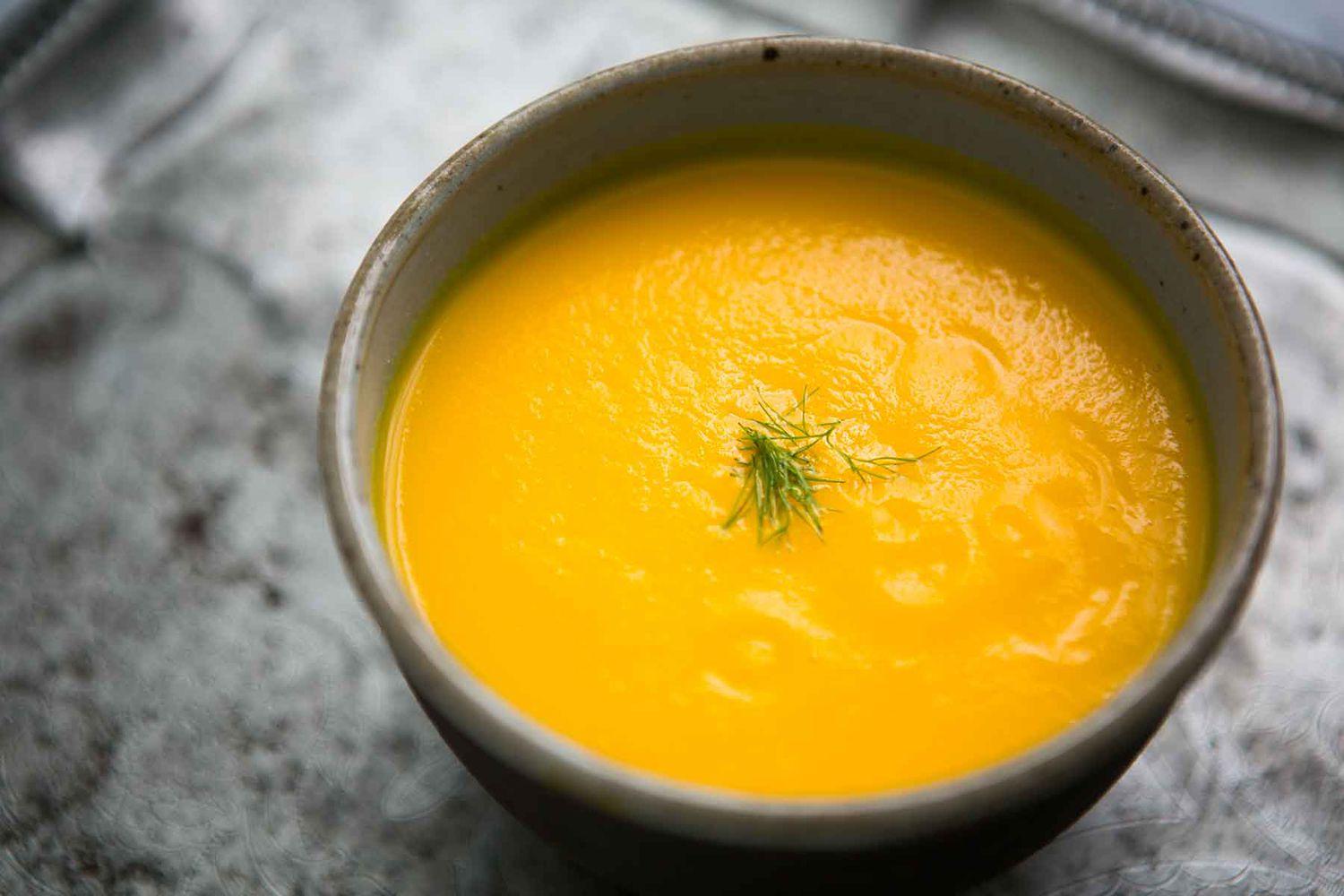
Focus on low-glycemic, plant-based foods to manage blood glucose levels, incorporating high-fiber options like legumes, whole grains, and vegetables to promote satiety and improve insulin sensitivity. Limit intake of refined carbohydrates and sugary foods, while ensuring adequate protein through sources like tofu, tempeh, lentils, and nuts to maintain muscle mass and assist with glucose regulation. Include healthy fats from avocados, seeds, and olive oil for heart health, and monitor portion sizes to support weight management, which is crucial in type 2 diabetes management.
For Diabetes Mellitus Dm
Vegetarian
Day 1
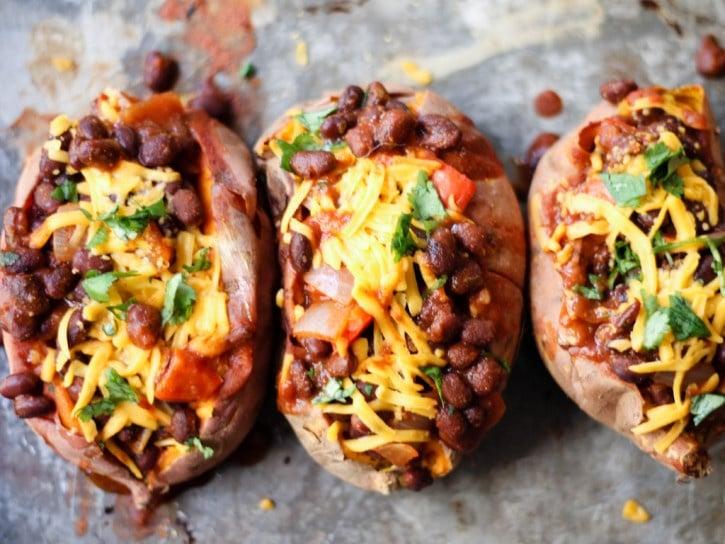
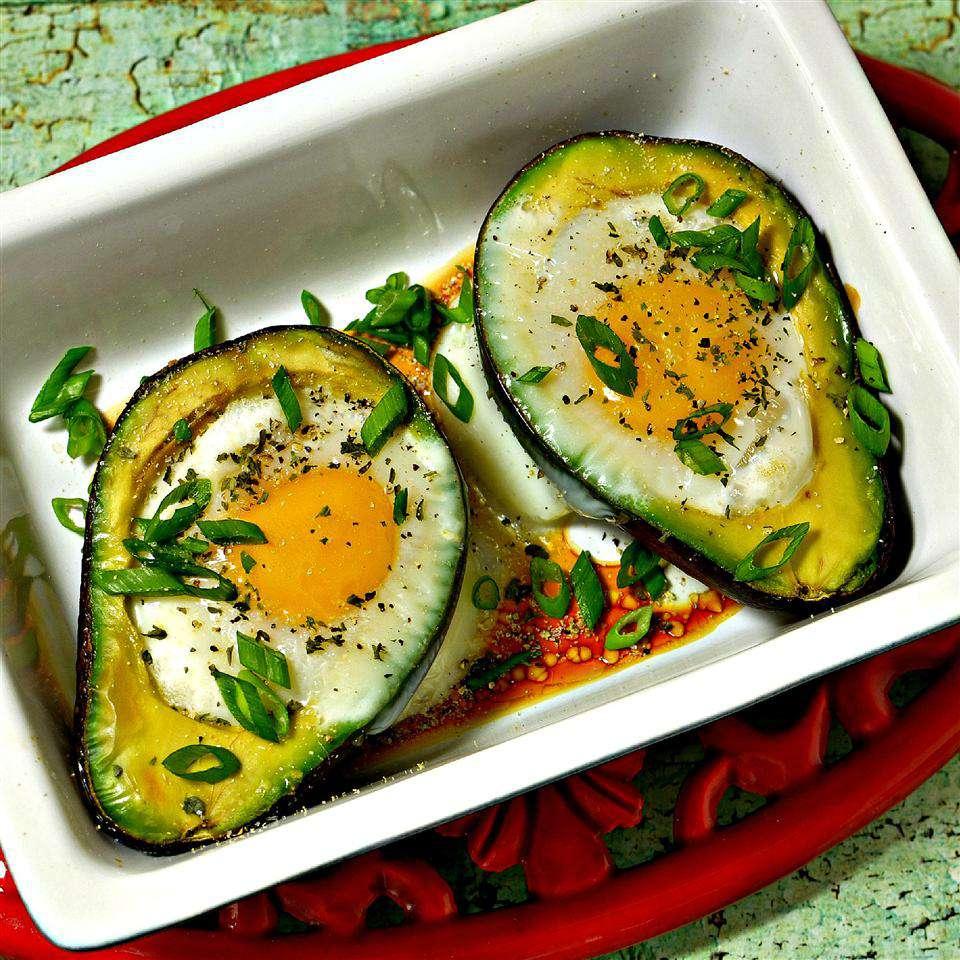
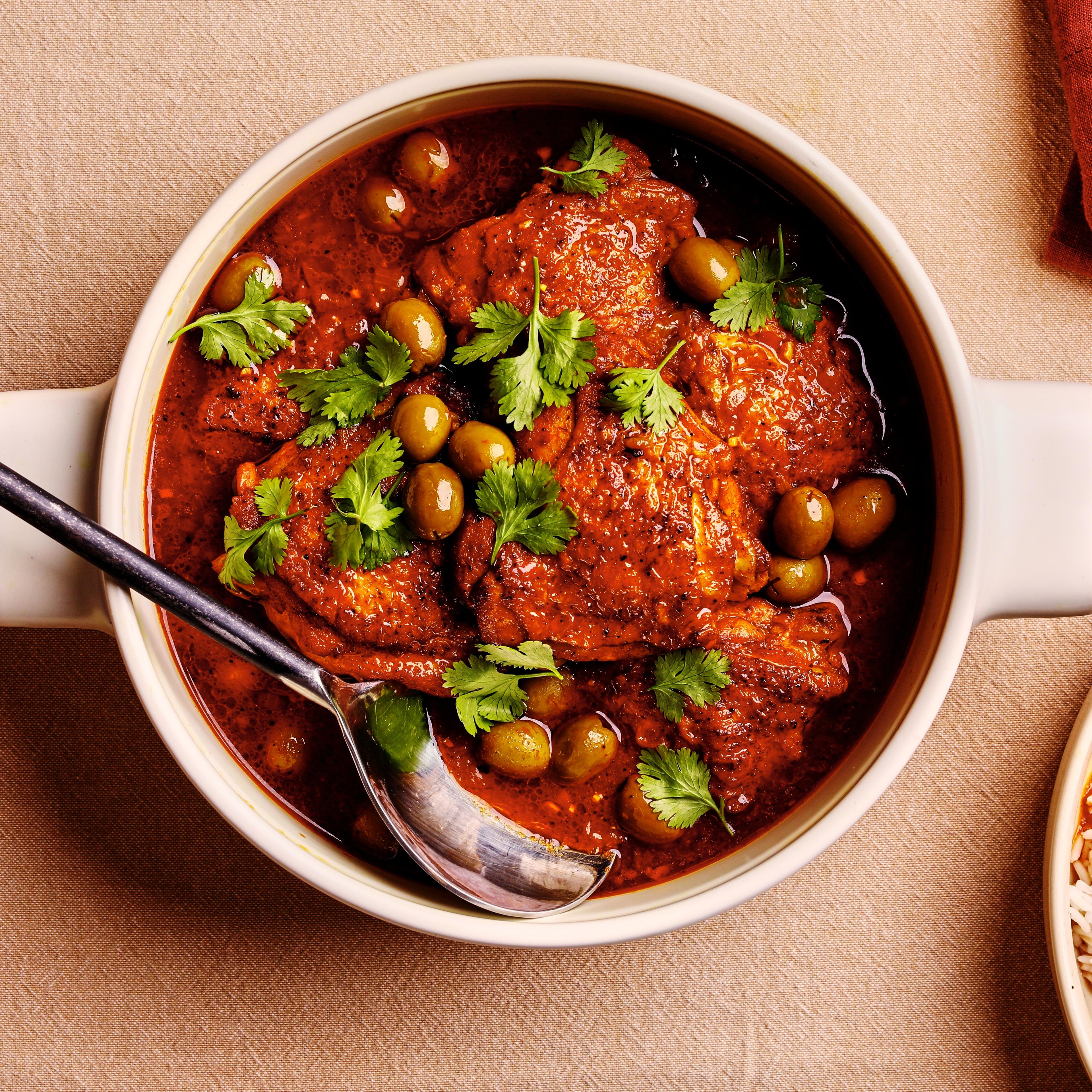
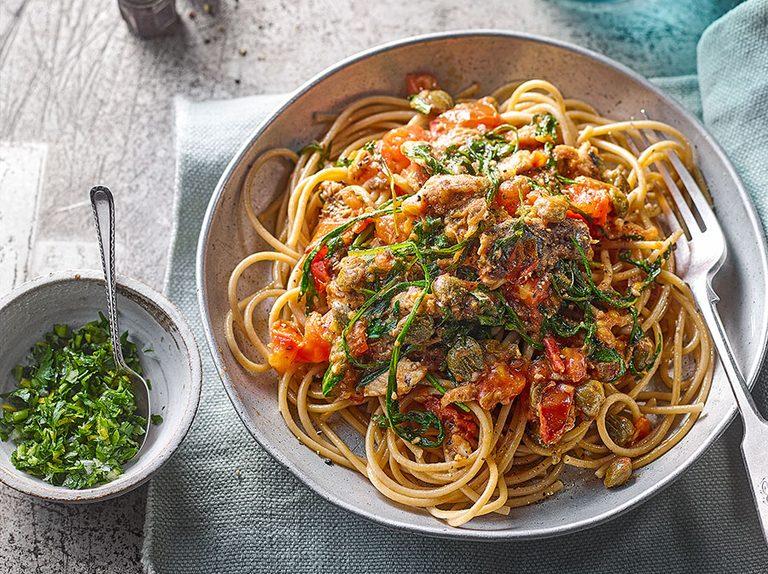
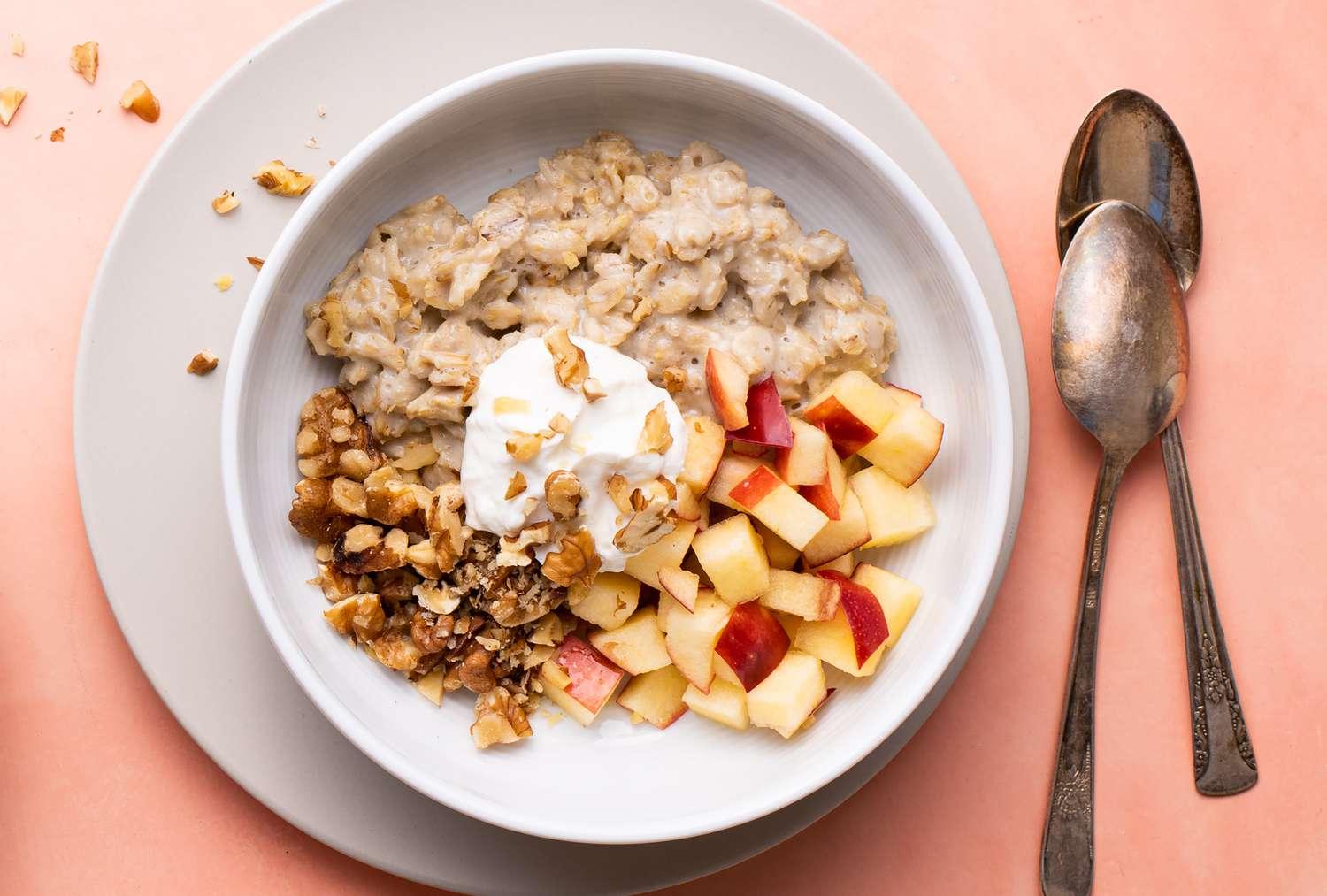
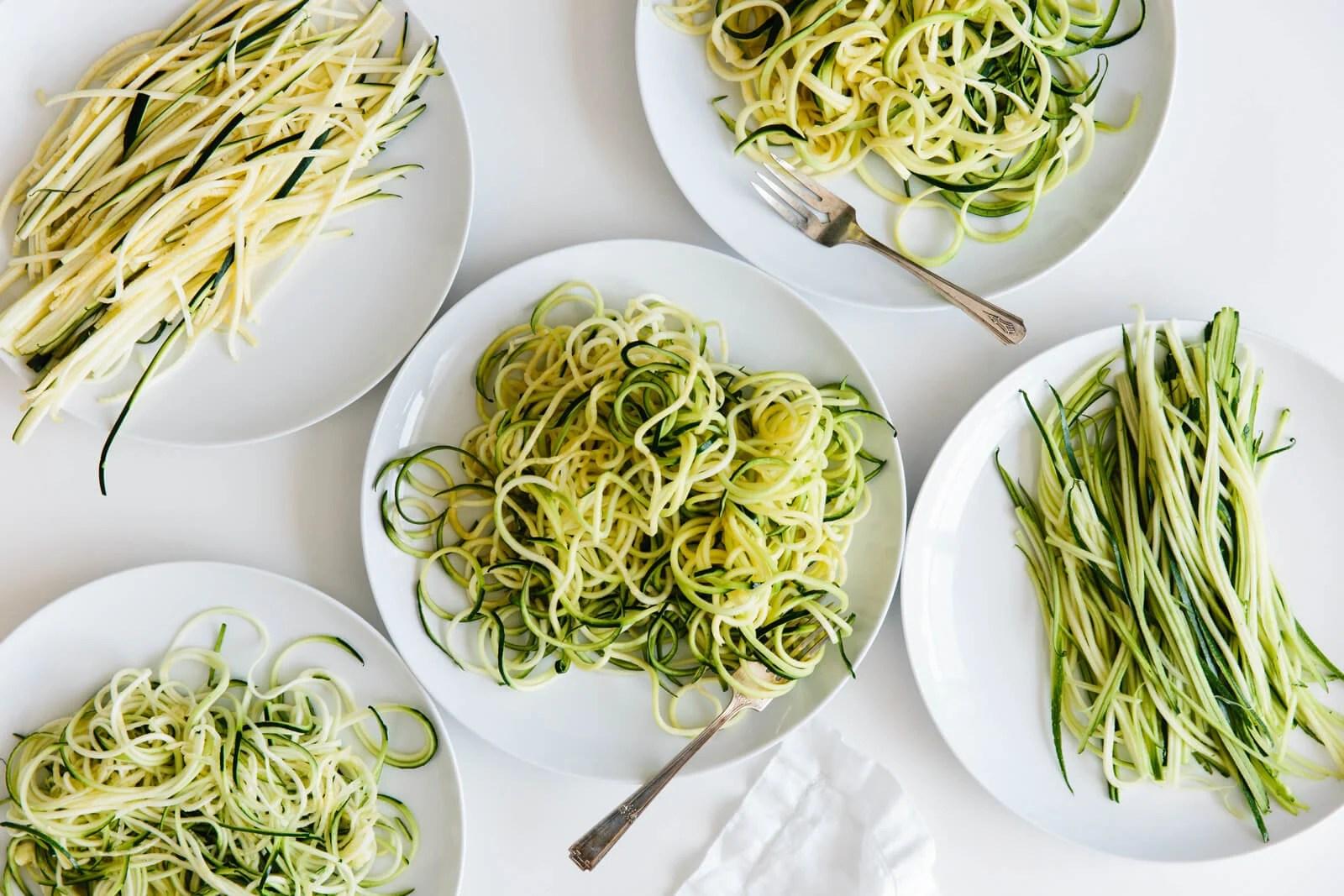
Focus on a low glycemic index to keep blood sugar levels stable; include high-fiber foods like vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Control carbohydrate intake across meals to manage blood glucose; emphasize portion control and distribute carbs evenly throughout the day. Incorporate lean protein and healthy fats to support satiety and provide essential nutrients for both mother and baby's development.
For Diabetes Related To Pregnancy Gestational
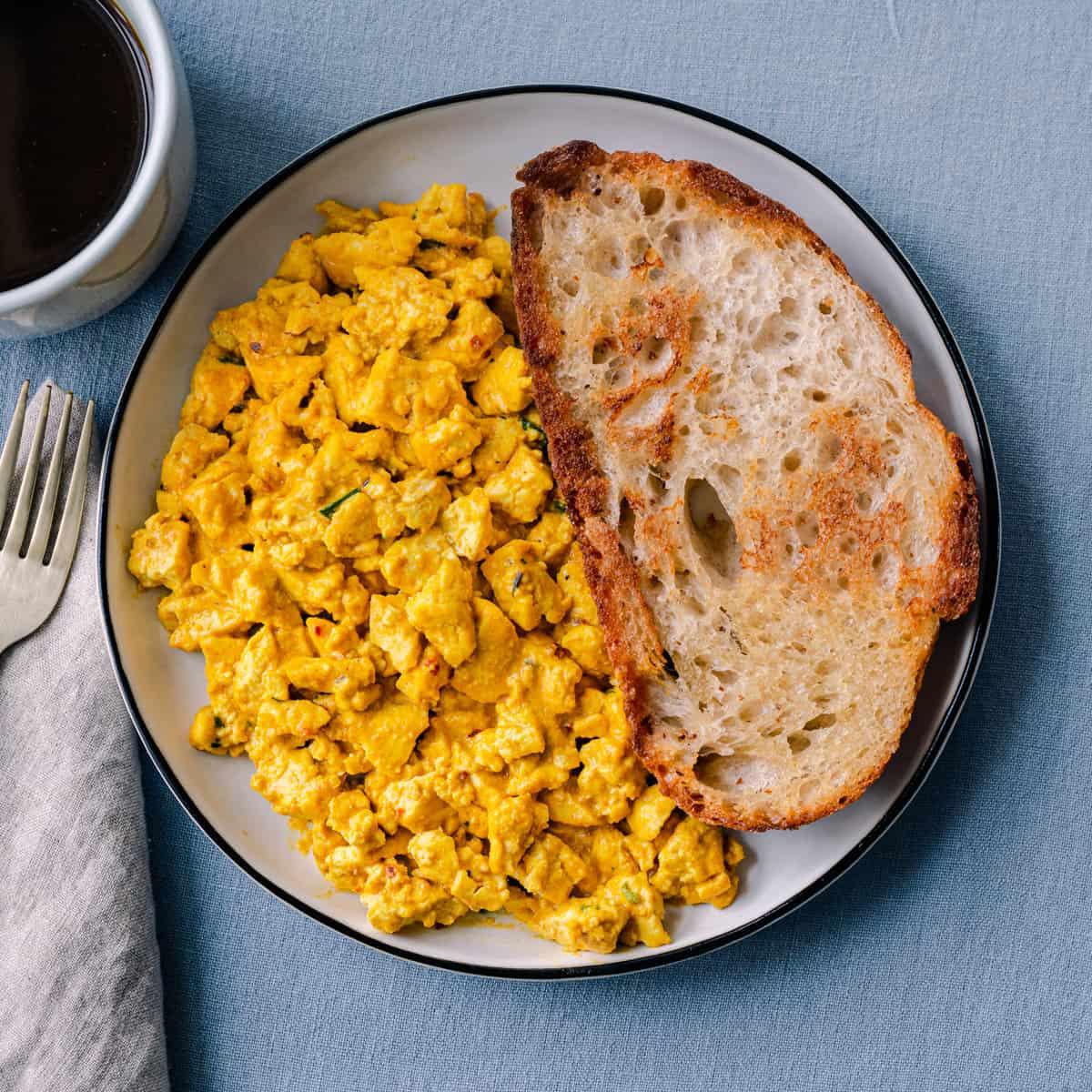
Balanced
Day 1
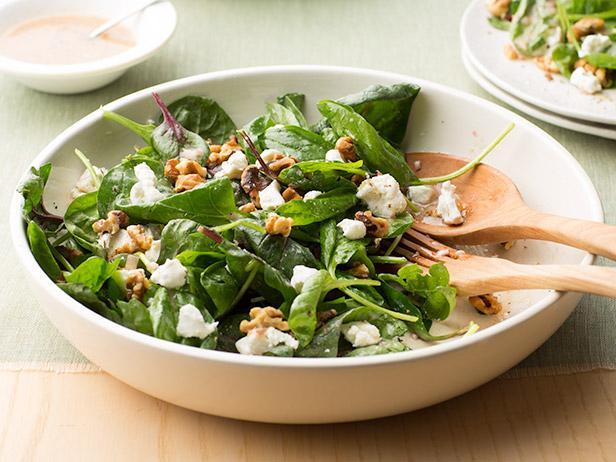
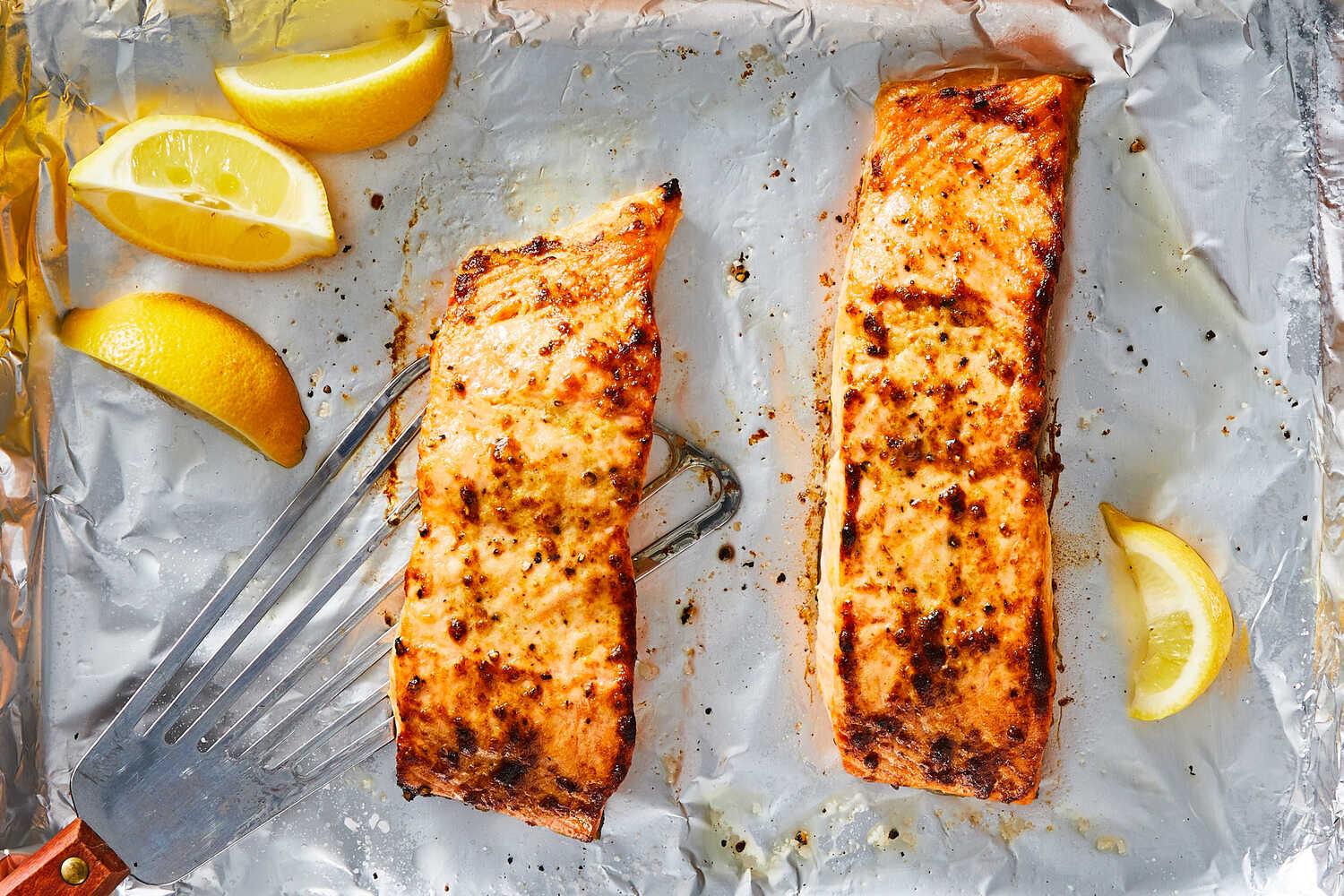
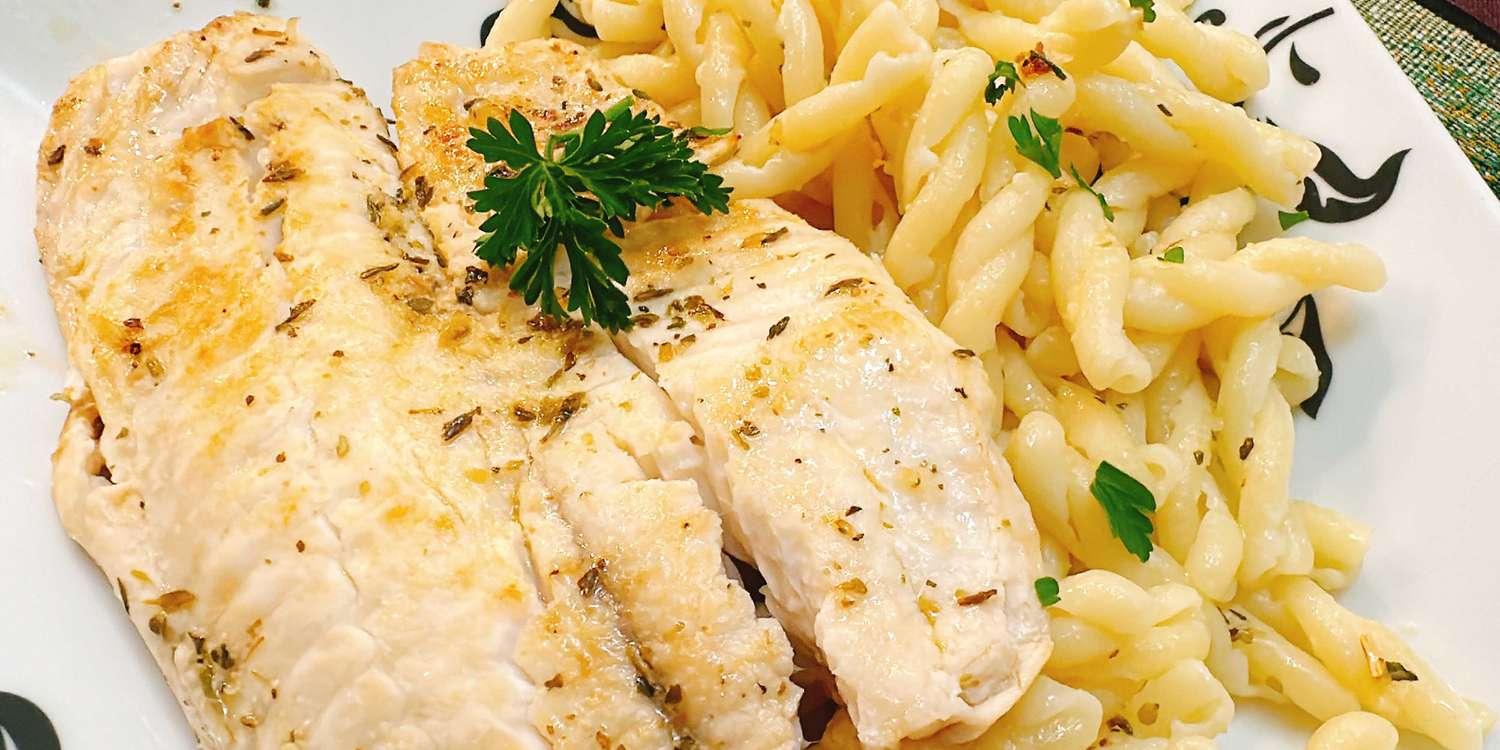
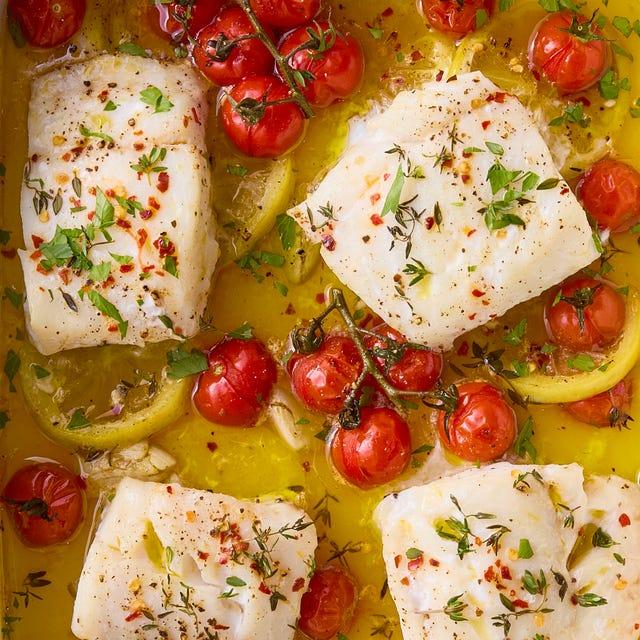
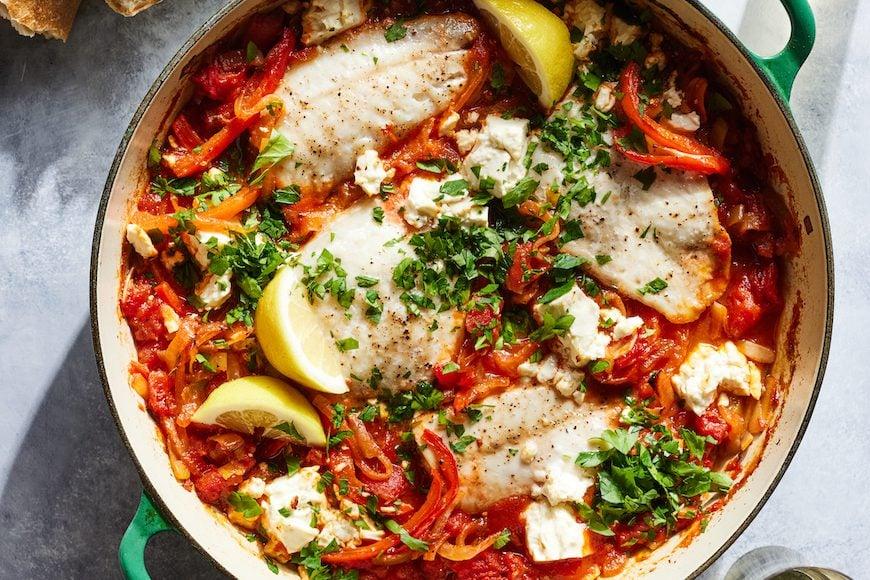
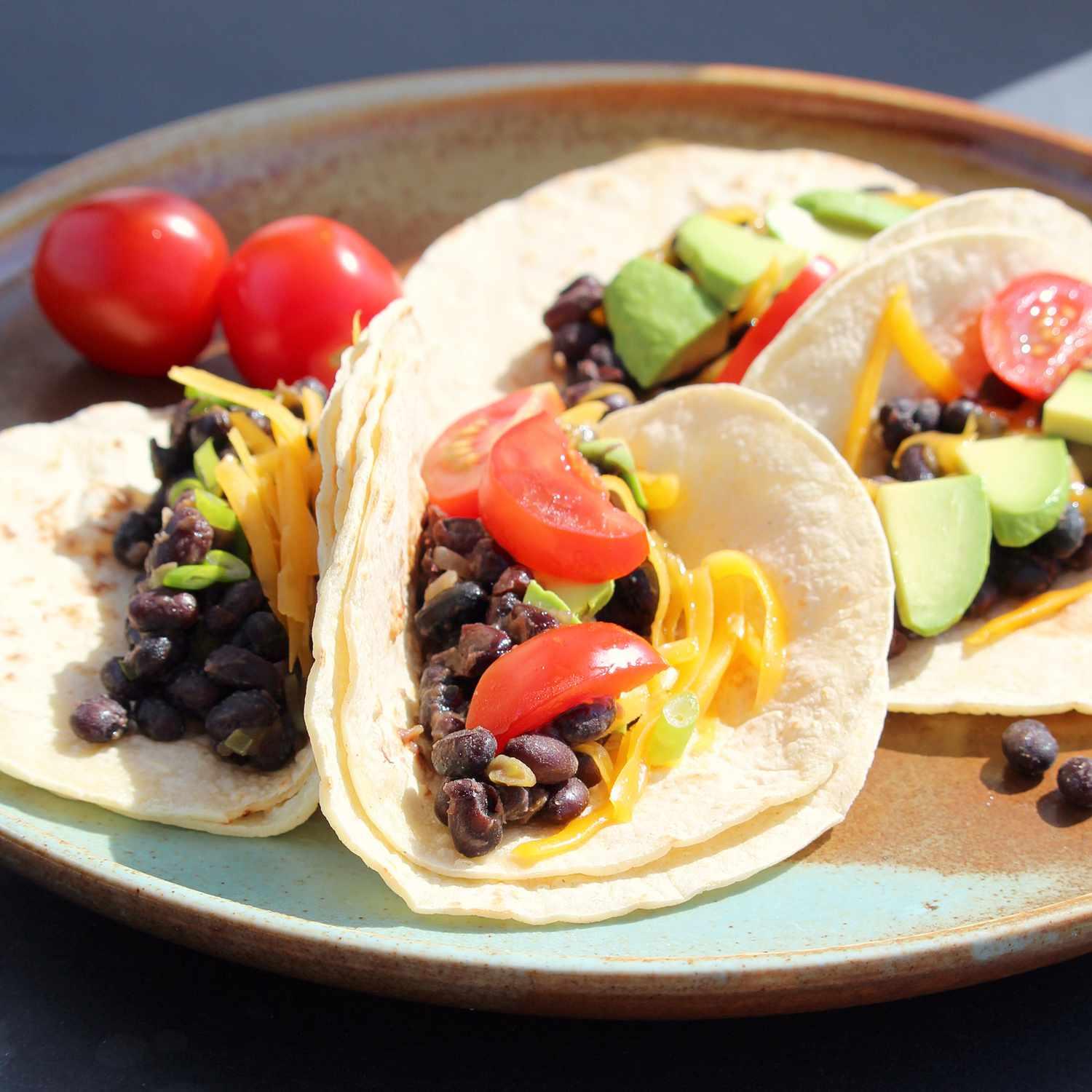
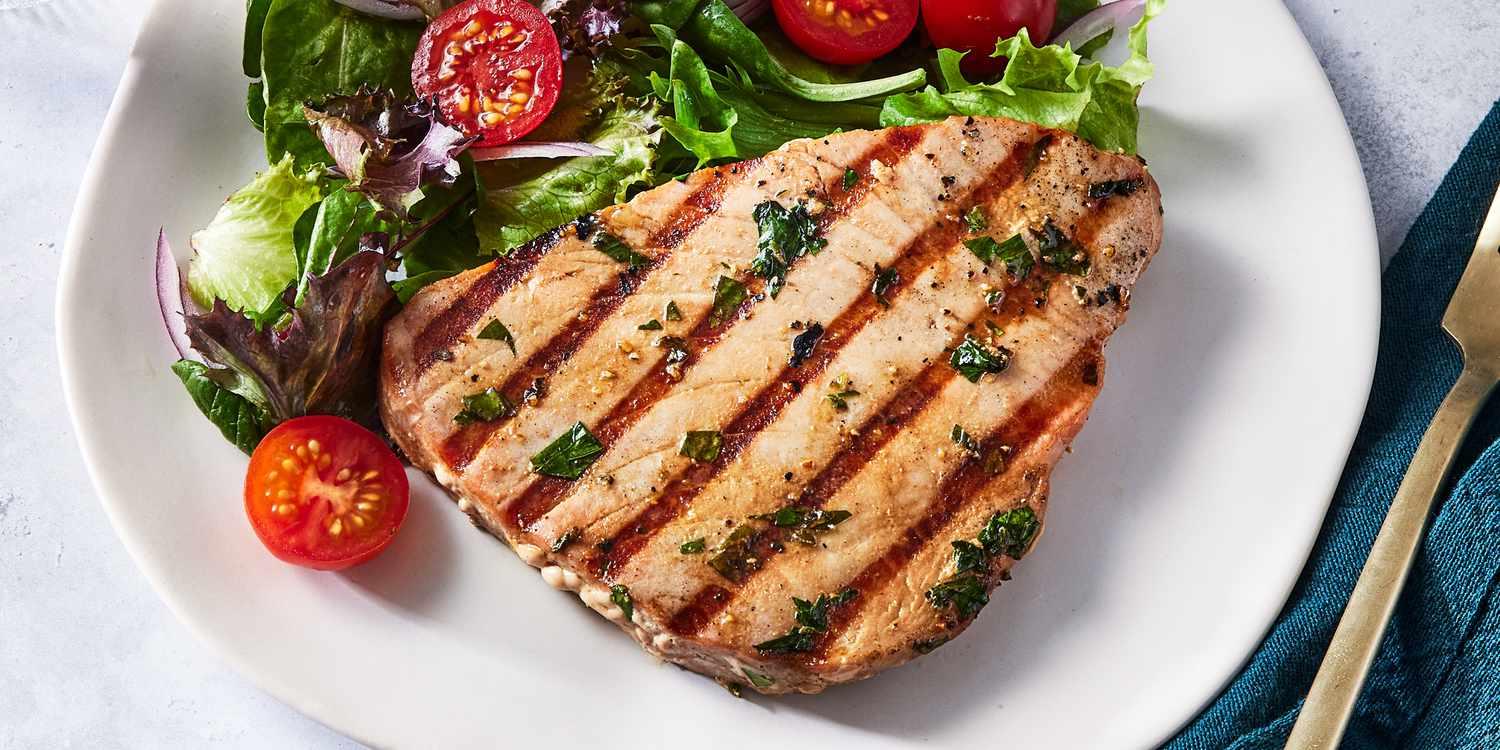
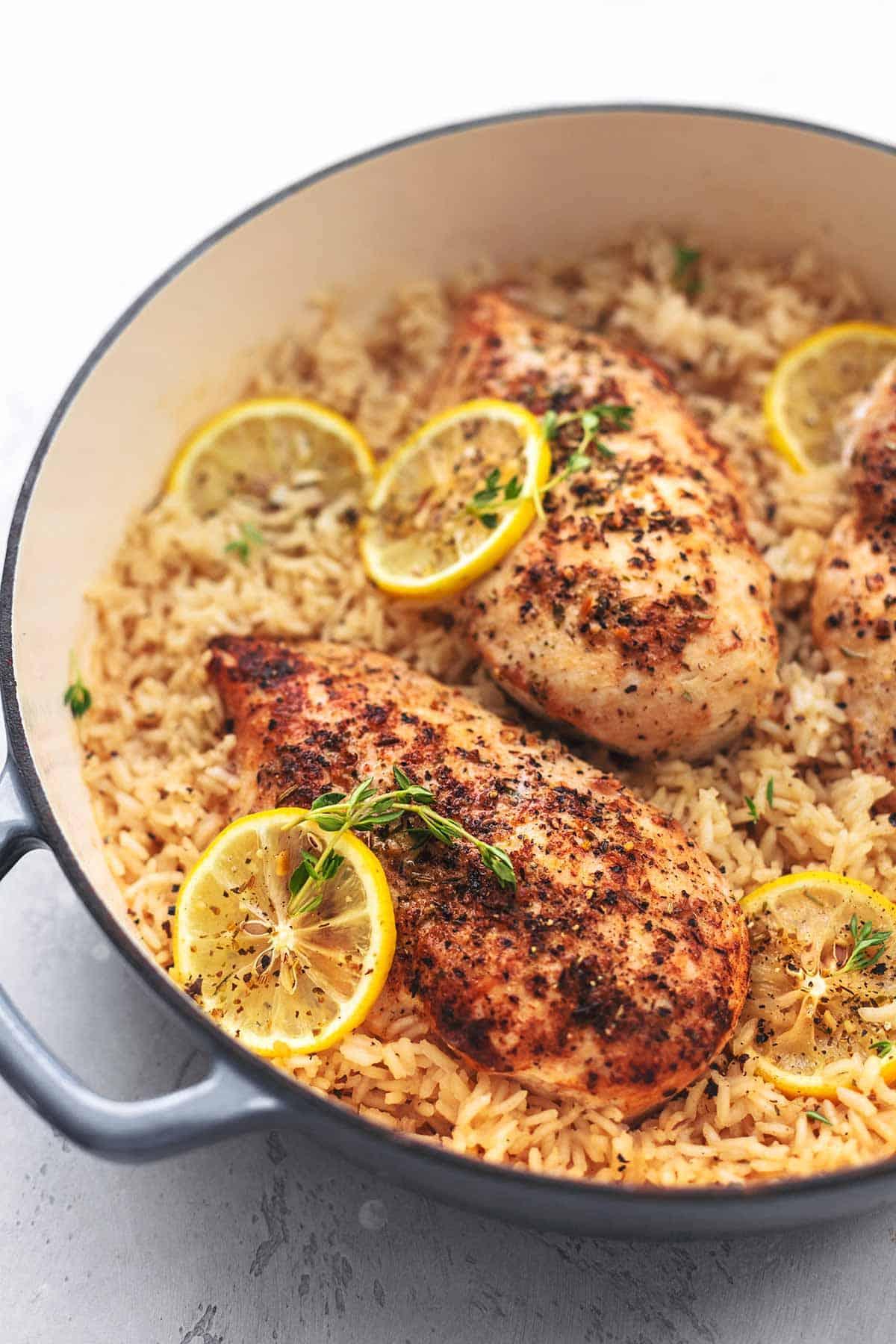
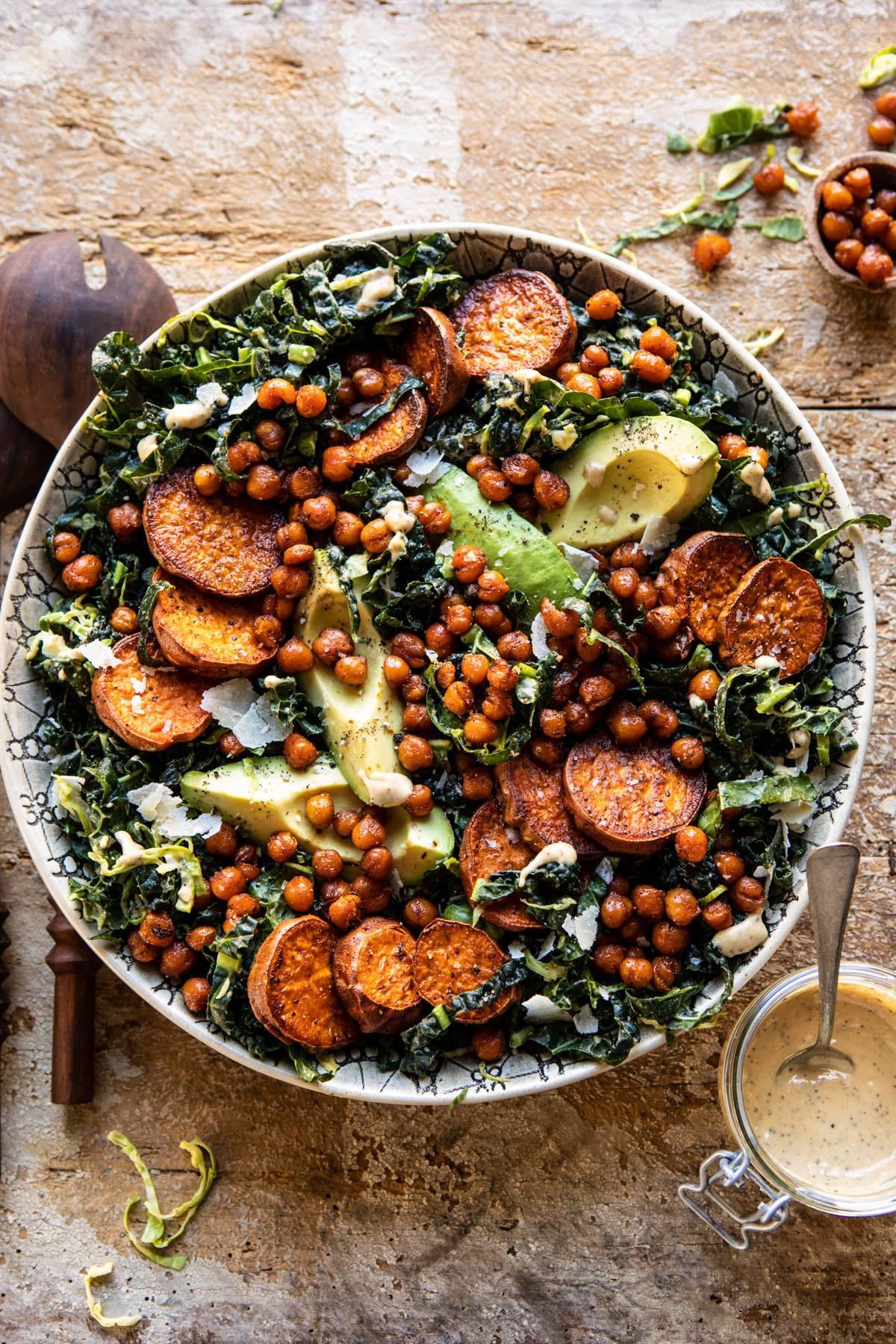
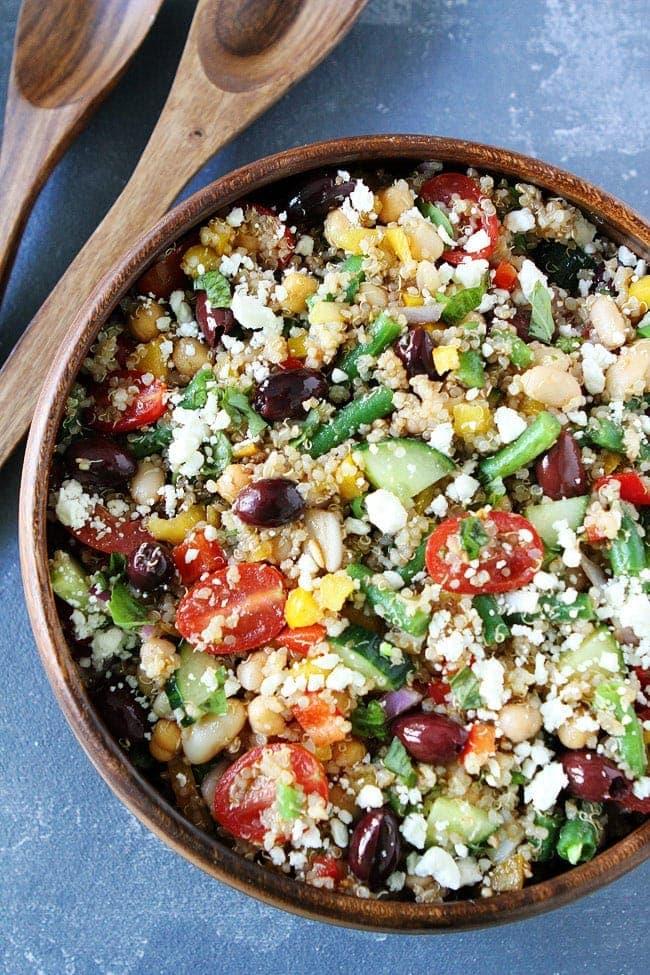
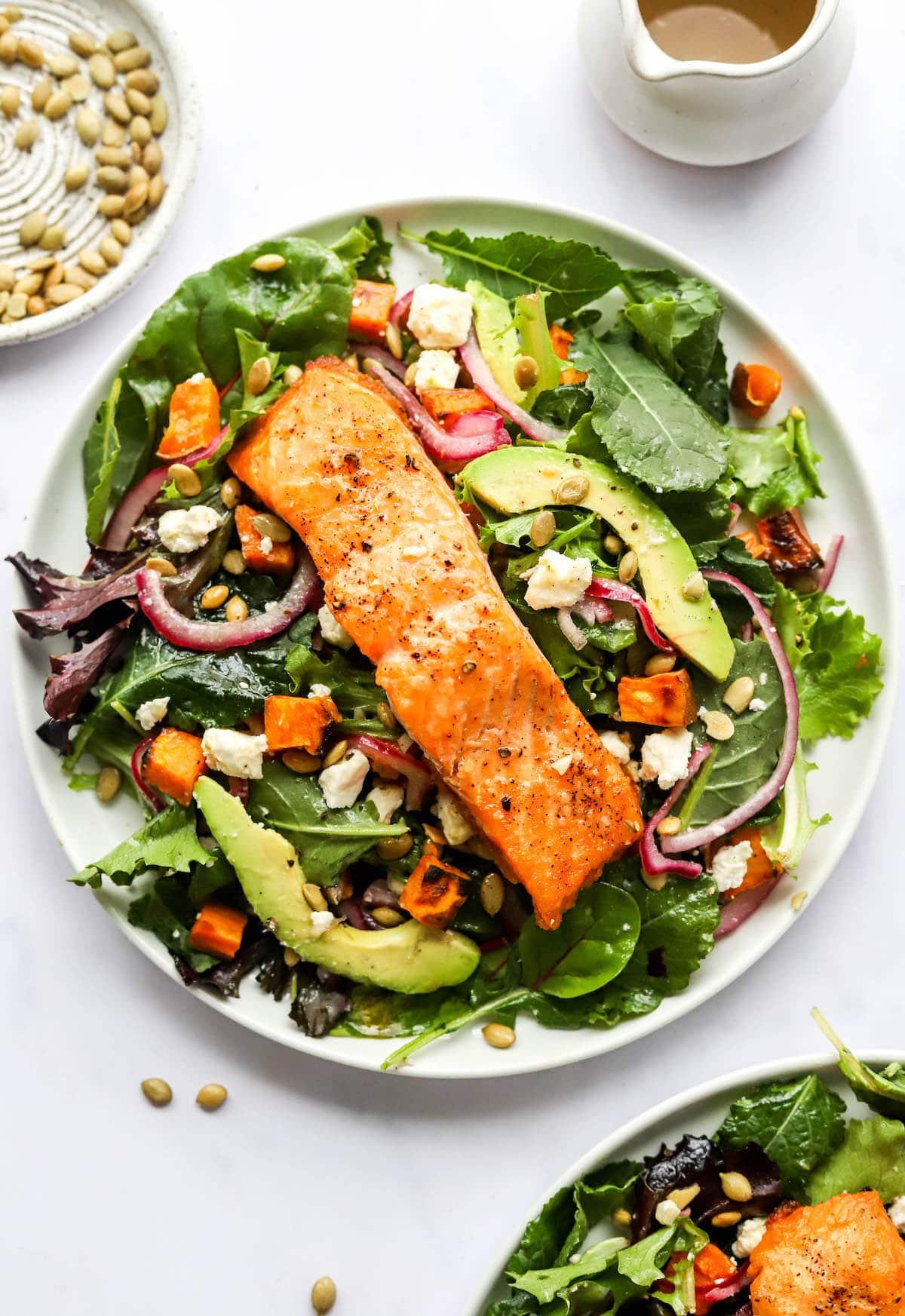
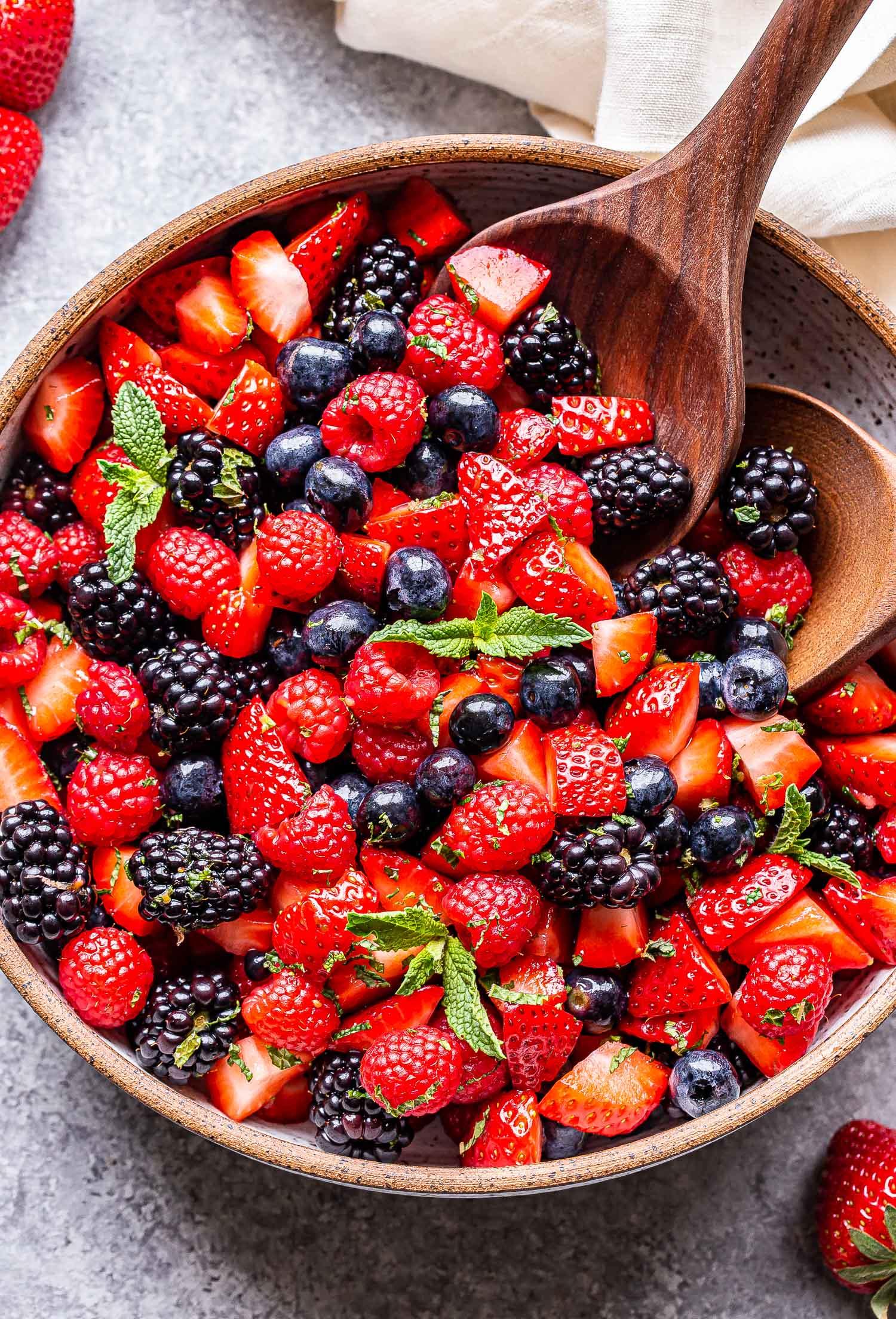
High in fiber-rich vegetables and whole grains to improve insulin sensitivity and promote steady blood sugar levels. Includes lean sources of protein like fish and legumes, and healthy fats from olive oil and nuts, to support heart health and weight management. Limits refined sugars and processed foods, focusing on fresh, plant-based ingredients characteristic of a traditional Mediterranean diet.
For Insulin Resistance
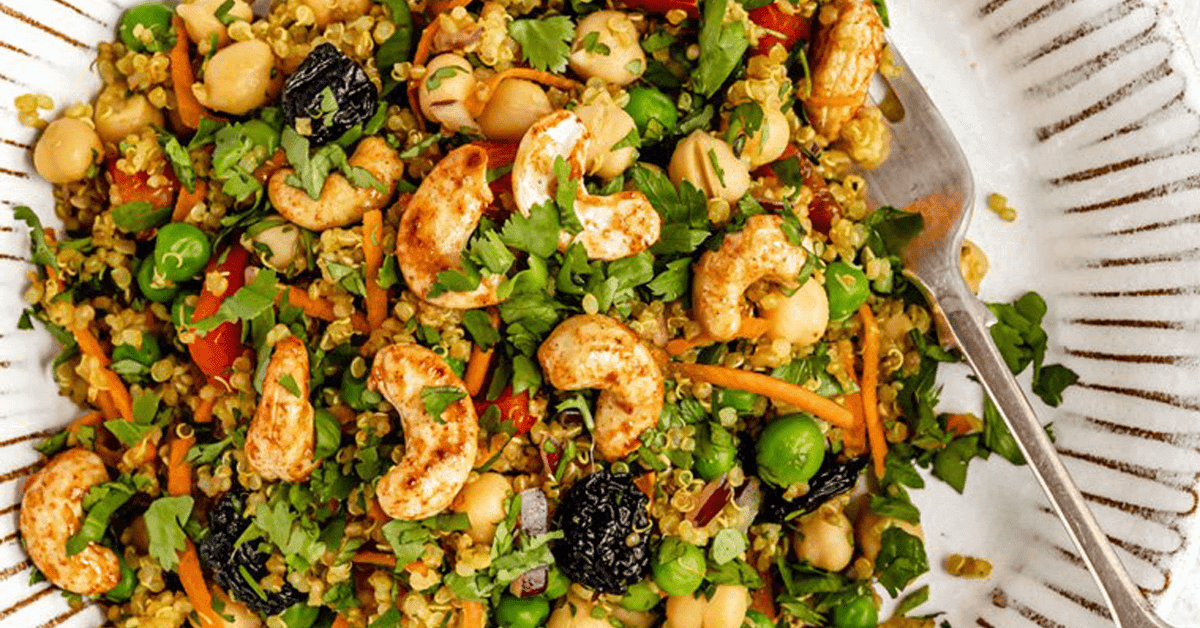
Mediterranean
Day 1


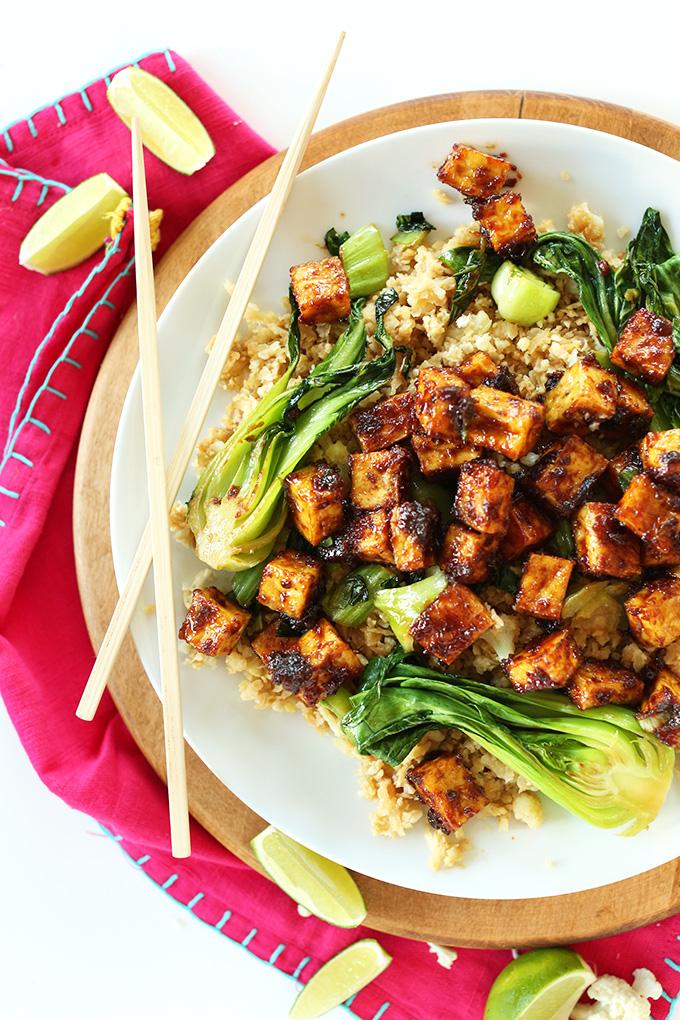
AI recipes for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus & Low Glycemic
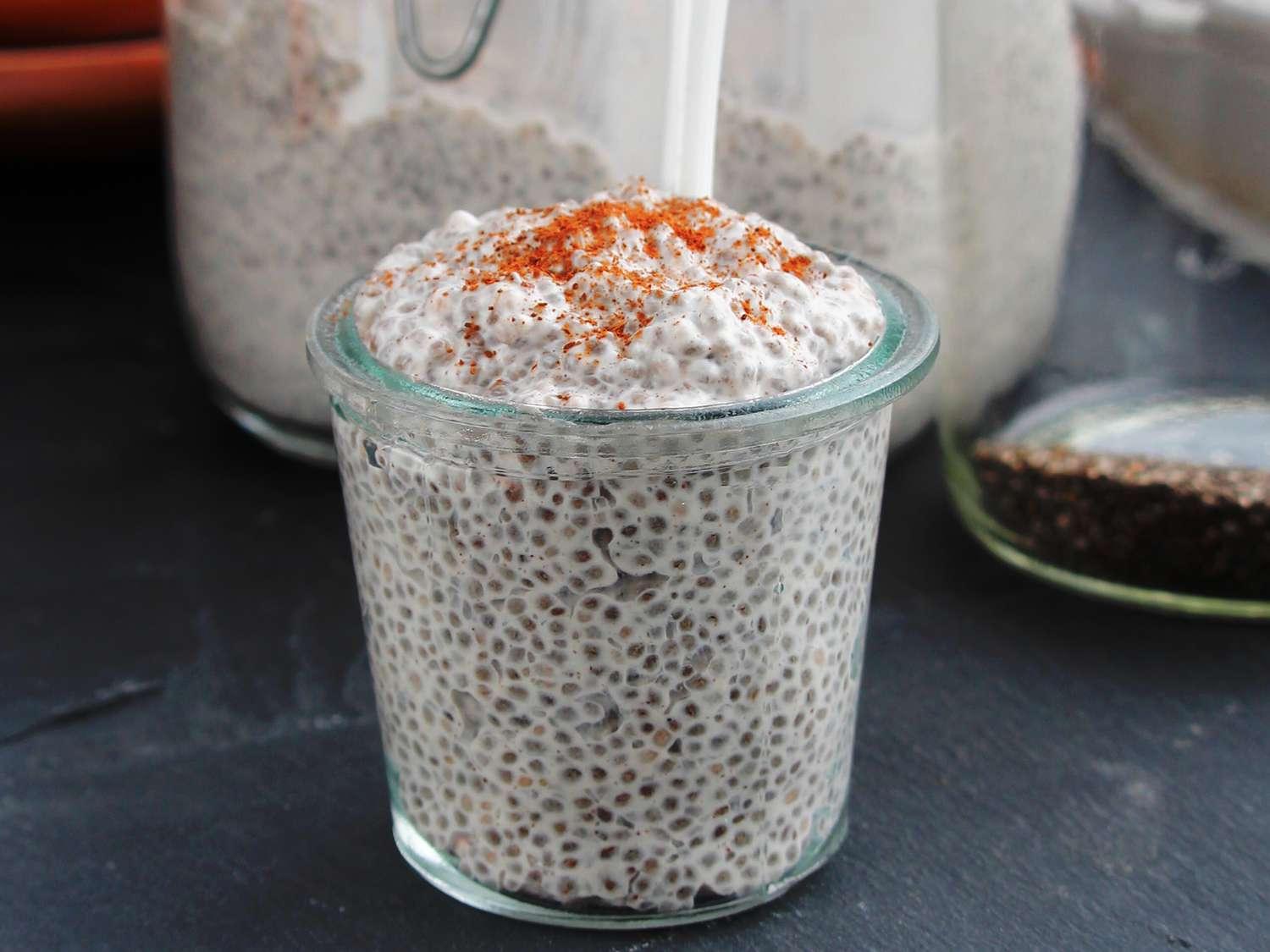
A meal plan for hyperparathyroidism should focus on maintaining normal calcium levels, often involving a reduced intake of high-calcium foods like dairy products and certain leafy greens to prevent excessive calcium in the blood. Protein moderation is crucial, so the plan should include adequate but not excessive amounts of lean proteins such as chicken, fish, and legumes, avoiding high-protein diets which can exacerbate calcium loss. The plan should also include foods rich in vitamin D and magnesium to support bone health and calcium balance, and limit phosphorus intake to prevent further imbalance in mineral metabolism.
For Hyperparathyroid
Protein Moderate
Day 1
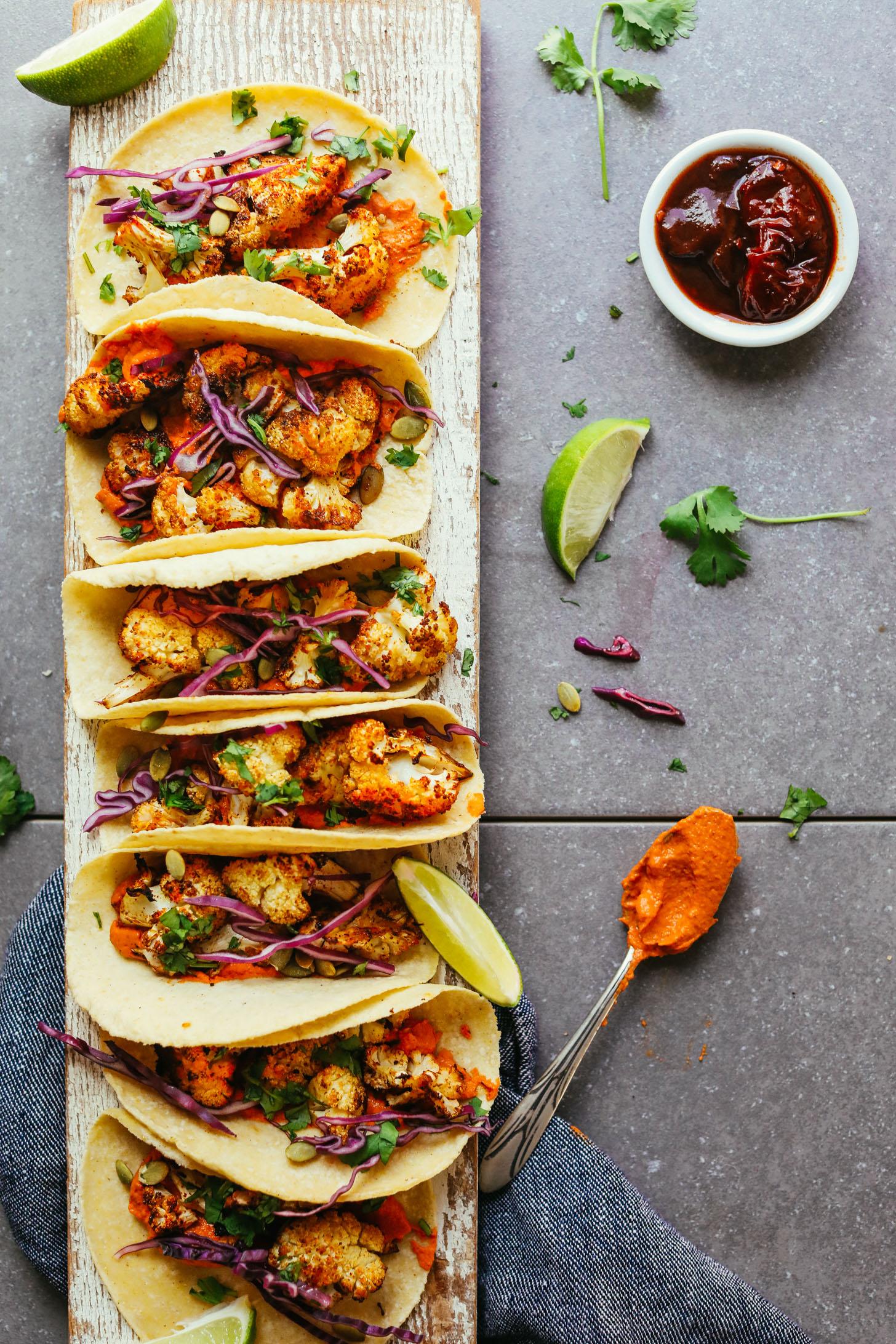
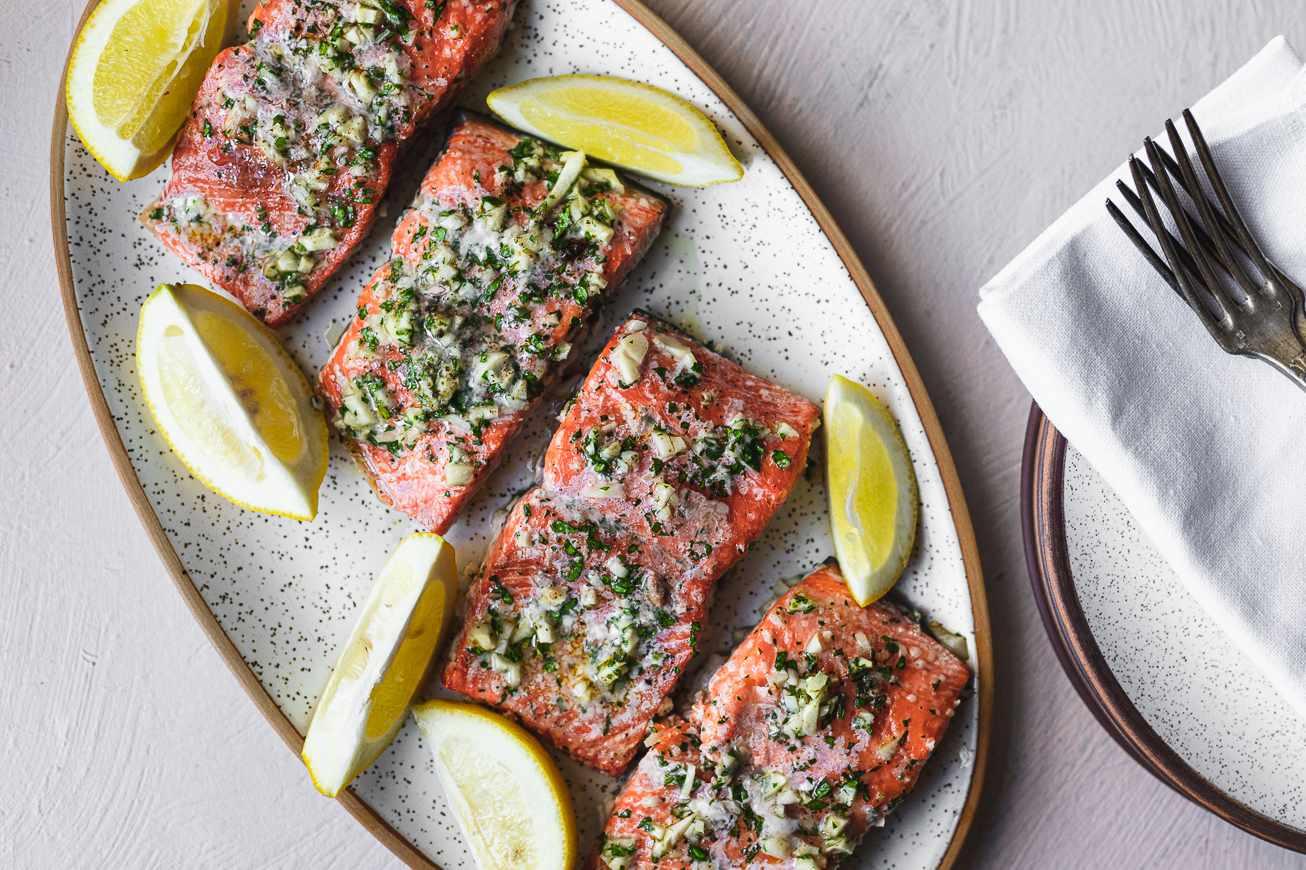
Focus on heart-healthy fats: Incorporate olive oil, nuts, and avocados, while limiting saturated fats from red meats and full-fat dairy products. Emphasize plant-based foods: Build meals around fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, which are high in fiber and can help lower cholesterol levels. Include lean proteins and fish: Opt for poultry, legumes, and especially fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids that support cardiovascular health.
For Cholesterol High
Mediterranean
Day 1
Focus on plant-based proteins like legumes, tofu, and nuts to meet protein needs without increasing cholesterol. Incorporate plenty of soluble fiber from foods such as oats, apples, pears, and beans, as it can help to reduce LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels. Limit intake of high-fat dairy and eggs, opting for cholesterol-free alternatives like fortified plant milks and egg substitutes to manage overall dietary cholesterol.
For Cholesterol High
Vegetarian
Day 1
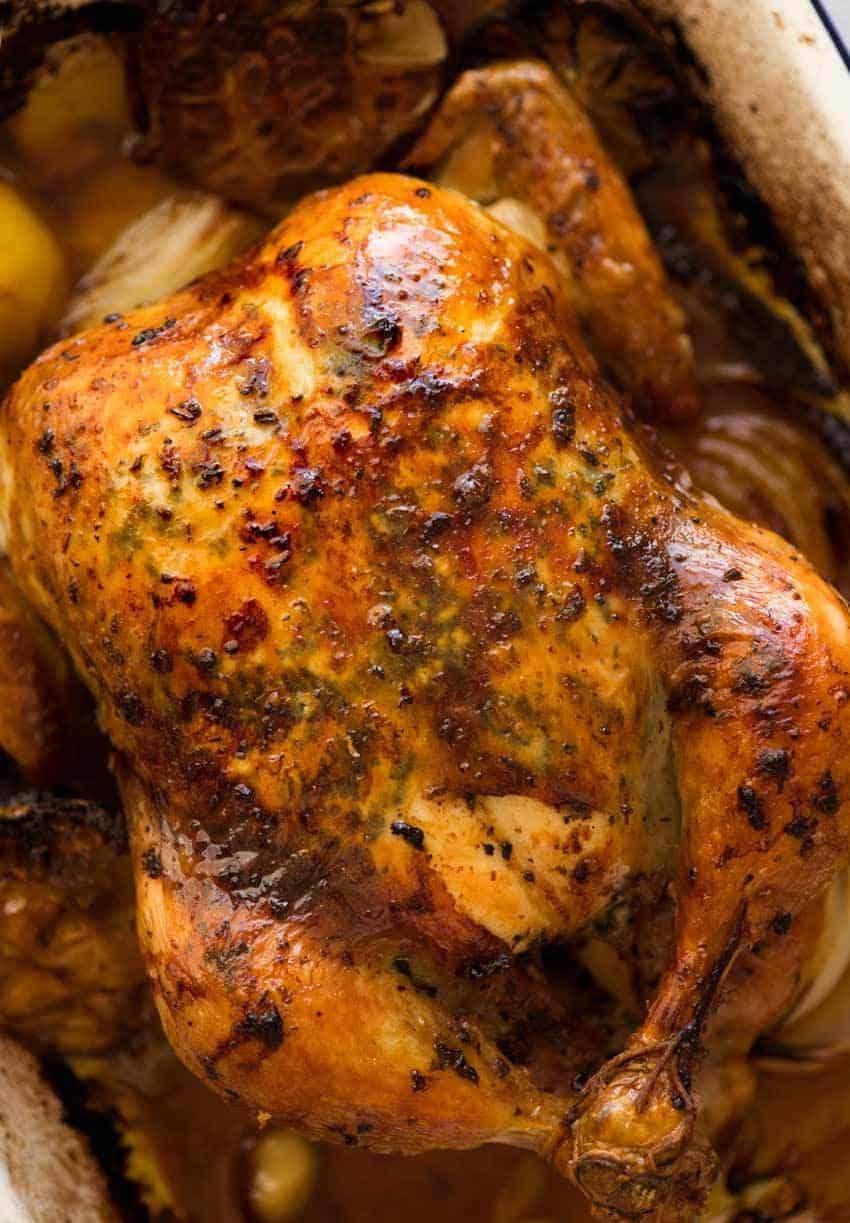
A meal plan for hypertension tailored to Mediterranean users focuses on incorporating heart-healthy fats, such as olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish, while limiting saturated fats and sodium. It emphasizes a high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, which are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals that support vascular health. The plan encourages moderate consumption of dairy, particularly low-fat options, and includes lean protein sources while reducing red meat and processed foods to manage blood pressure effectively.
For High Blood Pressure Hypertension Htn
Mediterranean
Day 1
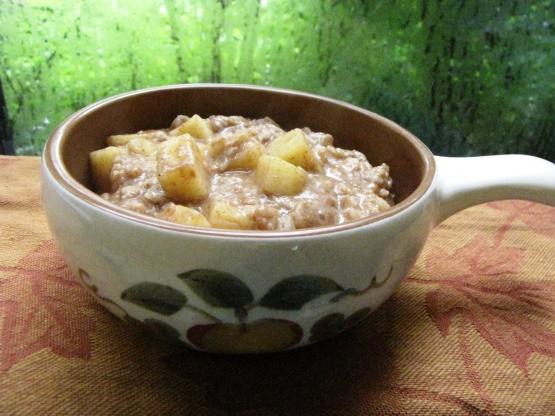
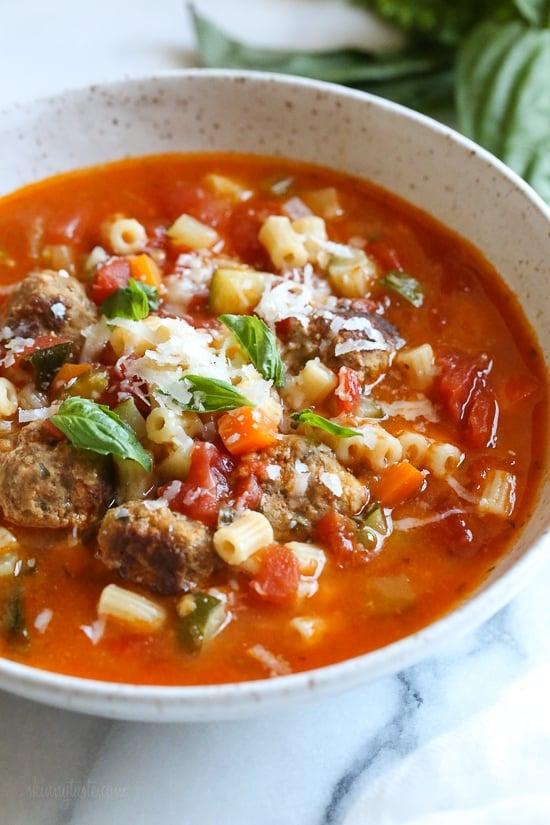
A meal plan designed for high blood pressure, often following the DASH diet principles, emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while being low in sodium, which helps to reduce blood pressure. It includes plenty of potassium-rich foods like bananas and sweet potatoes, which can counteract the effects of sodium and help to lower blood pressure. The plan limits high-sodium processed foods, fatty meats, and sugary beverages, while promoting nuts, seeds, and legumes that provide beneficial nutrients without raising blood pressure.
For High Blood Pressure Hypertension Htn
Dash
Day 1